Harvard
-
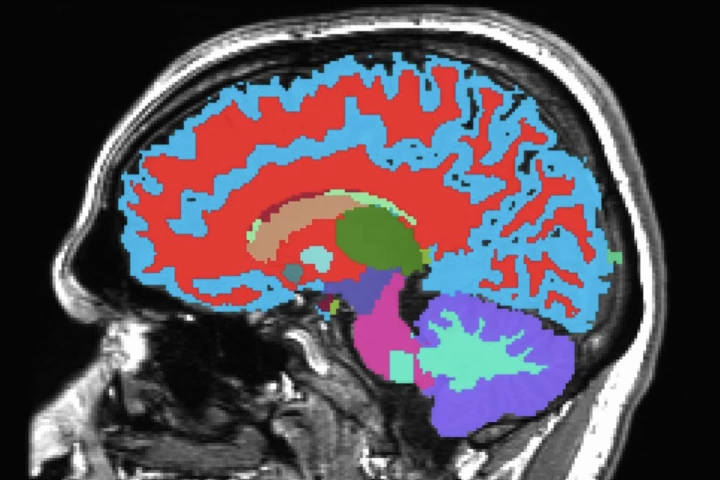
If you could get a quick, easy scan in your 40s, which could add decades to your life and aging healthily, would you? Scientists have made such a tool, letting you glimpse into a crystal ball that identifies age-related disease risk long before onset.
-
In a massive study of nearly 50,000 women spanning 30 years, researchers found that drinking more coffee – to a point – during the ages of 40-65 was linked to less chronic disease, physical mobility issues and cognitive decline in later life.
-
Even without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
Talk about thinking small: researchers at Harvard University have devised a new way to implant flexible bioelectronic devices in the embryos of frogs, mice, and lizards, enabling them to monitor brain activity as these creatures develop.
-
Even if you've built one of the world's best insect-inspired micro air vehicles, it won't be that useful if it can't stick a landing. That's why Harvard scientists have now given their RoboBee a set of long, jointed legs like those of the crane fly.
-
A study of over 220,000 people that looked at the consumption of butter versus plant oils has reached a conclusion that shows just how much better for you one is than the other. Making the switch might be one of the easiest ways to extend your life.
-
You may not know what a springtail is but man, those little things can jump! Scientists have now copied the creatures' jumping mechanism in a small robot that could one day explore places that people can't go.
-
Most people know that body fat stored around the midsection can spell disaster for cardiovascular health. But Harvard researchers have now discovered another problematic fat-storage location in the body that's been largely overlooked.
-
Dark chocolate has been extensively studied for its cardiometabolic health benefits, but findings have been inconsistent, spurring heated debates over whether this treat has pros that outweigh the cons. Now, new research puts dark chocolate back on the table, quantifying its impact on type 2 diabetes risk and weight gain in a study of nearly 200,000 US adults.
-
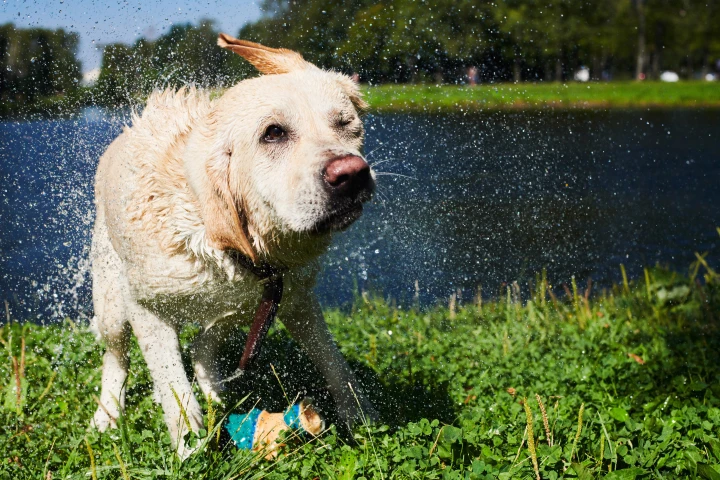
Ever been caught in the crossfire of a wet dog firing droplets of water away from their fur with a mad shake? Well, they can't help it. Scientists have identified the innate sense-motor function mechanism that drives dogs to twist and spout.
-
Treating life-threatening bloodstream infections in combat situations is challenging, especially when the pathogen responsible is unknown. So, DARPA has called on Harvard’s Wyss Institute to use its groundbreaking biotech to fight this deadly threat.
-
In a medical emergency, quick treatment is critical. But a widely used drug could be repurposed to induce a hibernation-like state, to slow down organ damage and save lives by giving patients more time to reach a hospital.
Load More