Infections
-
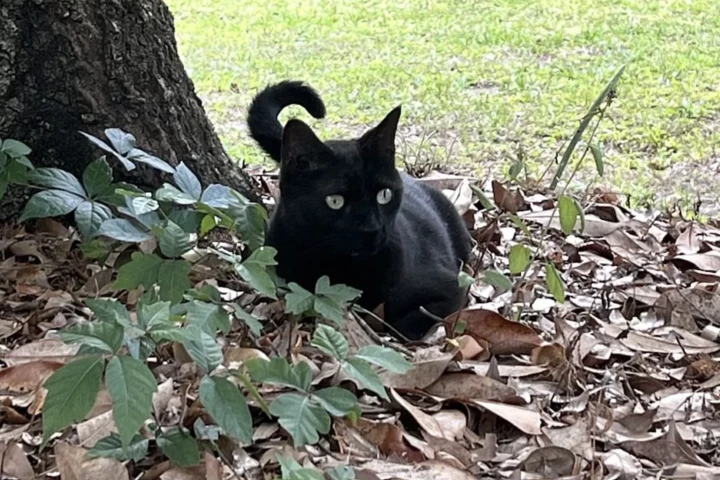
Black cats may be a symbol of bad luck in many Western societies, but one such sooty feline has brought good fortune to scientists, playing a key role in identifying a new virus that can infect humans. It's the second novel bug Pepper has hunted down.
-
Many persistent sinus infections involve biofilms – colonies of bacteria that group together to resist efforts to kill them. Now, researchers have developed biofilm-blasting bots that could handily deal with these, and other, bacterial infections.
-
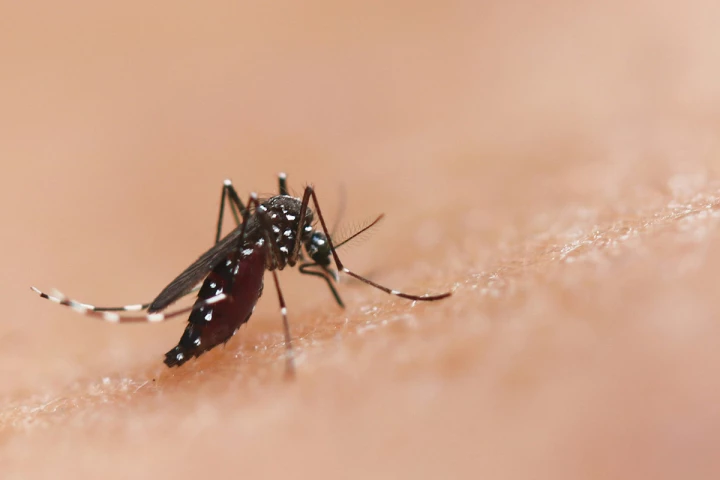
Mosquitoes have long been among humanity’s most formidable adversaries, causing more deaths than any other animal. With traditional control methods facing mounting resistance, researchers are seeking innovative ways to combat mosquito-borne disease.
-
As unspent antibiotics pass from our bodies, they contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Scientists are addressing this problem with a new technology which causes such drugs to only become active upon exposure to green light.
-
Babies and small children are prone to middle ear infections, which typically have to be treated with orally administered antibiotics. A new fast-acting topical gel could soon replace such drugs, however, potentially reducing unpleasant side effects.
-
Wearing face masks and maintaining social distances were a significant part of the world's reaction to the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, new research says the practices are not only effective at saving human lives, but chimp lives as well.
-
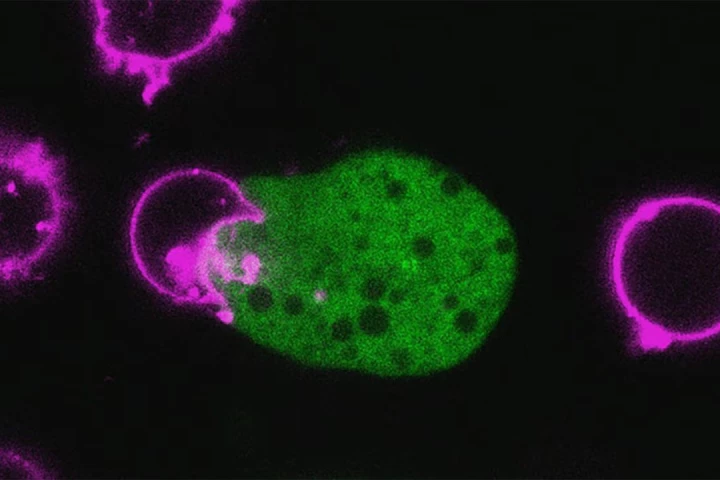
One type of parasite, Entamoeba histolytica, has developed a very intriguing way to evade the defences of our immune system. It rips pieces off human cells and steals the proteins to wear them as a disguise.
-
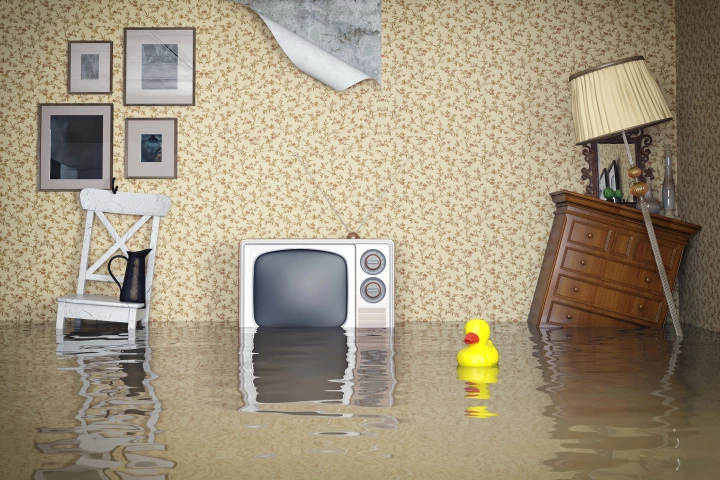
The world's largest study into the long-term health impact of floods has found that there are surges in hospitalizations for months after an event – and current responses are inadequate when it comes to treating cancer, diabetes, mental health and more.
-
Looking beyond jabs, sprays or tablets, scientists are thinking outside the box for delivering antiviral medication to prevent the spread of highly transmissible bugs. Their secret weapon? Chewing gum – but one made from a rather fascinating bean.
-
A three-year study has found robust evidence that one vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus offers older adults long-term protection, even if efficacy wanes. Despite this, just one dose cut serious illness by nearly two thirds across three seasons.
-
A decade-long study of 35 million Americans in 10 states has found that group A streptococcus infections have more than doubled. What's more, "strep" – which can cause a bizarre flesh-eating disease – has become increasingly resistant to antibiotics.
-
It's never a good thing, when a bacterial biofilm forms on the surface of a medical implant. There could soon be a new way of eradicating such films, however, using tiny remote-control liquid-bodied robots.
Load More