Dementia
-
Remarkable new findings about the sugar stores in neurons have unlocked an entire new method of treating cognitive decline, and it furthers our understanding of why GLP-1 weight loss drugs appear to provide a shield against Alzheimer's disease.
-
A readily available sleep aid has been shown to have a surprising side effect on brain health, seemingly protecting the organ from the buildup of the tau protein – a key biomarker in the development of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's.
-
Men who carry two copies of a common genetic variant are twice as likely to develop dementia than women with the same mutations. This discovery may now lead to early detection and novel interventions to block how these variants impact the brain.
-
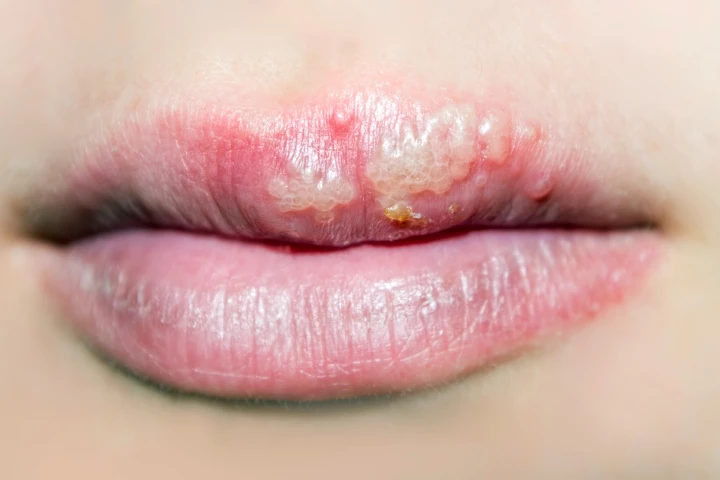
Another study has added to the growing evidence linking the cold sore-causing herpes virus with Alzheimer’s disease. It also found that those people who used herpes treatments such as antivirals were 17% less likely to be diagnosed with Alzheimer’s.
-
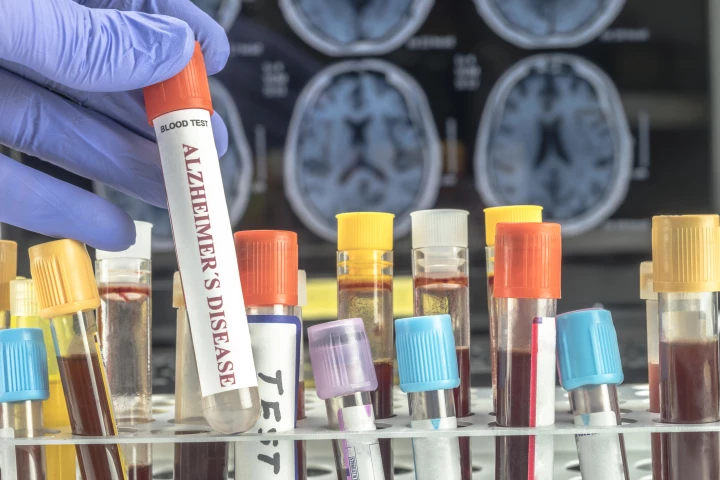
The first blood test for Alzheimer's disease detection has been green-lit by the US Food and Drug Administration, providing a simpler, quicker and less invasive method of diagnosis and speedier intervention. It's a milestone moment for medical science.
-
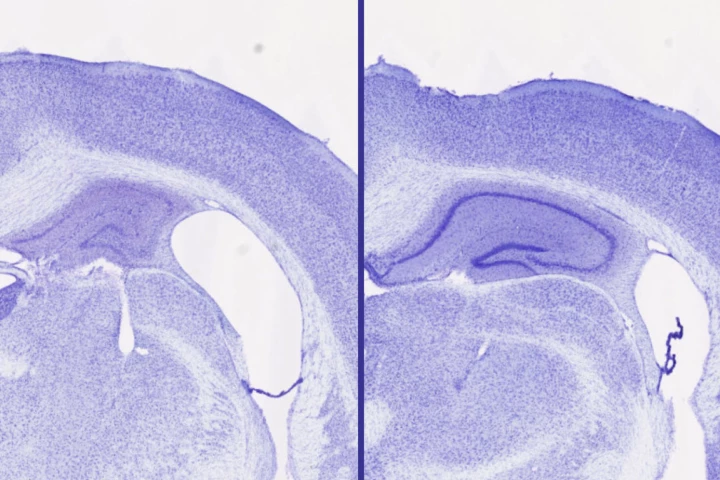
An unusual partnership between a vacuum maker, a race car legend, and the University of Edinburgh is leading to advances in understanding dementia. Their new study using living tissue has revealed the brain's sweet spot for tau proteins.
-
Consuming cannabis can certainly be a way to deal with some health conditions like chronic pain or insomnia. But when a user goes too far and winds up in the hospital, the negative consequences can reach far into the future, says a new study.
-
Taking advantage of a unique public health policy in the UK, a new study has found that receiving the shingles vaccine reduces dementia risk by 20%. The findings bolster growing evidence linking the vaccine to lower numbers of dementia cases.
-
A new blood test is not only able to identify Alzheimer's disease, but it can also indicate how far the disease has progressed with a 92% rate of accuracy. The finding offers hope for new personalized treatment and care options.
-
A long-term trial has found that a discontinued drug halved the onset of a genetic form Alzheimer's, from all but 100% to 50%. Buoyed by the results, scientists are now trialing anti-amyloid medication as a preventative for all types of the disease.
-
Long-term use of over-the-counter pain medication may reduce the risk of developing dementia. It's not the first time these drugs have been linked to preserving cognitive function, hinting at the importance of reducing inflammation for brain health.
-
A fascinating 2022 study found two common viruses may be working in tandem to trigger the earliest stages of Alzheimer’s disease. The findings were just the beginning of an ever-growing body of evidence implicating viral infections in dementia.
Load More