North Carolina State University
-
Unlike conventional fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites which last decades, UNC’s FRP composites could last 500 years. The breakthrough technology is not only stronger, but electrically melts a “healing” substance that seeps into damaged areas.
-
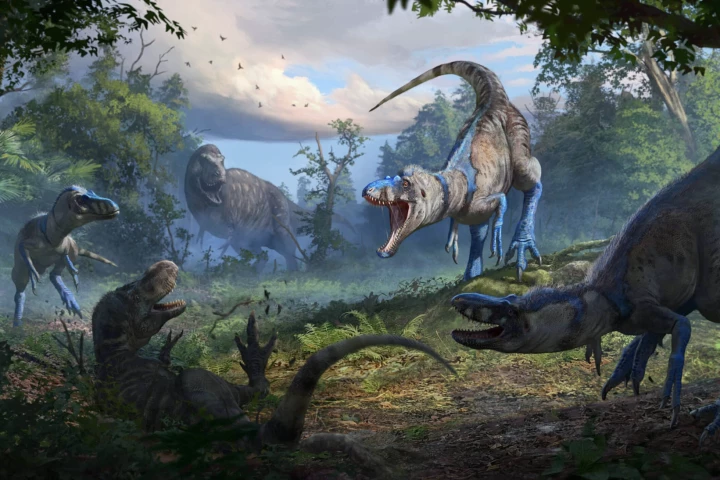
More than 60 million years on from its final day on Earth, there's a dinosaur we owe an apology. Paleontologists confirm that the Tyrannosaurus rex locked in combat with a Triceratops in the famous Dueling Dinosaurs specimen is not a T. rex after all.
-
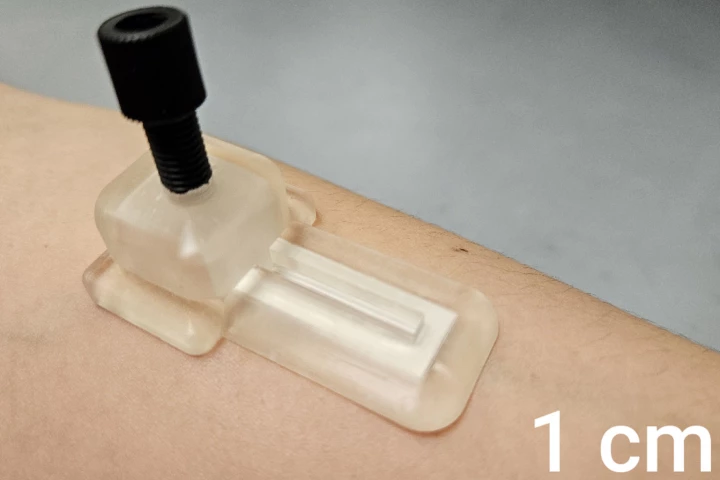
Nobody likes having blood samples taken, which is why it's always good to hear about possible alternatives. One of the latest takes the form of a self-powered skin patch that painlessly gathers biomarker chemicals for up to 24 hours at a time.
-
In a recent experiment that sounds more sci-fi than science class, researchers have demonstrated a novel vaccine platform that uses ordinary dental floss embedded with tiny, dissolvable microneedles showing how everyday materials can be reimagined.
-
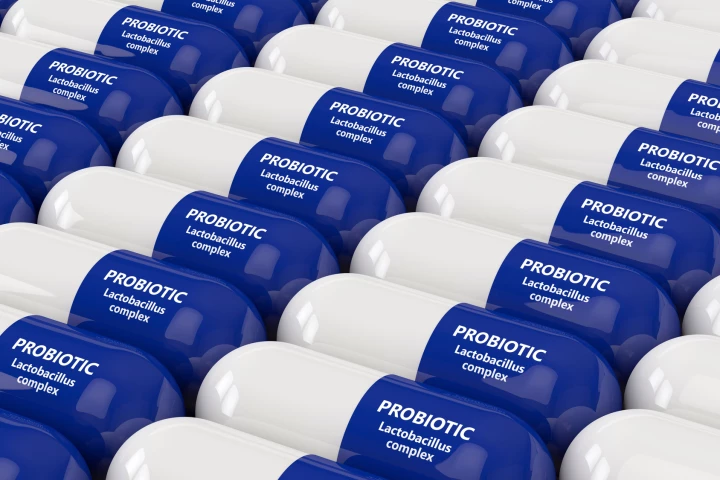
Not all probiotics are created equal. A new study found that one commonly available strain made a gut infection worse, while another helped stop it in its tracks, thanks to a powerful natural antibiotic and an unexpected ally from the gut’s own ranks.
-
Cable cars are handy for transporting cargo up mountain slopes, but what if you want to do the same sort of thing on a smaller scale? Well, you could try using a tiny new light-powered robot, which is cable of carrying items up thin mid-air tracks.
