Diagnosis
-
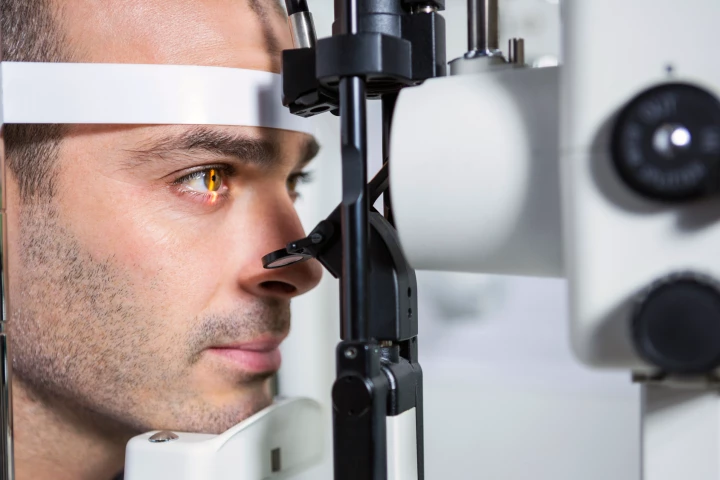
Researchers have developed a simple, non-invasive method of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease early using an eye scan. It could mean treatment can start sooner or, alternatively, could be used to monitor the disease’s progression.
-
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the accuracy and speed at which serious and often deadly pathogen infections can be diagnosed and treated. Often, this is time that is critically important in saving a patient's life.
-
Scientists at Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) have developed a new blood test for pancreatic cancer, one of the most deadly forms of the disease. Tests showed up to 85% accuracy in detection, even in early stages.
-
Is obesity a disease or a risk factor for disease? It's a contentious question. In a new report, the Global Commission on Clinical Obesity strives to settle the enduring debate, introducing a new framework that seeks to redefine obesity.
-
Spanning nearly 100 laboratories in 45 countries, a landmark study has, for the first time, shown an association between genetic brain shape and size and the prevalence of neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease and ADHD.
-
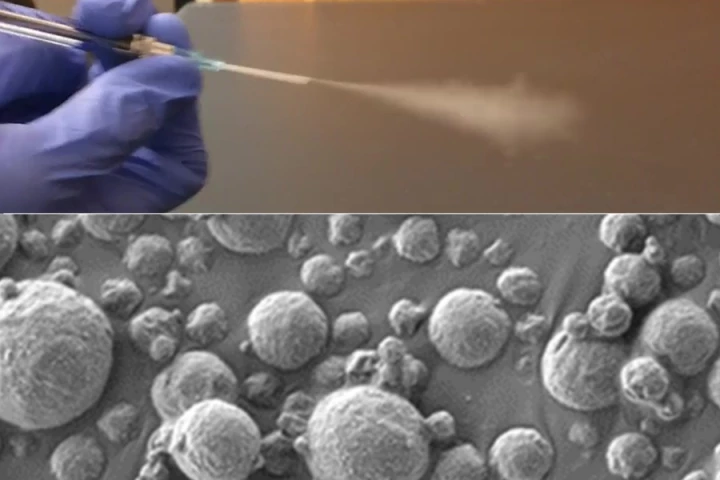
Nobody enjoys giving blood samples, but it’s a necessary part of doctor visits. Soon we might not have to, thanks to a new device that can isolate biomarkers for different diseases using sound waves, from a single drop of blood, in around an hour.
-
A new technique, which involves melting bacterial DNA found in blood samples, could deliver diagnoses of potentially fatal infections faster than ever before. Results may be obtained in a few hours, instead of days.
-
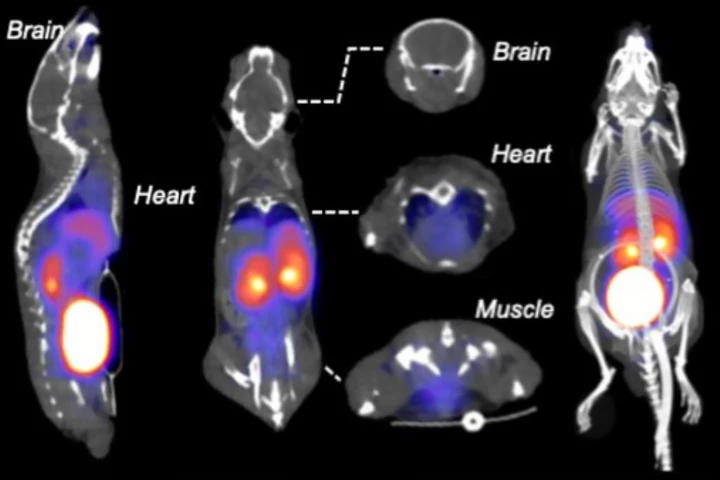
A radioactive form of fructose, a natural sugar found in fruit, can illuminate cancer and inflammation in medical scans. This approach has the potential to make diseases easier to spot than current techniques, leading to better early detection.
-
Researchers engineered a probiotic bacteria to release a marker that can be detected in the urine after it comes into contact with bowel cancer, even when it's in the early stages. The novel test may mean avoiding messy poo-based screening tests.
-
A study has found that a rectal exam alone or in combination with a blood test doesn't improve prostate cancer detection, suggesting the exams could be omitted from prostate cancer screening in men who don’t have clinical signs and symptoms.
-
MIT scientists have developed an easier method for diagnosing lung cancer – breathe in some inhalable nanoparticle sensors, then pee on a stick. The method should be less invasive than CT scans, and easier to perform in low-income regions.
-
Researchers have found that inexperienced doctors performing AI-assisted colonoscopies significantly improved their detection of polyps. Using AI in this way could lower the chances of missing these potential precursors to colorectal cancer.
Load More