Johns Hopkins University
-
Does the feeling of standing up too fast and suddenly getting lightheaded sound familiar? Tracking your blood flow can explain why this is happening, and that’s what sets Lumia 2 apart from other similar energy-management devices.
-
Scientists have developed a powerful new dual-imaging tool that maps the retina’s structure and oxygen use in unprecedented detail. This breakthrough could one day help doctors spot sight-stealing diseases long before symptoms appear.
-
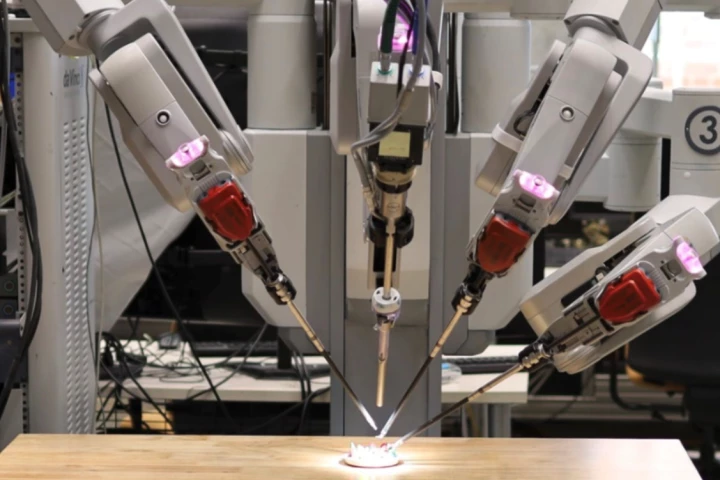
We're a step closer to entering an operating theater without any human life besides ours, following the world's first surgery performed by a robot responding and learning in real time. Its precision and skill matched that of experienced surgeons.
-
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University have come up with a better prosthetic hand that uses a hybrid design and a complex sensor system to carefully grip various objects with just the right amount of pressure.
-
Scientists have identified new gene modifications that can make tomatoes and eggplants grow bigger, which could help boost yields in developing countries.
-
A tiny chip with a unique surface can accurately detect the blood biomarkers of a heart attack within minutes, a fraction of the time taken by current methods. The researchers behind the device see it being used as an at-home diagnostic tool.
-
Leaf-blowers are the bane of suburban Sunday mornings. Now a team of engineering students at Johns Hopkins University has invented a kind of silencer attachment to radically reduce noise, which could be on shelves in a few years from Black & Decker.
-
Researchers found that applying a gentle electric current to the head during virtual reality training helped budding surgeons to more easily transfer the skills they’d learned to a real-life setting.
-
In what may put some of us to shame, apes instantly recognize family and friends that they haven’t seen in more than two decades, which is the longest ‘social memory’ in a non-human animal ever documented.
-
Scientists at Johns Hopkins have developed a new spinal stimulator that can help restore lower limb function to paralyzed patients. The tiny device can be non-invasively implanted through a syringe.
-
Researchers have created a nanoscale electronic ‘tattoo’ that attaches to an individual cell without damaging it. The breakthrough development could be used to monitor cell health and puts us one step closer to getting the jump on disease diagnosis.
-
A bright red waterfall isn’t something you’d expect to see on the icy landscape of Antarctica, but that’s what’s pouring out from the foot of Taylor Glacier. Scientists now claim to have solved the mystery behind the crimson waters of Blood Falls.
Load More