Metals
-
Exposure to common metals has again been linked to ADHD and specific symptoms. It builds on existing research that has found a strong association between environmental contaminants like lead and a higher rate of people diagnosed with the condition.
-
In studying the conditions that emerged just after the Big Bang using the Large Hadron Collider, scientists turned lead into gold – for just fractions of a second. Not a whole lot of gold, but gold nonetheless.
-
You know how EVs and practically anything else that runs on lithium batteries aren't really all that 'green' because producing lithium takes a huge toll on the planet?
-
Metalworking usually requires very high heat and pressure, but scientists in Singapore have now demonstrated a way to make very pure metal structures at room temperature. It’s inspired by the exoskeletons of crabs and insects.
-
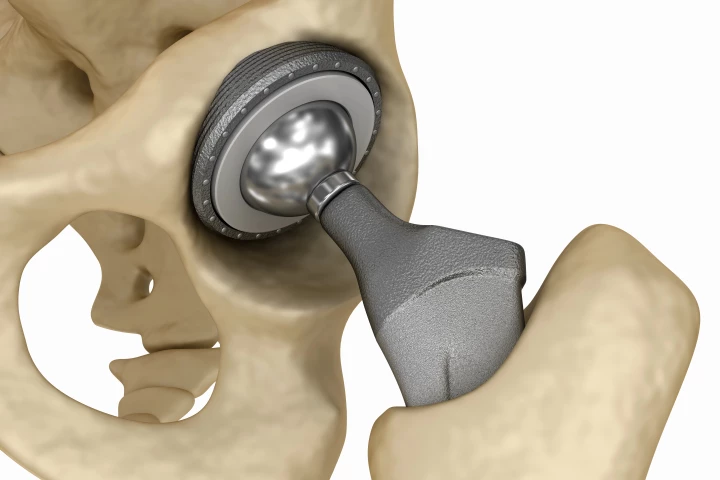
While titanium hip and knee implants do restore mobility to a great many people, they're still subject to failure. A new alloy could help change that, simply by adding a smidge of bendy, bacteria-killing gallium to the mix.
-
The first study to measure the concentration of metals in tampons has found that several brands contain concerning amounts of lead, arsenic and cadmium. More research is needed to determine whether the presence of these toxic metals poses a health risk.
-
For the first time, scientists from across North America have formed a clear picture of Alaska's 'rusting' rivers and streams, tracking 75 areas in the remote Brooks Range that are flushed with the bizarre hue so bright it's even visible from space.
-
Unusually high levels of lead and uranium has been found in the urine of teenagers who frequently use e-cigarettes. But experts have warned that, due to research flaws, not enough has been done to ensure the link isn't just smoke and mirrors.
-
In a few billion years, the Sun will destroy the solar system’s inner planets – and if it’s lucky, it might get a big cool scar to brag about. That’s what happened to a newly found white dwarf, which appears to have a bizarre metal scar on its surface.
-
Small Modular Reactor (SMR) construction shifts into high gear, as UK company Sheffield Forgemasters welds a full-size nuclear reactor vessel in under 24 hours instead of the usual 12 months. The rollout of this game-changing tech could be massive.
-
Among the cargo that just blasted off from Cape Canaveral, Florida, bound for the ISS were two firsts: the world’s first metal 3D printer designed especially for use in orbit and the first miniaturized surgical robot to be sent to the station.
-
The hot interior of planets isn’t somewhere you’d expect to find snow, but “iron snow” could fall on Earth’s core. A new study has modeled the dynamics in the lab and found that iron snow could make magnetic fields switch on and off in some planets.
Load More