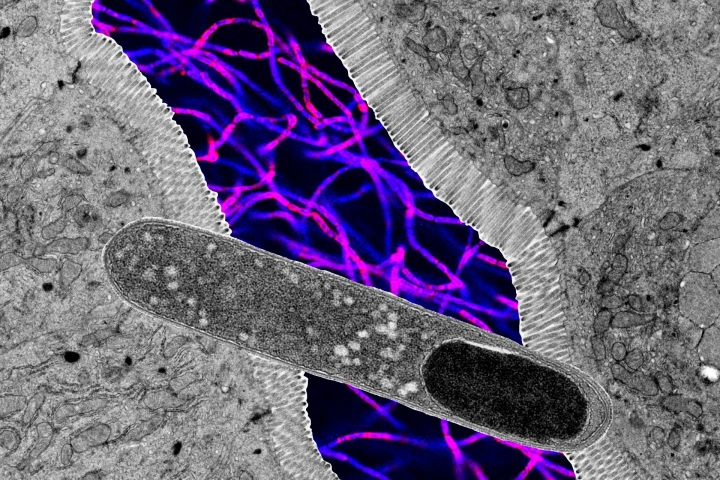
Microbes
-
In the South China Sea, the aqua-colored waters of an expansive shallow reef platform suddenly gives way to a near vertical shaft of vast darkness – an ocean sinkhole almost entirely devoid of oxygen and, in turn, marine life as we know it.
-
Researchers have homed in on a single gut microbe that acts to prevent fat gain, even with a high-fat diet. The discovery adds to the booming science of finding ways to enlist the microbes that already live in our bodies to help us improve our health.
-
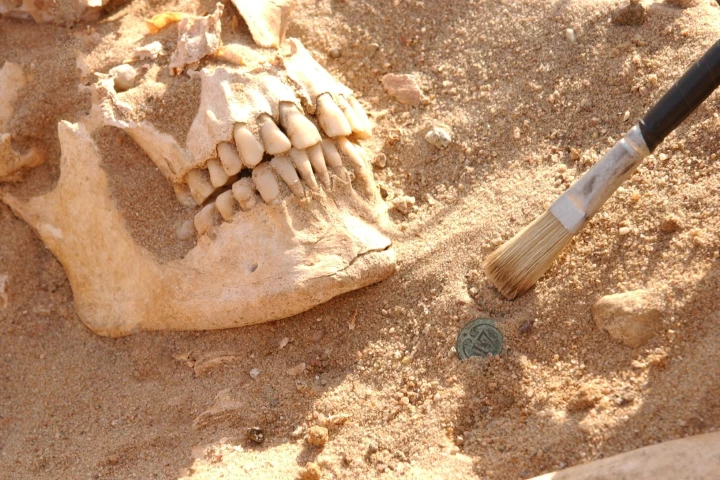
One of the first events to signal the collapse of Napoleon's reign was his crushing defeat after an invasion of Russia in 1812. Researchers have long thought that the disease typhus played a role, but modern DNA analysis paints a different picture.
-
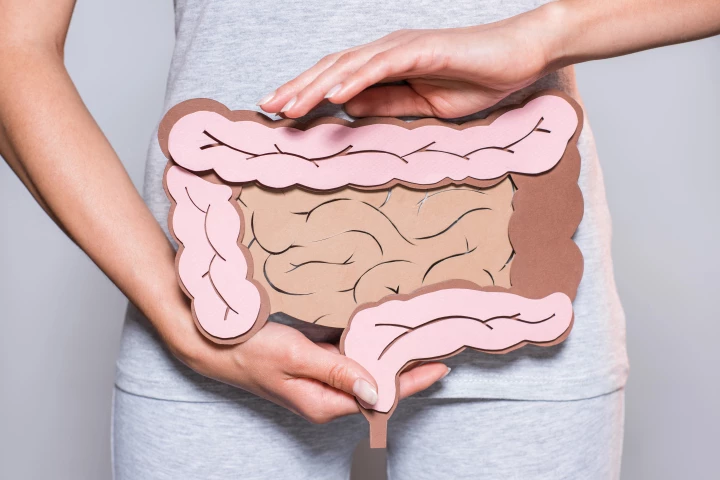
A novel treatment for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is on the horizon, with the discovery that two specific gut microbes produce serotonin that protects against inflammation and damage.
-
For the first time, scientists have identified 27 bacteria and fungi in our mouth that contribute to pancreatic cancer. Collectively, carrying all of these “bad” microbes increases cancer risk by 250% – 3.5 times higher than in the general population.
-
A study of nearly 400,000 people has for the first time found a causal link between gut bacteria and insomnia, confirming that some microbes aid sleep while others disrupt it. Fourteen bacterial taxa were found to contribute to the risk of insomnia.
-
A small daily dose of kombucha made from black tea has been shown to meaningfully reshape the gut microbiome in adults – particularly those with obesity – without any dietary changes. It also reveals a lot about the importance of micro-biodiversity.
-
A new study from scientists at Michigan State University sheds light on a recently discovered microbe and its potential for scavenging pollutants in deep soil. Further work could lead to novel solutions in providing clean drinking water worldwide.
-
Even without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
Researchers have found an indication of depression in a slightly unexpected place – the microbiome inside our mouths. The finding opens a new route of inquiry that could lead to novel antidepressant treatments and help other ailments as well.
-
If you're going to try "tattooing" a microscopic animal, it would make sense to select one of the toughest creatures on the planet. That's what scientists have done with the tardigrade, and the tech they used may have some valuable applications.
-
A rice wine native to the Philippines has grabbed the attention of researchers looking into new, natural ways to slow biological aging. But it's not the wine itself – sorry – in the spotlight, but what's leftover after the liquid is ready to bottled.
Load More