Diabetes
-
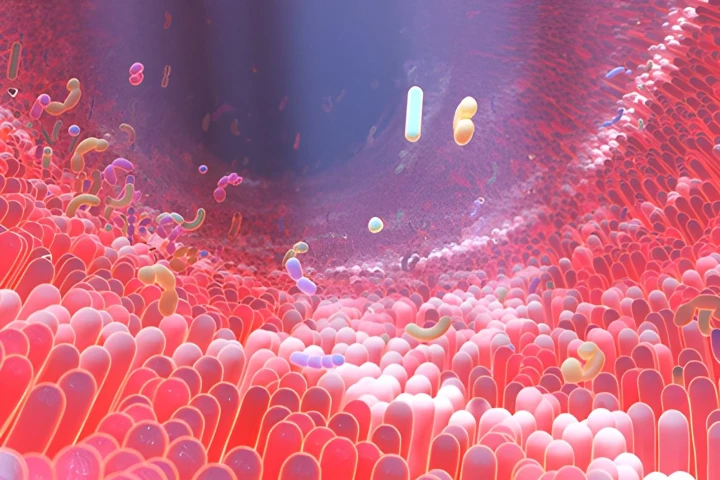
Adding to the growing body of research that proves our microbiome is a powerful ally in fighting disease, scientists have found that an easy-to-get nutrient in our food causes our guts to produce powerful insulin-regulating compounds.
-
Researchers at MIT have developed blood glucose sensing tech that uses near-infrared light to scan tissue in your skin and accurately measure blood sugar – no needles necessary.
-
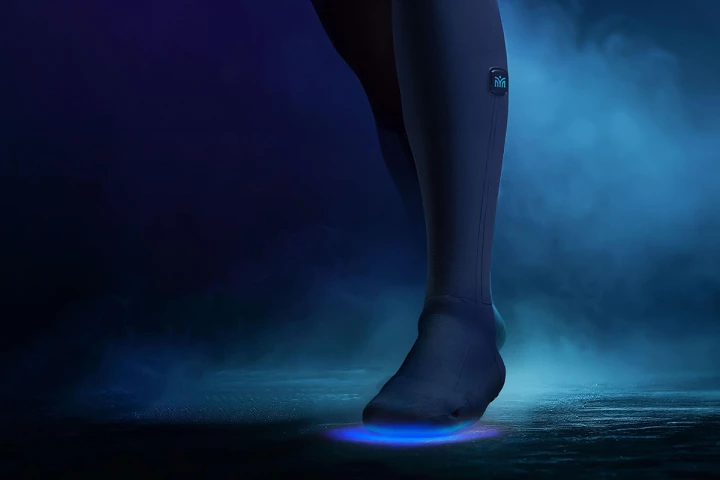
Researchers in Switzerland have stuffed a bunch of chips and sensors into socks to help people who suffer from some of the worst symptoms of diabetes – chronic pain and a loss of sensation in the feet that make it hard to walk.
-
A blend of natural compounds that blocks sugar damage extended lifespan in mice by curbing hunger and improving metabolism in a new study. It hints at a new way to fight obesity, diabetes, and aging without cutting calories.
-
An existing transplant drug has shown promise in slowing the progression of type 1 diabetes in newly diagnosed young people, potentially paving the way for the first therapy that modifies the disease after diagnosis.
-
A fermented food that has been a staple on plates in Korea for thousands of years has gone global in the past decade, with new research revealing that kimchi can naturally lower triglycerides and blood pressure and regulate fasting glucose levels.
-
In a massive study of more than nine million pregnancies, a strong link has been found between gestational diabetes and children born with neurodevelopmental conditions – it translates to a 36% increased risk of ADHD and a 56% higher risk of autism.
-
People who eat high ultra-processed diets have a specific elevated health marker that's a telltale sign of chronic inflammation – even without any symptoms. This inflammation is a slow burn, contributing to diseases likes heart conditions and diabetes.
-
After reviewing a series of studies involving hundreds of thousands of participants, a team of researchers found three eating plans that significantly reduced the development of type 2 diabetes. All are relatively easy to follow.
-
The fitness community regularly touts the health benefits of getting in 10,000 steps per day. But a new study says that a good deal fewer steps can still deliver significant benefits, including a 47% reduction in dying prematurely.
-
Adding to the growing body of evidence supporting the health benefits of cramming all your weekly exercise into two days, a large new study has found that it can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality in adults with diabetes.
-
The US Food and Drug Administration has instructed all GLP-1 drug-makers to update warning labels to include the risk of serious kidney injury that can result from dehydration. This comes after cases of acute kidney injury have required hemodialysis.
Load More