Northwestern University
-
Researchers have shown they can achieve some control over what people are dreaming, bringing a theme that has been frequently explored in the sci-fi and horror genres off the screen and into the lab. Puzzle-solving was at the heart of the research.
-
A new study from Northwestern University offers hope to Alzheimer's patients and their caregivers. If researchers there are correct, their new small-molecule NU-9 drug may be able to stop the disease long before it begins ruining lives.
-
Scientists at Northwestern University have developed a sub-scalp device that beams light through bone into the brain, teasing a future of drug-free pain relief, cybernetic control of robotic limbs, and the simulation of sight, hearing, and touch.
-
For the first time, scientists have demonstrated how tanning beds cause fundamental DNA damage across almost the skin's entire surface that results in a threefold risk of developing melanoma. It puts beyond doubt the dangers of using these devices.
-
Engineers at Northwestern University have developed a device that goes on your fingertip to feel the sensation of interacting with textured surfaces on a touchscreen. It could be a major step forward in how we interact with personal tech.
-
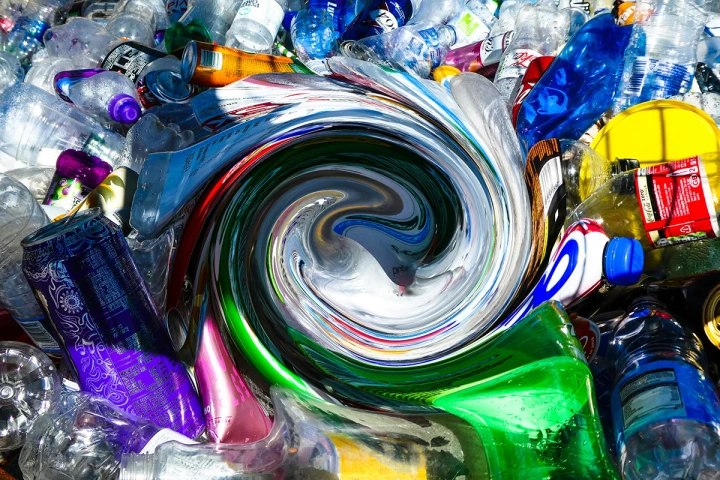
An inexpensive catalyst that selectively breaks down the most common single-use plastics in recycling processes negates the need for tedious and expensive sorting. This could give recycling the nudge it need to keep pace with plastic production.
-
A common asthma medication could be the key to preventing life-threatening reactions to food allergies. Researchers at Northwestern University identified a previously unknown biological trigger for anaphylaxis – and a surprising way to target it.
-
A cannabinoid our bodies produce naturally has been found to play a role in the fear responses characteristic of conditions like anxiety and PTSD. The discovery opens the door to developing a treatment that targets this specific chemical.
-
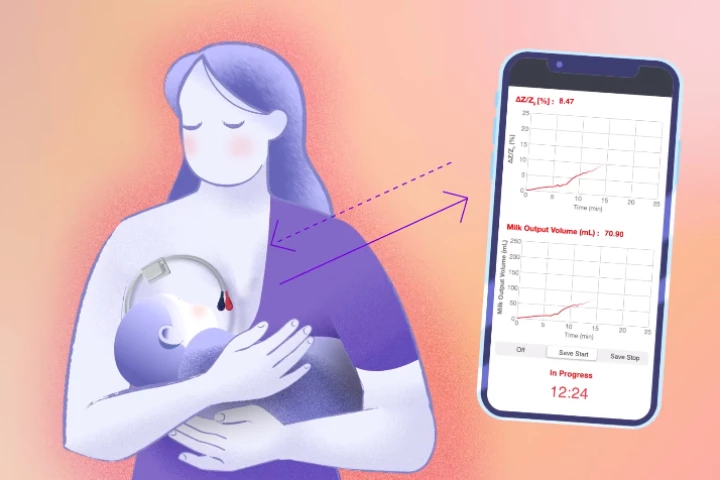
While many parents extol the virtues of breastfeeding, it can be hard to tell how much milk a breastfeeding infant is consuming. A new wearable device addresses that problem, using an electrical current to gauge milk intake in real time.
-
Did you know you emit gases through your skin? These vapors, which include CO2 and volatile organic compounds, can provide insights about your metabolic status, disease states, and overall health. A new wearable can help make sense of it all.
-
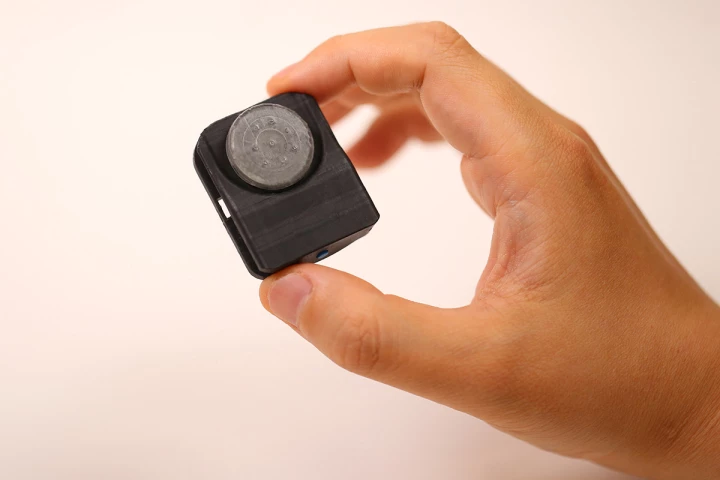
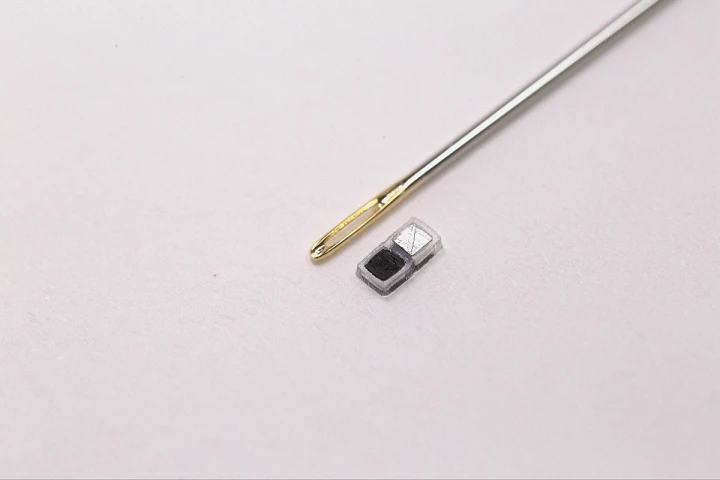
Engineers at Illinois' Northwestern University have developed the tiniest pacemaker you'll ever see. It's several times smaller than a regular pacemaker, and it's designed for patients several times smaller than the average pacemaker user.
-
You don't often find crowds flocking to take in the pungent scent of rotting flesh, yet that's just what happens when a corpse flower blooms at a public garden. But this iconic endangered plant is now facing a new threat – our aversion to paperwork.
Load More