DNA
-
Your next favorite true crime podcast might have some new forensics jargon to make sense of. Researchers in Australia have developed a new way to identify humans – similar to how we do with DNA – that could come in handy while investigating crimes.
-
For the first time, scientists have demonstrated how tanning beds cause fundamental DNA damage across almost the skin's entire surface that results in a threefold risk of developing melanoma. It puts beyond doubt the dangers of using these devices.
-
Most pet dogs carry a little wolf inside them; tiny snippets of wolf DNA that slipped into dog genomes after domestication. Now a new study has found almost two-thirds of dog breeds have a small amount of wolf genes, including some breeds you wouldn't expect.
-
See how scientists can now watch DNA repair in real time. A new glowing sensor developed at Utrecht University reveals how cells fix double strand breaks live.
-
After two decades in the making, scientists have cracked the code on a drug that can repair DNA, setting the scene for a new class of therapeutics that can fix tissue damage that occurs through heart attack, inflammatory disease and other conditions.
-
Scientists have sequenced RNA from a nearly 40,000-year-old woolly mammoth leg, the oldest ancient RNA ever recovered. These fragile molecules could reveal which genes were active in the animal’s final hours.
-
An ambitious plan to generate sequence genomes for 1.85 million species on our planet is underway. It's a major undertaking that'll dramatically enhance our understanding of biology, and inform conservation efforts. Thankfully, AI is lending a hand.
-
A new gene-editing technique from the University of Texas at Austin uses bacterial retrons to replace entire sections of dangerously mutated DNA with healthy genetic code. It could "reno" multiple mutations simultaneously.
-
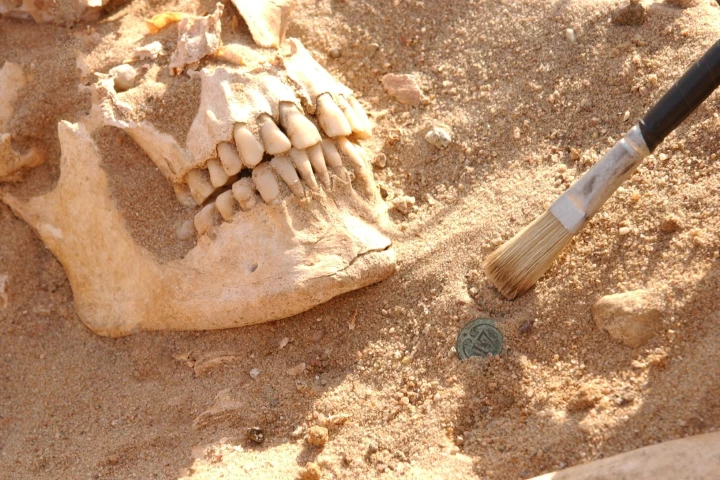
One of the first events to signal the collapse of Napoleon's reign was his crushing defeat after an invasion of Russia in 1812. Researchers have long thought that the disease typhus played a role, but modern DNA analysis paints a different picture.
-
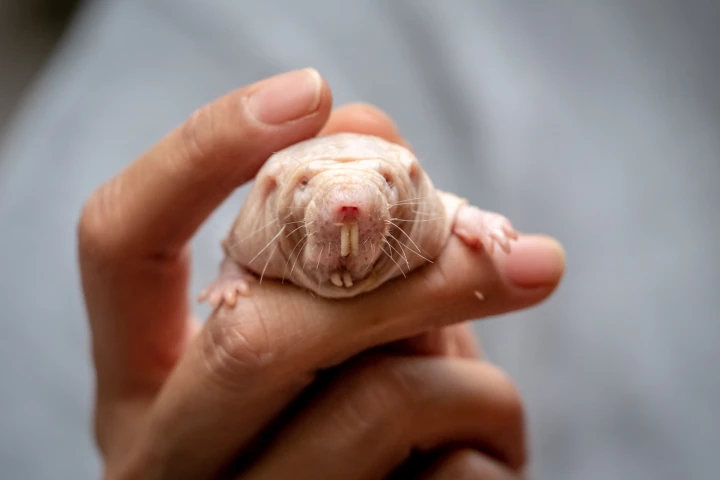
What naked mole-rats lack in the looks department they make up for it in longevity, living healthily for nearly four decades. Now, scientists have found just how they repair their DNA – and it has the potential to be harnessed by humans to do the same.
-
Researchers believe they have developed the first blood test to diagnose chronic fatigue syndrome, or myalgic encephalomyelitis, and it has the potential to be a game-changer for millions around the globe suffering with the debilitation condition.
-
A groundbreaking study has revealed that your mom and dad’s DNA don’t just pass on telomere length, they actively reshape it in the first days of life, influencing how we age and our risk of developing diseases such as cancer.
Load More