Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich
-
A loss of smell can be one of the earliest warning signs of Alzheimer’s disease, but the cause of this sensory change have been unclear. Now, a study reveals that the problem may not lie in the nose or olfactory bulb itself, as previously thought.
-
When we’re given a choice about where we want to be touched, the touch is significantly more pleasurable, a new study has found. The findings have implications for interpersonal relationships, communication, health and well-being.
-
In two separate studies, researchers have identified the mutation that can lead to the autoimmune disease lupus. The discovery opens the door to new therapeutic approaches and testing for the mutation, which would ensure early disease diagnosis.
-
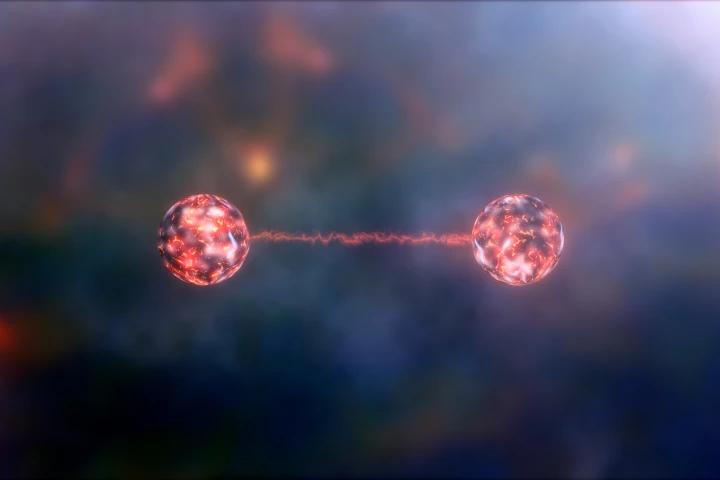
Researchers in Germany have demonstrated quantum entanglement of two atoms separated by 33 km (20.5 miles) of fiber optics. This is a record distance for this kind of communication and marks a breakthrough towards a fast and secure quantum internet.
-
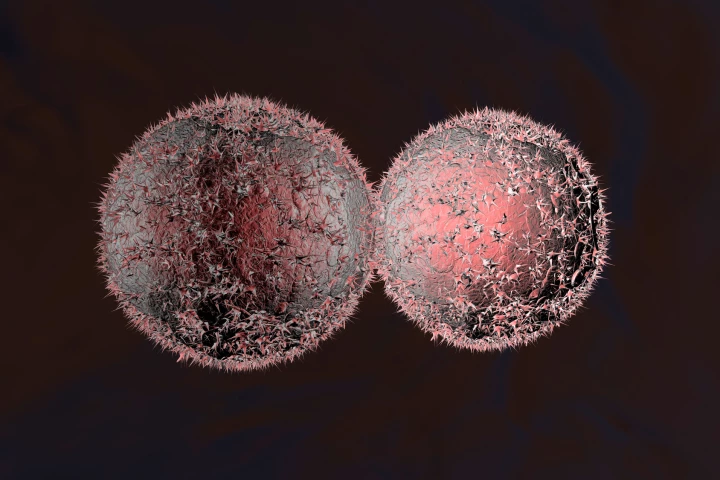
Researchers have found that the “mother” of stem cells, known as totipotent stem cells, have a much slower rate of DNA replication, which helps improve their differentiation efficiency. This could lead to major breakthrough for regenerative medicine.
-
Not all planets orbit stars - some drift freely through the cosmos on their own. These cold, dark worlds don’t make great candidates for hosting life, but a new study suggests that their moons could be more habitable than they might seem.
-
Killing cancer cells isn’t too hard – the tricky part is doing so without harming healthy cells. Now researchers have developed nanoparticles that selectively release drugs inside tumors, while keeping them safely locked away when in healthy cells.
-
One argued silver lining of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide levels is that plants will be better off. But a new study has found that the more extreme heat and drought brought on by climate change would cancel out most of the benefits for trees.
-
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is one of the most common and most devastating muscular diseases. Now researchers have managed to use the CRISPR gene-editing tool to correct the condition in pigs, bringing the treatment ever closer to human trials.
-
Chameleons are well-known for their ability to change colors, but scientists have just discovered a new visual trick in the creature’s repertoire. Under UV light many types of chameleons have been found to fluoresce in vibrant patterns, which they may use to communicate with others of their species.
-
Many lizards are capable of breaking off and regrowing their tail, in order to escape predators. The newly-described Geckolepis megalepis gecko, however, possesses a rather interesting trait. When a predator tries to eat it, that creature often just ends up with a mouthful of tear-away scales.