Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
-
Heart failure caused by a heart attack is a leading cause of death worldwide and the risk factors associated with this cardiovascular disease are well known. Now, new research indicates aircraft noise should be added to that list.
-
The analysis of volcanic gases allows scientists to determine what processes are taking place deep within volcanoes. And while big, expensive drones have previously been used to sample those gases, a small consumer model can now do the job.
-
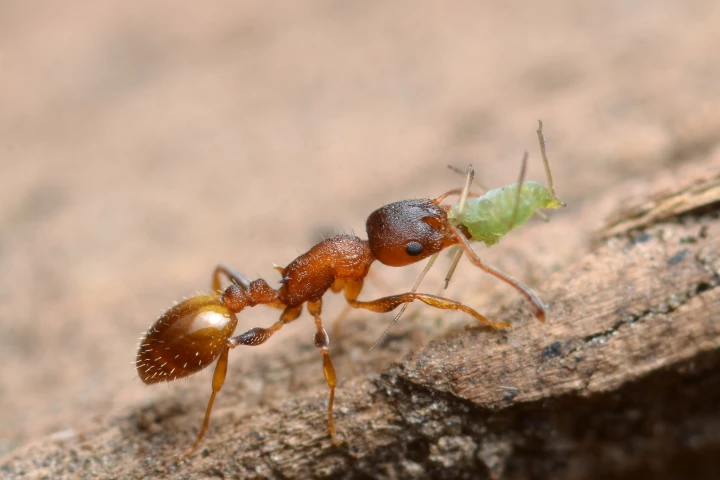
The first thing many of us might wish for is eternal youth, but there’s always a catch. Now, scientists have discovered a version of this story playing out in ant nests, as parasites drastically extend the lifespan of worker ants – at a terrible cost.
-
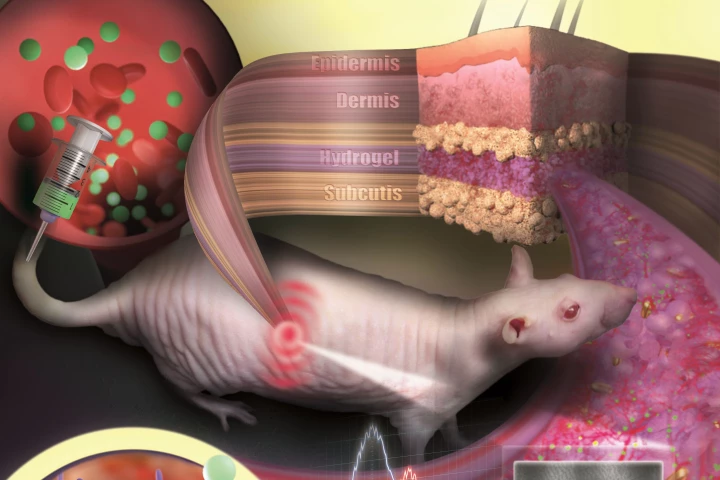
When a patient is receiving medication, it can be difficult to determine how much of the drug is actually making its way into their bloodstream. A new subdermal "tattoo" could help, thanks to its color-changing gold nanoparticles.
-
Taking inspiration from the way sea cucumbers can strengthen their exterior when in danger, scientists in Germany have developed a novel wafer-thin paper material that can transition from firm to soft via an electrical switch.
-
In January scientists reported the detection of very low-frequency gravitational waves. Now astrophysicists have investigated two possible sources – the universe cooling down after the Big Bang, and a field of particles that could be dark matter.
-
If evolution works by selecting for the most advantageous genes, why haven’t we evolved immortality? A new study has identified genes that promote reproductive success in youth but aging later in life, and found that switching off those genes dramatically extended the lifespan of worms.
-
A team of physicists have just created the world's smallest working engine from a single electrically-charged atom. With an equivalent efficiency (if scaled to size) of an average automobile engine, it actually produces a significant amount of power
-
As part of the quest to come up with a room temperature superconductor, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz have developed new record high-temperature superconductor – and it smells like rotten eggs.
-
Scientists have replicated the flexible-but-tough internal structure of the sea sponge, to create a material that might find use in body armor.
-
What does riverboat traffic on the Rhine have to do with solar cycles?