Massachusetts General Hospital
-
Wired devices called oximeters are the gold standard when it comes to monitoring oxygenation in transplanted tissue, but scientists may have found a better way forward in the form of a paint-on bandage that glows instead.
-
A new study has shone a light on the health benefits of short bursts of vigorous exercise, finding that they can produce “striking” effects on the metabolites circulating through the body and lead to improvements in a wide range of bodily functions.
-
An experimental drug has been shown to slow the progression and prolong survival of patients suffering from the neurodegenerative disease ALS. With Phase 2 human trials complete, the company developing the treatment is working to accelerate its approval.
-
A team of researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, trawling through hospital admission data, may have found a simple blood-based biomarker that can help doctors assess those patients most at risk of suffering the worst effects of COVID-19.
-
HIV is an insidious virus, hibernating inside cells ready to re-emerge if treatment is stopped. Now a team of researchers has found a way to shrink that viral reservoir by adapting a cancer immunotherapy technique to supercharge immune cells in mice.
-
The results of the largest clinical trial ever conducted into the relationship between vitamin D and depression suggest the vitamin does not improve mood or prevent depression. The trial did not investigate subjects with pre-existing vitamin D deficiencies.
-
Two new studies, published in The Lancet Neurology, are suggesting increasing levels of a particular brain protein, detected in blood and spinal fluid, could be the earliest sign of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s.
-
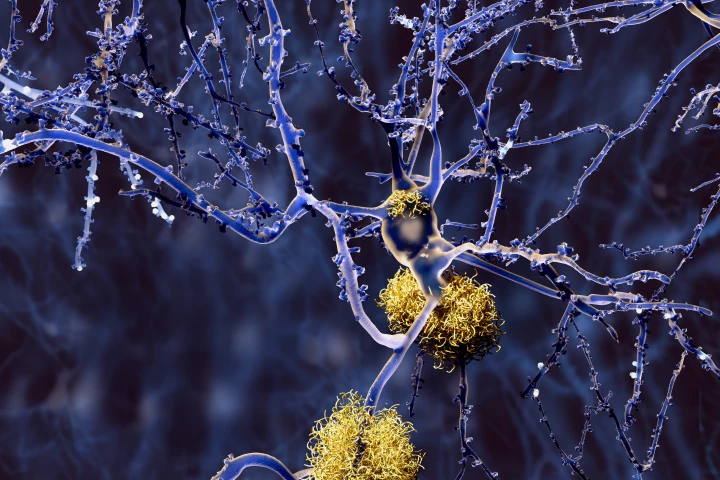
A new mouse study from Massachusetts General Hospital has for the first time established a connection between elevated levels of calcium in mitochondria and neuron death associated with Alzheimer's disease.
-
It sure sounds like an online pop-up ad, but Harvard scientists have created and tested a new treatment that melts away body fat. The new technique involves injecting an icy saline solution directly into fat deposits to shrink them by half.
-
A leading suspect in the onset of Alzheimer's disease is a toxic plaque called amyloid-beta, which new research has found could be better cleared away by harnessing natural oscillations in the blood vessels known as vasomotion.
-
When someone has a severe burn, a protective covering needs to be temporarily grafted onto the wound site. Although that covering typically consists of skin from a human cadaver, live-cell pig skin has now been used on a patient for the first time.
-
Freezing is one of the simplest methods of preserving food, biological tissue and other perishables, but the formation of ice crystals can damage cells. Now, researchers have developed a new way to “supercool” water in a liquid form well below the usual freezing point.
Load More