Gut health
-
Researchers have homed in on a single gut microbe that acts to prevent fat gain, even with a high-fat diet. The discovery adds to the booming science of finding ways to enlist the microbes that already live in our bodies to help us improve our health.
-
Adding to the growing body of research that proves our microbiome is a powerful ally in fighting disease, scientists have found that an easy-to-get nutrient in our food causes our guts to produce powerful insulin-regulating compounds.
-
You may be sitting on – so to speak – a very valuable asset that scientists would love to get their hands on: your poop. As well as blood, plasma and organs, you can now donate fecal samples to stool banks for research and use in transplants.
-
Scientists have made history with a device that successfully eavesdrops on the neuronal chatter between the brain and the gut, furthering our understanding of its intrinsic interconnectedness – and how it drives health and disease throughout the body.
-
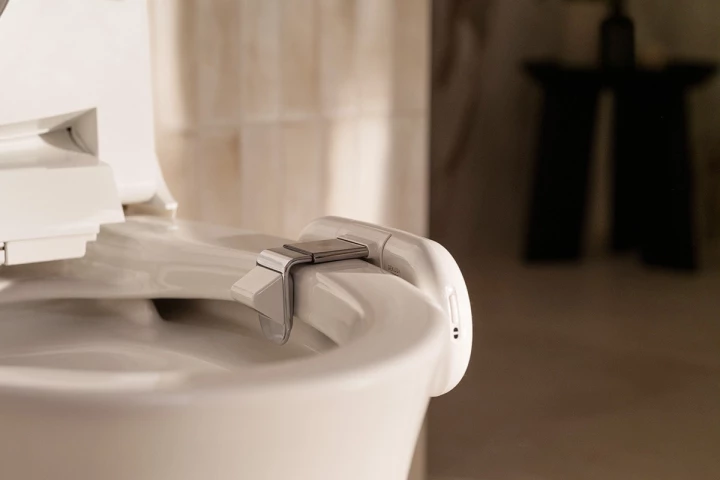
For just $600, you can finally say goodbye to the tedious hassle of snapping pictures of your excrement every day in the bathroom – Kohler's new camera will automatically do it for you. It's for your gut health, promise.
-
A novel treatment for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is on the horizon, with the discovery that two specific gut microbes produce serotonin that protects against inflammation and damage.
-
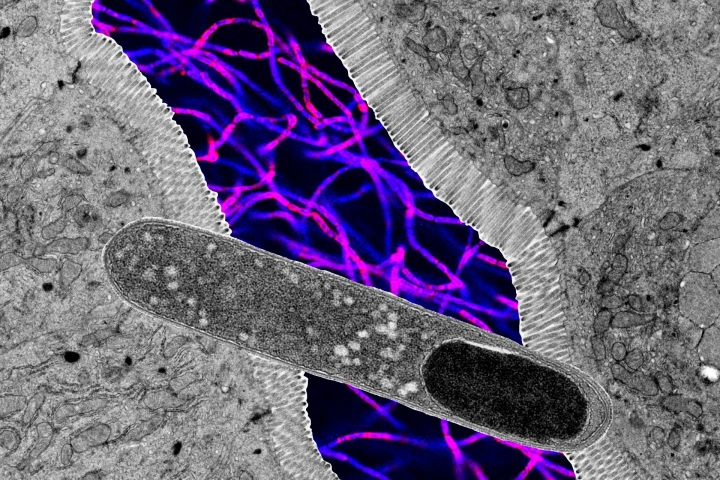
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have cultivated and then awoken more than 100 new viruses found within different human gut microbes, providing a remarkable look at our bacteria and forms the very first living model of the "gut virome."
-
For the first time, scientists have used innovative tech to demonstrated that a healthy microbiome needs a consistent flow of the right foods, finally proving that the "hunch" advice of 5 A Day is spot on, as far as your gut bugs are concerned.
-
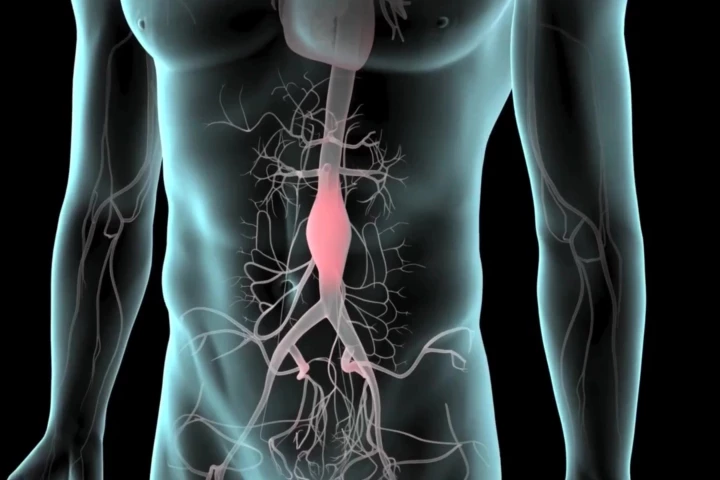
Scientists have implicated a gut byproduct from meat and other animal foods in the growth of deadly abdominal aortic aneurysms. Often symptomless, as it develops, a ruptured aneurysm has a mortality rate above 80%. And currently, treatment is limited.
-
Smoking's not often touted for its health benefits. But it's been known to help those suffering from colitis even though it exacerbates Crohn's disease. New research that could help treat the conditions says it all has to do with bacteria migration.
-
We know by now that exercise is good for the body and mind at any age, but new research has found that your workouts may be benefiting a less obvious area: Inside your gut. It's yet another sign that the gut microbiome is central to overall health.
-
A new study has added strong evidence that red meat consumption is a trigger for inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammation, demonstrating just how it alters gut bacteria and immune activity, resulting in widespread tissue damage in the colon.
Load More