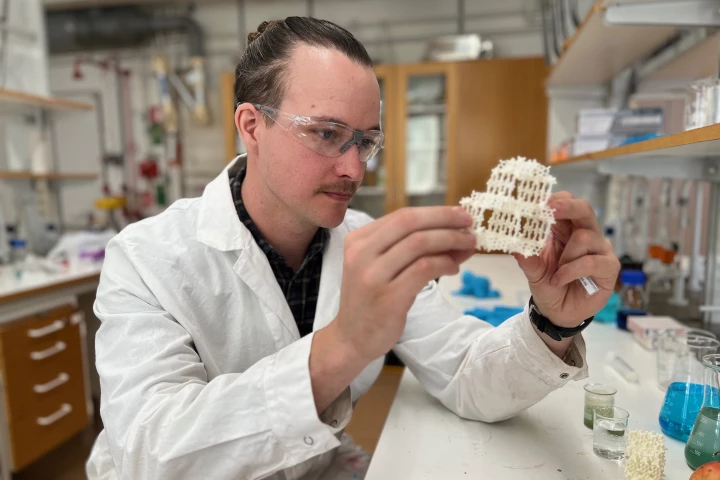
metal-organic frameworks
Stories on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which have the highest surface area of all known materials, high porosity and selective absorptivity
-
Nobody wants harmful bacteria on objects such as medical implants, yet we also don't want them building up a resistance to antibiotics. Well, help may be on the way, in the form of metal structures that kill the microbes by poking holes in them.
-
In recent years, pomegranate-derived compounds have been shown to slow cellular aging, protect unborn babies' brains, and serve as additives in better automotive materials. Now, they've also been used to remove pharmaceuticals from wastewater.
-
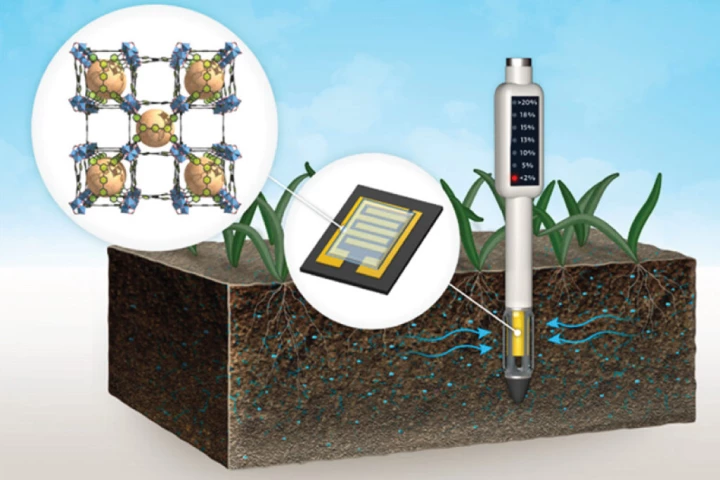
Soil moisture sensors can help farmers save water, by letting them know when their crops actually need to be watered. A new sensor could be particularly helpful, as it incorporates a special material which makes it highly sensitive to moisture.
-
With the world focused on addressing climate change, scientists have had to get creative when it comes to developing sustainable building materials that tackle CO2 emissions. A team has now engineered wood that is stronger and traps carbon dioxide.
-
While the purification of wastewater once just involved the removal of traditional pollutants, it now also entails the removal of microplastics. A new powder reportedly does the job much quicker and more thoroughly than has previously been possible.
-
Engineers at the University of Vienna have developed a new composite material that makes an efficient filter for removing organic pollutants from water. The system uses super-porous “nano-sponges” embedded on a sheet of graphene.
-
Scientists have developed an efficient new way to convert methane into methanol at room temperature. The technique could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provide a cleaner way to make key products.
-
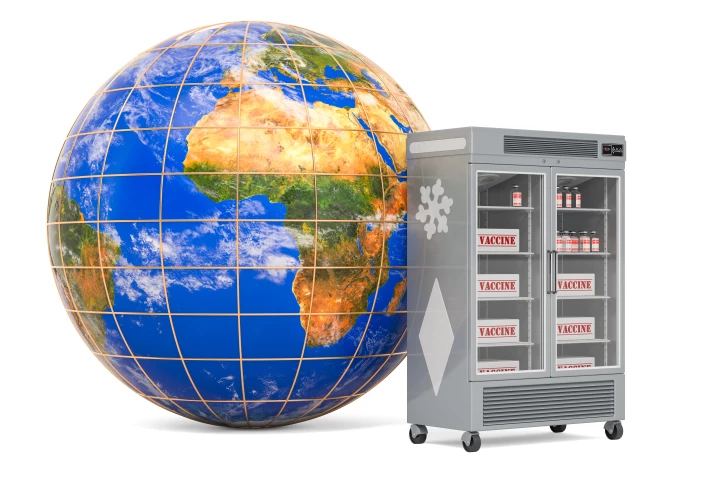
Researchers at Australia’s CSIRO have demonstrated a method for protecting the integrity of vaccines against high temperatures. A proof-of-concept study has shown the method keeps vaccines viable at temperatures up to 37 °C (98 °F) for three months.
-
Engineers at Dartmouth College have developed a new crystal structure that can stretch to twice its size when it encounters a specific chemical. The team says that the material could be used to selectively absorb impurities in water.
-
Researchers have developed a new type of vaccine against urinary tract infections that has shown promise in tests in mice. The treatment uses a whole dead bacterial cell, wrapped in a protective cage, to trigger an immune response.
-
Researchers at Lancaster University have developed a new material that can store energy for months, and potentially years, at a time. The material can be activated by light, and then release the pent-up energy on demand in the form of heat.
-
Getting CRISPR into cells can be challenging. Now Australian researchers have packaged the tool inside porous materials called metal organic frameworks (MOFs) coated in a green tea compound, and used it to silence key genes in prostate cancer cells.
Load More