Global Warming
-
AI tools like ChatGPT have changed our personal and professional worlds, with around 52% of American adults regularly using a large language model. But at what cost? A new study details the large environmental price we're paying for our AI assistants.
-
In 2025, around 24 million Americans are estimated to suffer from sleep apnea, and around 90% of these cases are undiagnosed. Now, a groundbreaking new study warns that the prevalence of this serious condition will soar as the planet warms.
-
In what may not come as much of a shock, the Doomsday Clock has inched closer to midnight and is now just 89 seconds from 12. It's the closest the hands have ever been to the symbolic 'end of times' number on the clock face in its 80 years.
-
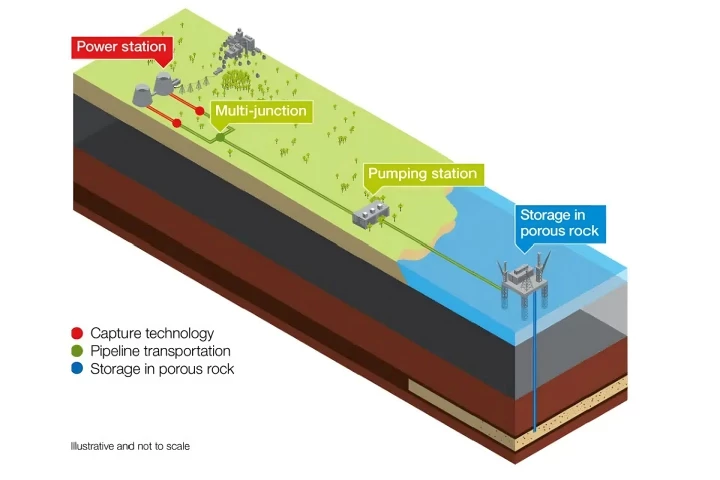
ExxonMobil just signed a lease for 271,068 acres of undersea land off the coast of Galveston, Texas to capture and permanently inject carbon emissions into the underwater rock bed, making it what will be the largest CO2 dump in the United States.
-
A 3,775-year-old log discovery has lent credence to the idea of burying wood to sequester the carbon it contains. Known as a wood vault, the concept helps keep CO2 out of the atmosphere while allowing the soil to be used for crops and other purposes.
-
Earth saw its hottest day on record this week – twice. According to the Copernicus Climate Change Service data, Sunday claimed the top spot for highest global average temperature since the records began in 1940, only to be broken again on Monday.
-
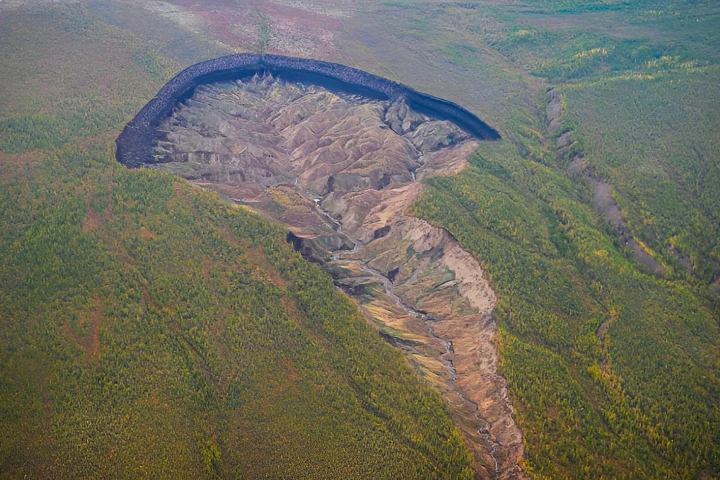
Whether a John Carpenter fan or not, you shouldn't need much convincing to see that the thawing of subterranean permafrost at the poles is not really a good thing. Siberia's biggest sinkhole is now devouring the landscape around it at an alarming rate.
-
Despite a 2024 so far marked with serious conflicts that threaten to escalate further, climate uncertainty and the rapid ascension of AI technologies, the famous Doomsday Clock has remained paused at 90 seconds to midnight, the same time as last year.
-
Current evidence suggests many organisms will struggle to keep pace with a changing climate. However, unlucky for us, some pathogens may thrive – including, as this new study suggests, the bugs that cause the common diarrhea illness campylobacteriosis.
-
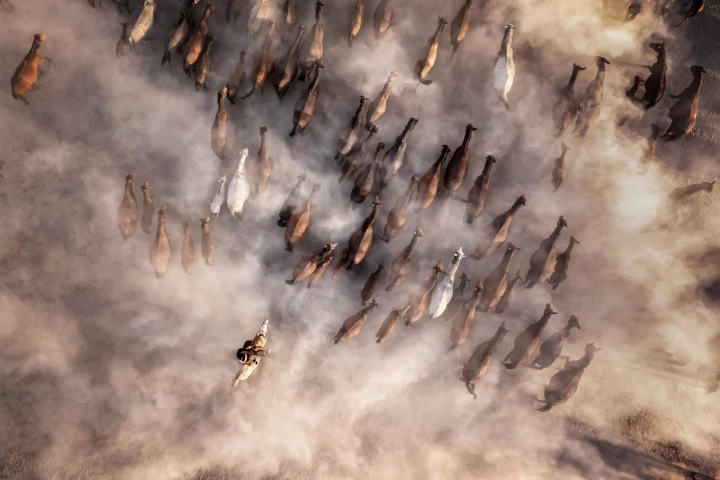
Photo contests offer a window to the world around us, and in this case, it's one full of grand beauty but also, increasingly of extremes. These images capture both the fight for survival and our resilience as we face life on a rapidly changing planet.
-
The 2023 James Dyson Award global winners have been announced. The prizes have gone to three different student teams, each of which offers novel solutions to modern issues including global warming and providing care in war and disaster zones.
-
If an enemy you were previously safe from turned up in your neighborhood, what would you do? That's a problem currently being faced by barnacles in northern Mexico, which are growing sideways to thwart invasive predatory snails.
Load More