Heart
-
Coffee is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances on the planet, yet despite more than two billion cups being drunk each day, its impact on heart health remains surprisingly complex – and often misunderstood. This year we got answers.
-
In the first long-term and real-world reflective study of its kind, scientists have uncovered new detrimental health impacts of the artificial sweetener aspartame that echoes those found in shorter research.
-
Caffeine appears to do the opposite of what you might think when it comes to the heart. Scientists have found that a cup of coffee a day actually protects the heart from atrial fibrillation – a condition that can lead to stroke and heart failure.
-
A study has compared yoga and conventional exercise, looking at the impact of both on vascular function. Surprisingly, the results challenge a popular narrative, finding yoga may not be as effective as traditional workouts in boosting heart health.
-
A report based on data compiled between 1990 to 2023 across 204 countries found that cardiovascular diseases remain the most common cause of death among humans. Heart conditions are behind one in every three deaths on the planet.
-
Heart attacks in younger adults aren’t always due to clogged arteries. A new major study reveals striking differences between men and women, with nontraditional causes playing a big role in women’s heart health.
-
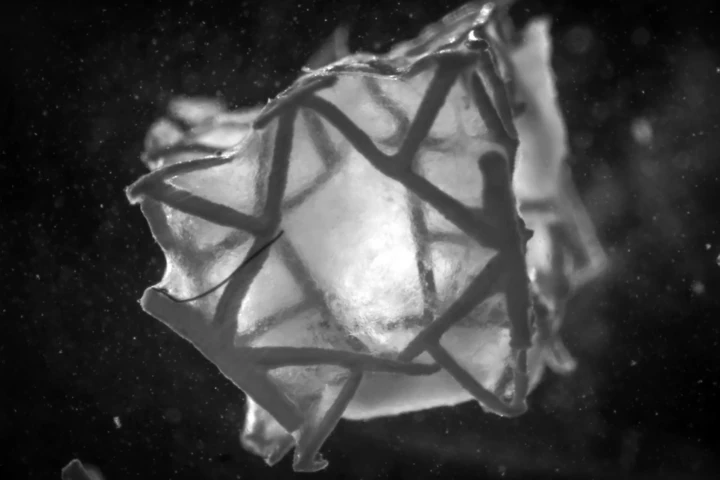
A team of researchers have developed a 3D-printed, biodegradable heart patch that seals holes in heart tissue and supports tissue regeneration, showing promise as a safer alternative to current surgical materials.
-
Gender-affirming hormone therapy does more than reshape the body; it shifts the heart’s electrical rhythm, too, helping it align with a person’s gender identity, according to new research into cardiac changes in transgender individuals.
-
Scientists have found that bacteria on your tongue play a critical role in how nitrate-rich beets impact vascular health. However, that impact is not across the board, revealing a previously unknown link between aging, the oral microbiome and health.
-
Most people imagine a heart attack as a dramatic clutch-the-chest collapse. But a new study shows the common mental image of heart attack symptoms rarely reflects reality, and that misunderstanding could cost precious minutes when it matters most.
-
A new study has found a link between the bacteria responsible for gum disease and atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It emphasizes the importance of adopting a holistic approach to medicine.
-
For the first time, surgeons have successfully performed a heart transplant in which the donor organ never skips a beat, limiting muscle damage and improving acceptance and recovery. It ushers in a new era of our approach to this lifesaving operation.
Load More