Harvard
-
After an analysis of data from over 131,000 people, researchers found that drinking coffee and tea daily seems to guard against the development of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of cognitive decline - caffeine may be the key protective compound.
-
The sustainability of weight-loss drugs is under scrutiny as new research shows that people who stop taking GLP-1s regain the pounds and return to their original size after 1.7 years. It questions whether we're relying on this "magic cure" too heavily.
-
Does the feeling of standing up too fast and suddenly getting lightheaded sound familiar? Tracking your blood flow can explain why this is happening, and that’s what sets Lumia 2 apart from other similar energy-management devices.
-
For the first time, researchers have shown that tackling obstructive sleep apnea’s two root causes at once, using both oxygen and a jaw-forwarding device, can dramatically cut breathing interruptions during sleep.
-
A massive study of more than 200,000 US adults has revealed that not all potatoes are created equal – as different forms dramatically shift your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. But there's also some good news for lovers of the often-maligned spud.
-
Adding to the growing body of evidence supporting the health benefits of cramming all your weekly exercise into two days, a large new study has found that it can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality in adults with diabetes.
-
For decades now, obesity has been defined by a number on a scale or where you land on the body mass index measure. But a groundbreaking study has found that it’s far more complex, finding 11 distinct biological types, each with their own health risks.
-
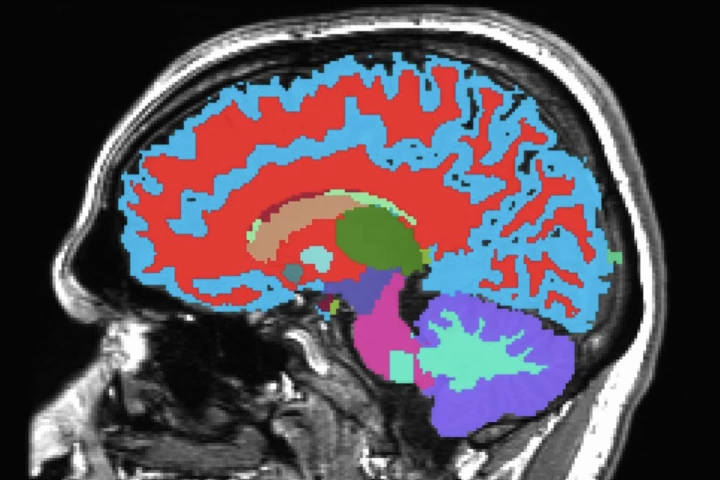
If you could get a quick, easy scan in your 40s, which could add decades to your life and aging healthily, would you? Scientists have made such a tool, letting you glimpse into a crystal ball that identifies age-related disease risk long before onset.
-
In a massive study of nearly 50,000 women spanning 30 years, researchers found that drinking more coffee – to a point – during the ages of 40-65 was linked to less chronic disease, physical mobility issues and cognitive decline in later life.
-
Even without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
Talk about thinking small: researchers at Harvard University have devised a new way to implant flexible bioelectronic devices in the embryos of frogs, mice, and lizards, enabling them to monitor brain activity as these creatures develop.
-
Even if you've built one of the world's best insect-inspired micro air vehicles, it won't be that useful if it can't stick a landing. That's why Harvard scientists have now given their RoboBee a set of long, jointed legs like those of the crane fly.
Load More