Infections
-
Researchers have discovered a certain kind of sugar that is only found on the surface of bacteria. Targeting it could lead to an entirely new class of immunotherapeutic drugs designed to target and eliminate at least one deadly, drug-resistant bug.
-
Americans are being urged to be extra vigilant, as a new influenza A variant is spreading more rapidly and evading our abilities to fight it off. With more than 110,000 hospitalizations so far, scientists expect this wave to worsen as the season peaks.
-
Deep in the growth rings of Pyrenean trees lies the strongest evidence yet for what set the Black Death in motion – a direct link between a sudden climate shift and the plague’s arrival in Europe, where it killed millions between 1347 and 1353.
-
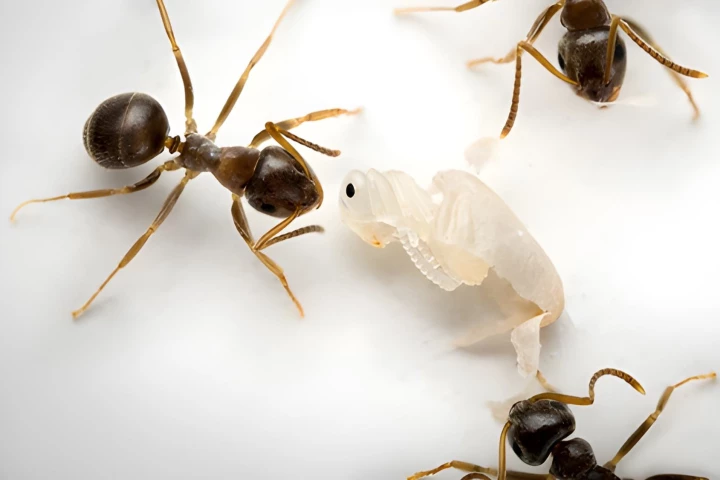
In a wide range of social species, when an animal is sick, it takes itself away from its group. Ant pupae are unable to move, however, so they've developed a unique mechanism that leads them to sacrifice their own life for the betterment of the nest.
-
Avian influenza viruses have a gene that makes them incredibly resistant to heat, rendering our body's natural defense system – fever – powerless in fighting infection. In fact, higher temperatures actually help those bird-derived bugs replicate.
-
Following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the world responded with public health measures, including social distancing practices. But it appears that humans aren’t the only ones to modify their environment to mitigate epidemic risk.
-
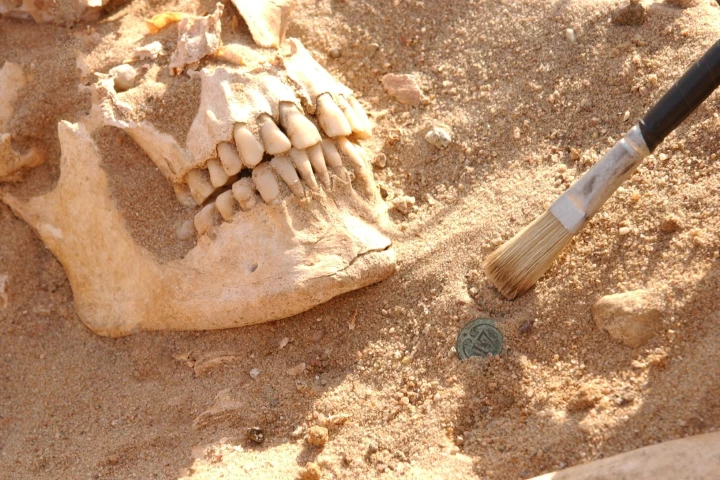
One of the first events to signal the collapse of Napoleon's reign was his crushing defeat after an invasion of Russia in 1812. Researchers have long thought that the disease typhus played a role, but modern DNA analysis paints a different picture.
-
Even in death, cells leave a trace. Scientists have discovered a microscopic “Footprint of Death” that not only helps the immune system clean up but can also give viruses a new way to spread infection.
-
A new study suggests that a father’s COVID-19 infection could do more than make him sick – it may leave epigenetic marks on his sperm that pass anxiety to his offspring, revealing how viral infections can echo across generations.
-
The active ingredient in a common over-the-counter allergy spray may do more than ease hay fever symptoms. A new clinical trial found azelastine cut COVID-19 infections by 70%, hinting at a cheap, accessible way to add protection alongside vaccines.
-
One of the most dangerous microorganisms on Earth, Naegleria fowleri has a well-earned nickname as the "brain-eating amoeba," and infection almost always leads to death. Now it's infiltrated the treated drinking water supplied to two Australian towns.
-
An epidemic that's been sustained for 44 years might finally be quelled, with the milestone approval of the first HIV drug that offers 100% protection with its twice-yearly injections. It's a landmark achievement set to save millions of lives.
Load More