Opioids
-
A new experimental painkiller has shown promise in dulling or eliminating pain without the addictive qualities exhibited by today's most popular opioids. The drug also sidesteps common opioid side effects like constipation and sedation.
-
In a breakthrough finding, researchers have discovered that immune cells near the spinal cord are triggered by estrogen and progesterone to produce a natural painkiller called enkephalin. The finding could change the way we treat chronic pain.
-
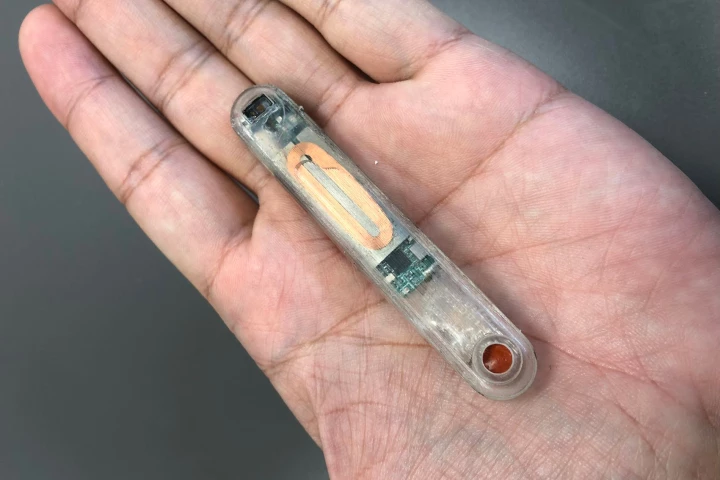
When someone overdoses on opioids, it's critically important that they receive a dose of the opioid-reversing drug naloxone as soon as possible – otherwise, death is a distinct possibility. That's where a new implant comes in, as it automatically dispenses naloxone from within the body.
-
A new study has found that exposing babies to prescription opioids while they’re in the womb can increase their risk of developing immune-related conditions – particularly infections, eczema and asthma – in early childhood.
-
A new study has found that there was no association between using cannabis and non-medical opioid use in people receiving pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorder. The findings neither confirm that using cannabis leads to opioid use nor that it's effective in reducing it.
-
Spread by sandfly bites, the leishmania parasite causes ulcers that for many people are unexpectedly pain-free. For decades scientists have been puzzled by these painless lesions but new research is now homing in on the unusual analgesic mechanisms.
-
Researchers are close to human clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of vaccines to prevent heroin and fentanyl overdoses. If approved, they could revolutionize the treatment of opioid addiction and reduce deaths from overdose.
-
Researchers have developed an antibody that targets the opioid fentanyl and its derivatives, reversing overdose better than currently available treatments. The novel therapy could be a more effective way of treating life-threatening opioid overdoses.
-
Clinical trials of a novel non-opioid analgesic have found it to be effective in reducing acute postoperative pain, opening the door to a new way of managing short-term pain that avoids the pitfalls associated with using opioids.
-
Despite their risks, opioids are commonly prescribed as a first-line treatment for acute lower back and neck pain. Researchers have found that, compared to opioids, a placebo is more effective in reducing acute – short-term – back and neck pain.
-
While opioids are among the most powerful painkillers, they're also highly addictive, which makes them hard to get. A new finding may offer hope to pain patients in the form of powerful drugs that lack the most severe side effects of current options.
-
A new study has shown that for people with chronic pain taking opioids over the long term, incorporating an internet-based self-management program into treatment may help reduce both pain and opioid intake.
Load More