Oxygen
-
We all know the equation – hydrogen plus oxygen equals water. But now scientists have captured molecular-scale video of that famous meeting in action, which could lead to a new way to generate large amounts of drinking water.
-
Even young, healthy passengers put their heart health at risk when they consume alcohol before sleeping on a flight, particularly a long-haul flight, according to a new study. The researchers say it's an underestimated risk that could easily be avoided.
-
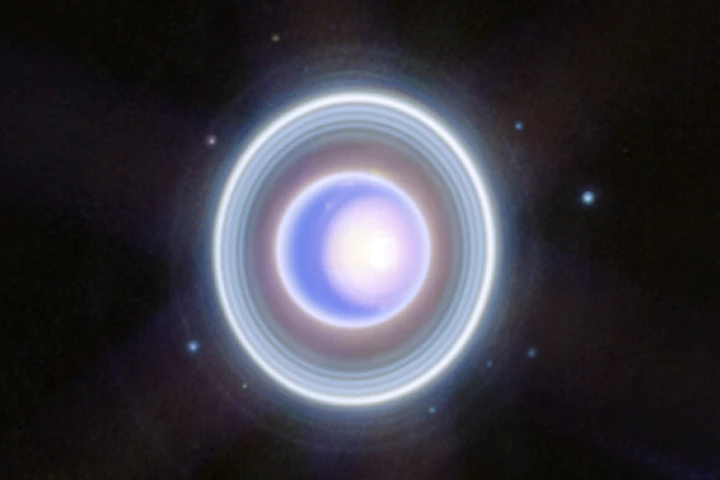
Scientists have discovered the potential existence of a bizarre new molecule related to water. Dubbed “aquodiium,” this ion could form under extreme conditions and may explain some of the weirdness of our solar system’s ice giant planets.
-
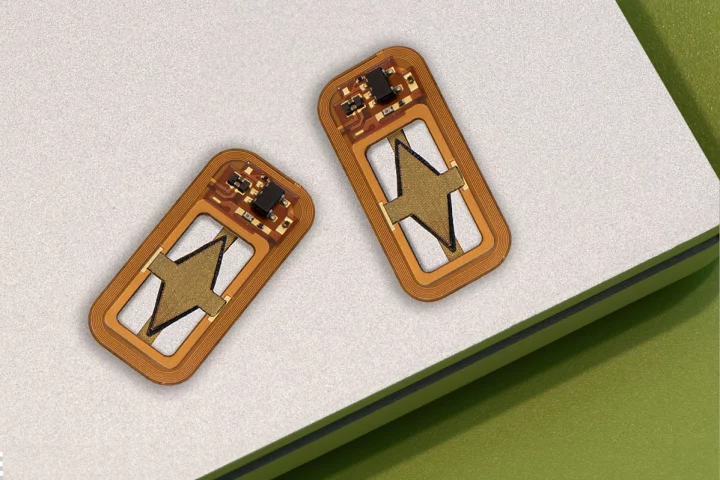
A new sensor could soon allow hospital patients' blood oxygen levels to be checked via their breath. The technology is claimed to be more reliable and less painful than existing traditional methods.
-
Look at the development of Earth-bound tech and you'll find fire at the heart of it, says a duo of researchers. And what does fire need to burn? Oxygen, whose chemical signature could provide clues to technological societies on worlds beyond our own.
-
Researchers have created a paint containing living cyanobacteria that produces oxygen and can capture carbon dioxide. The bacteria’s ability to withstand extreme environments means the paint could even be used in outer space.
-
Daily insulin injections are painful and inconvenient, which is why scientists are developing implants that treat diabetes without any need for needles. A new one looks particularly promising, as it produces oxygen to feed onboard islet cells.
-
A new study has found that brief treatment with 100% oxygen can substantially improve motor learning in young, healthy adults. It may have opened the door to using this simple treatment with people who are re-learning motor skills they’ve lost.
-
A large new study has found that healthy older adults taking a long-term low dose of aspirin may be at increased risk of developing anemia. The researchers say their findings suggest that these patients may need regular monitoring.
-
EPFL engineers have built and tested a solar reactor that generates hydrogen gas from sunlight and water. The system is not only highly efficient at producing hydrogen, it also captures the “waste” products of oxygen and heat to put them to use too.
-
Respiratory ailments may hamper the body's ability to draw oxygen from the lungs, which is why patients' blood oxygen levels often need to be checked. New research now suggests that people could track those levels at home, using their smartphone.
-
If humans are to one day survive and thrive on Mars, ready access to breathable oxygen will be a necessity, and an interesting technology sent along with the Perseverance rover is beginning to show exciting promise on this front.
Load More