-
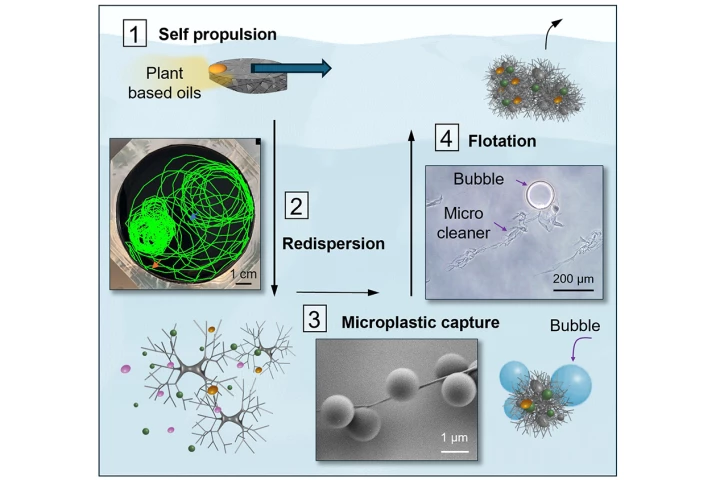
Wouldn't it be great if there were a way of chasing down waterborne microplastic particles and catching them for removal, as opposed to just passively filtering them out of water bodies? Well, new "microcleaners" can reportedly do that very thing.
-
Scientists at North Carolina State University have created a magnetic “metasheet” that can move objects and liquids around without needing robot arms or grippers.
-
It was just two years ago that a tiny robotic manta ray became the world's fastest-swimming soft-bodied robot. Well, one of its descendants has now smashed that record – and it uses less energy than its predecessor, to boot.
-
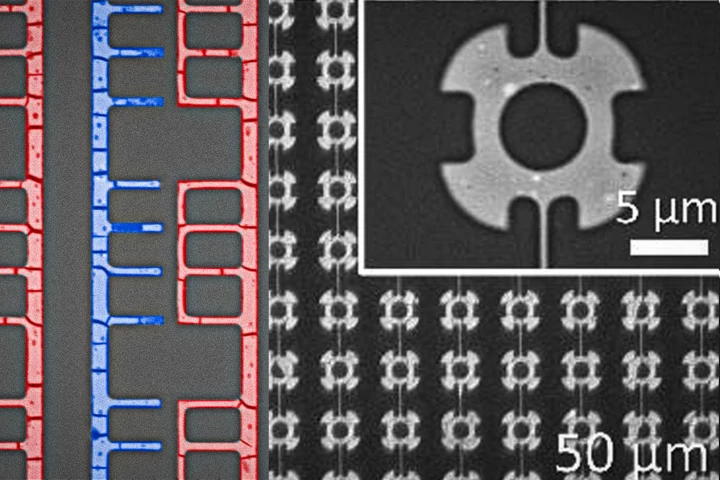
A remarkable proof-of-concept project has successfully manufactured nanoscale diodes and transistors using a fast, cheap new production technique in which liquid metal is directed to self-assemble into precise 3D structures.
-
Despite what you might say when drunk, you’re not the best backflipper in the world. That honor belongs to a tiny little bug called a globular springtail, whose superfast backflips have now been caught on slow-motion camera for the first time.
-
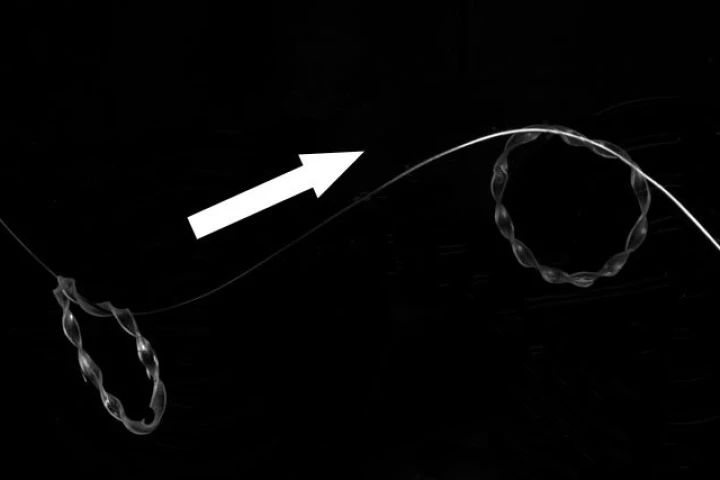
A full DNA computer is a step closer, thanks to a new technology that could store petabytes of data in DNA for thousands or even millions of years. The system can also process data, as demonstrated by solving sudoku puzzles.
Load More