Genome
-
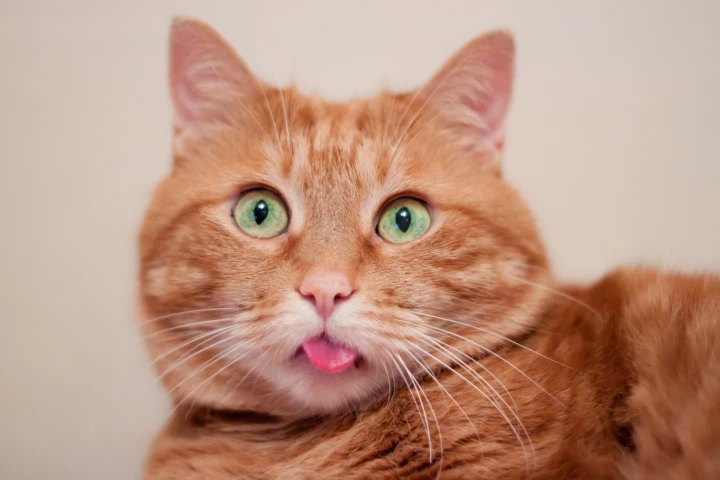
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
Researchers at UCSF have developed a single genomic test that can quickly detect virtually any kind of pathogen in a patient. This allows for much quicker diagnoses, enables targeted treatment to begin sooner, and could lower healthcare costs.
-
Scientists have stored the entire human genome on a five-dimensional crystal capable of storing up to 360 terabytes of information and is built to survive for billions of years. The tech could be used to create an enduring record of human, animal, and plant genomes.
-
Scientists have assembled the most complete woolly mammoth genome in 3D, thanks to an incredible “freeze-dried” specimen. With its DNA preserved in a glass-like state, chromosomes were found for the first time, and even gene expression patterns.
-
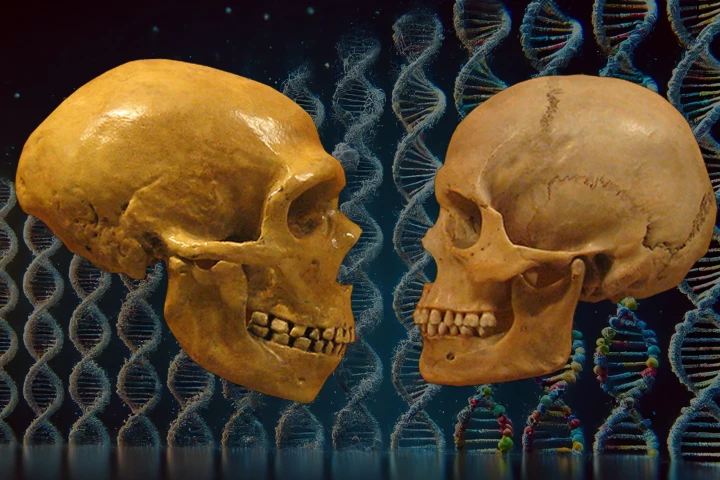
Since Neanderthals' whole genome was sequenced, there’s been growing interest in how their genetics influences our health. New research has found that genetic variations derived from our ancient relatives are associated with an increased susceptibility to autism.
-
Scientists have discovered the organism with the largest known genome. At 160 billion base pairs, it's 50 times bigger than the human genome, and the organism it’s describing is a tiny fern you wouldn’t even notice if you tripped over it on a hike.
-
We now know just how the earliest land plants, ancient algae, conquered terrestrial Earth hundreds of millions of years ago and laid the (literal) groundwork for all subsequent life. It highlights the fascinating genetic strategies of plant evolution.
-
Researchers have identified two genetic markers that may explain the link between eating red and processed meat and bowel cancer. Understanding the disease process and the genes underlying it can help develop better prevention strategies.
-
Studying a species of microscopic worms exposed to high radiation from the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, researchers couldn’t find signs of genetic damage caused by the exposure. The findings are set to forge a path towards a better understanding of cancer.
-
Researchers identified 317 million gene clusters belonging to oceanic microbes, creating the world’s largest open-source catalog that offers a tool for exploring how these genetic resources could be used in medicine, energy, food and other industries.
-
Researchers have developed a ‘smart tweezer’ that can pluck a specific bacterial strain from a microbiome of trillions and sequence its genome better than current methods allow. The tool could lead to breakthroughs in disease diagnosis and treatment.
-
The term ‘personalized medicine’ is being used more and more frequently. But what does it mean? This explainer outlines what personalized medicine is, its advantages and some concerns that have been raised in relation to it.
Load More