Neurological
-
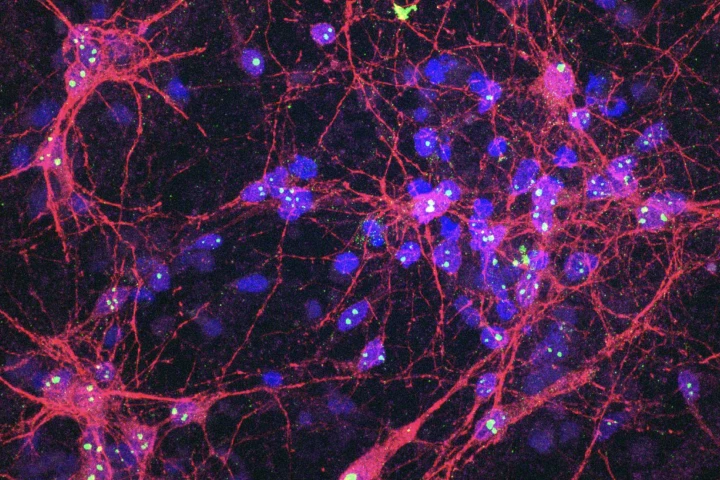
For the first time, Cortical Labs' mini-brain system has shown how its breakthrough biological computer system can, in response to drug intervention, alter activity and improve performance. It's a huge milestone for synthetic biological intelligence.
-
Exposure to common metals has again been linked to ADHD and specific symptoms. It builds on existing research that has found a strong association between environmental contaminants like lead and a higher rate of people diagnosed with the condition.
-
A new experimental painkiller has shown promise in dulling or eliminating pain without the addictive qualities exhibited by today's most popular opioids. The drug also sidesteps common opioid side effects like constipation and sedation.
-
Neighborhoods near golf courses are often considered desirable locations. However, a new study suggests that houses within a few miles of manicured fairways and greens may not be such hot property for your health and wellbeing.
-
Scientists have uncovered an odd superpower triggered by tapping your finger to a beat – it may help you understand someone talking to you in a noisy place, like at a busy cafe. While it sounds a little woo-woo, there's emerging science behind it.
-
In an effort to enhance the research abilities of biologists, Stanford University researchers have discovered that applying a popular food coloring to the skin of mice allowed them to see through to the rodents' internal organs and other structures.
-
Based on fractal patterns in neurons, researchers believe our brains exist at or near a state called criticality where they're extremely close to shifting from one state of matter to another. They also admit they don't know what either state is.
-
A pioneering once-a-day pill that regenerates nerve cell connections damaged by ALS has been FDA-approved for ongoing clinical trials. The drug is now being given to those with ALS and could be a watershed moment in the treatment of the fatal disease.
-
If someone you know has gone through chemotherapy, you might be familiar with the side effect 'chemo brain.' Scientists have now demonstrated a simple way to protect brain cells from damage using flashing lights and sounds at a certain frequency.
-
Researchers have created a single-dose genetic therapy that, in mice, cleared the protein blockages that cause motor neurone disease and frontotemporal dementia, two incurable neurodegenerative diseases that eventually lead to death.
-
A team has reported the first-ever evidence of human-to-human transmission of Alzheimer’s disease, demonstrating how a human growth hormone treatment transplanted toxic proteins into children and caused the development of early-onset Alzheimer’s.
-
Researchers have created an ultra-thin sensor that can wirelessly record deep brain activity down to a resolution of one or two neurons. The device has potential applications in conditions such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and chronic pain.
Load More