DNA
-
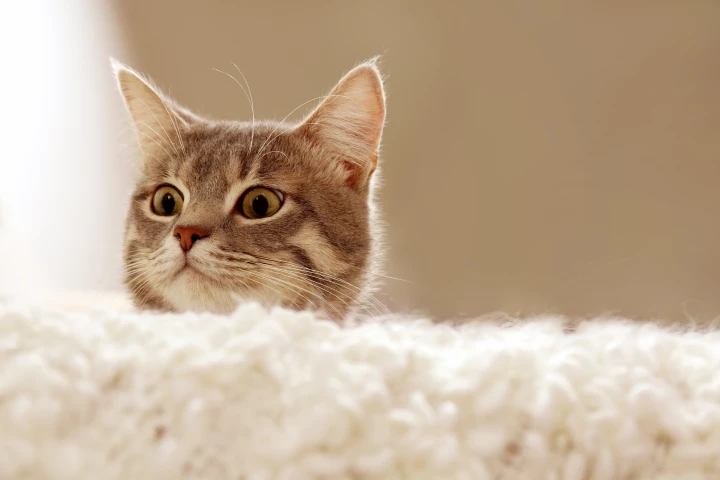
Lending new meaning to the phrase ‘cat burglar’, a single feline hair left at a crime scene can be traced back to an individual animal through a new method that can highlight a unique, rare genetic ‘fingerprint’. You could say it turns the cat into a rat.
-
Scientists have “painted” with DNA, creating 16 million colors to accurately reproduce digital images with 24-bit color depth. The resulting images are incredible, and represent not just a new art form but potential advances for storing data on DNA.
-
When doctors want to see if someone has a certain illness, they may check the patient's blood or urine for the DNA of a specific virus or bacteria, or for a mutated version of the person's own DNA. A new device should make doing so much easier.
-
Time capsules are a fun way to get a glimpse into life in the past, and now scientists have opened one from almost 3,000 years ago. The team successfully extracted DNA from inside an ancient clay brick, revealing the area's ecosystem at the time.
-
Ötzi the Iceman is one of the most well-studied individuals in human history, but there always seems to be more to learn about him. A new genomic study has now found that he looked very different from the way previous studies had imagined him.
-
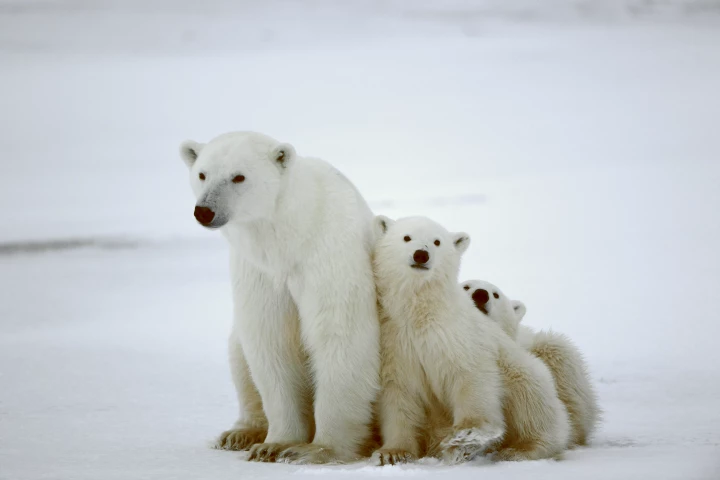
With grim predictions that all polar bears may be wiped out by the end of the century, it’s vital scientists find a way to better monitor the beasts to see if conservation efforts are having any impact. So they decided to 'fingerprint' them using DNA.
-
Move over, quantum dots – quantum rods could be the next big display technology. These tiny sticks could improve 3D displays for VR headsets, and now engineers at MIT have overcome a logistical hurdle by arranging them onto a scaffold made of DNA.
-
Certain gut bacteria have been linked to colon cancer, but now they might get a chance at redemption. Scientists have engineered “pickpocket” bacteria to detect colorectal cancer, with a 100% success rate in mouse tests.
-
In a fight against Iron Man, you might be better off betting on Glass DNA Nanolattice Man instead. Engineers have developed a very strong and lightweight new material out of DNA that self-assembles into lattices, and is then coated in glass.
-
Scientists have developed a new way to tap into the incredible data storage density of DNA in a more scalable way. A “biological camera” imprints images into the DNA of living cells, tagged with barcodes to retrieve data.
-
In a world first, scientists have mapped the dog epigenome. It opens the door to a better understanding of how environmental factors influence gene expression and to the development of new disease treatments for both us and our canine best friends.
-
Researchers have used nanowires to ‘catch-and-release’ DNA in urine, enabling them to detect mutations that signify the presence of a brain tumor. Their method may one day mean that invasive tissue biopsies are no longer required.
Load More