DNA
-
Sequencing mammoth DNA has already helped scientists map out how these Ice Age giants evolved, migrated, and survived. But there's a hidden layer of history still waiting to be decoded – the microbes that lived inside them.
-
A groundbreaking discovery reveals how HIV integrates its genetic material into human DNA, exposing a key viral vulnerability that could lead to new therapies and bring the world closer to a functional HIV cure.
-
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have mapped the most detailed genetic blueprint yet of frailty – the age-related decline that affects around 40% of people aged 65 and over. It provides new hope for developing precision anti-aging therapies.
-
A species loved by scientists has a new trick under its wings – a "time out" in youth that leads to significantly slower aging throughout life. This discovery, which shows that biological aging isn't fixed, is a breakthrough in human longevity science.
-
A groundbreaking study has revealed that white sugar doesn’t just feed bacteria in the gut – it rewires them. Consuming sugar can trigger physical flips in bacterial DNA, setting off a chain reaction that alters immune responses and gut health.
-
Humans have been getting infected by ancient bacteria and viruses for at least 37,000 years. Now, for the first time, pathogen DNA has uncovered a pivotal disease "turning point" that happened 6,500 years ago, which would forever change our lives.
-
Taking a vitamin D supplement can knock years off your biological aging, according to the results of a large, long-term study. This may not seem like a lot, but it's a significant amount as you become increasingly susceptible to disease as you age.
-
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have identified a bunch of genes linked to obesity in dogs – and found the very same ones in humans predisposed to putting on weight too.
-
A new study is presenting a radical new theory of aging, suggesting two competing theories are actually intertwined. And even more controversially, the billions of dollars being invested in anti-aging treatments may be targeting the wrong mechanism.
-
Researchers at UCSF have developed a single genomic test that can quickly detect virtually any kind of pathogen in a patient. This allows for much quicker diagnoses, enables targeted treatment to begin sooner, and could lower healthcare costs.
-
Gathering genetic material from treetops in tropical rainforests would be a near-impossible task to perform safely by hand. That's why scientists have developed a system that allows a drone to do the job, without even touching the trees itself.
-
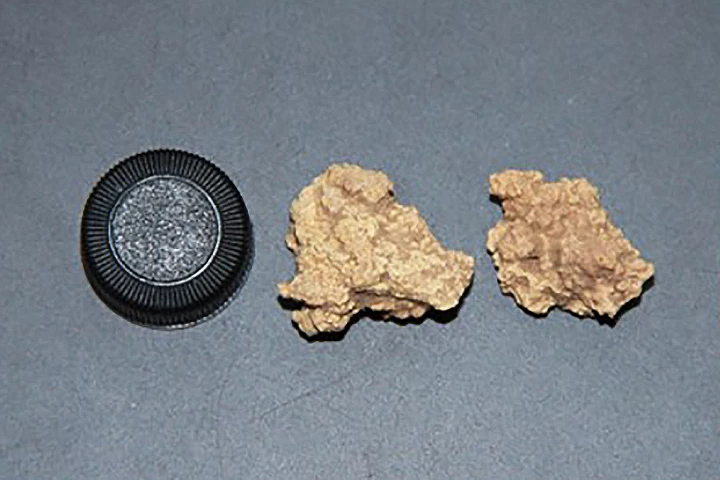
Bizarre clumps of organic matter found buried alongside Bronze Age mummies in China have now been identified as cheese. New DNA analysis has finally solved a long-standing mystery, and it makes it the oldest cheese ever found, dating back 3,600 years.
Load More