Heart
-
A new study has found a link between the bacteria responsible for gum disease and atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It emphasizes the importance of adopting a holistic approach to medicine.
-
For the first time, surgeons have successfully performed a heart transplant in which the donor organ never skips a beat, limiting muscle damage and improving acceptance and recovery. It ushers in a new era of our approach to this lifesaving operation.
-
If someone is afflicted with heart disease, it's important that their cardiac activity be monitored as accurately as possible. An experimental new wearable device is designed to make that happen, by copying the body structure of the starfish.
-
A man has lived for more than 100 days with a maglev heart beating inside his chest. In a landmark moment, he was discharged earlier this year, becoming the first person in the world to leave the hospital with the device embedded in his body.
-
Heart attacks are dangerous not just because of the initial event, but the long-term damage afterwards. Now scientists have discovered a dormant gene that could be reactivated to regenerate heart tissue, preventing the progression to heart failure.
-
From fighting memory decline to warding off some cancers, drinking coffee continues to emerge as a way to improve your health. Now, a new study says that the time of day during which you drink your daily brew is key to boosting some of its effects.
-
Scarring of heart tissue can be slowed but not stopped, and can lead to heart failure. But a new study has shown that an existing immunotherapy could stop scar tissue formation after heart attacks.
-
A new injectable, temporary pacemaker could help correct a heart arrhythmia in an emergency. This nanoparticle gel can regulate the heart’s electrical signals for up to five days before dissolving harmlessly in the body.
-
For babies born with a certain heart defect, implantation of a "shunt" is essential to their survival. A new type of shunt can be expanded using light after it's been implanted, potentially eliminating the need for more heart surgeries down the road.
-
A new medical 3D-printing method has been developed that takes its cues from the way tangles of worms interact in nature. The resultant material produced could patch up leaky heart parts or stabilize spinal discs, among other applications.
-
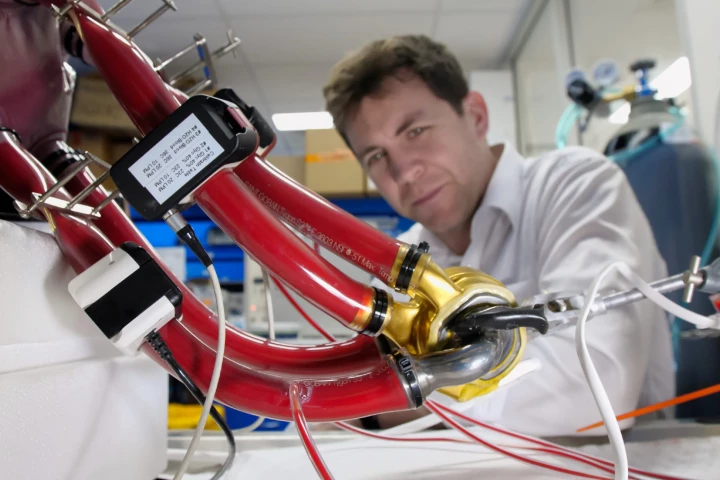
For the first time, the fully mechanical heart made by BiVACOR, which uses the same technology as high-speed rail lines, has been implanted inside a human being. The feat marks a major step in keeping people alive as they wait for heart transplants.
-
It turns out that blasting people with shockwaves during open-heart surgery is a really good idea. That's what researchers found who used the technique to reactivate heart cells and improve the post-op lives of patients in a groundbreaking study.
Load More