Plants
-
For years, we’ve admired plants for their ability to cleanse the air but our green ally might be contributing to air pollution in an unexpected way. While they may be just trying to fend off pests, this mechanism is also harming the environment.
-
The evolutionary ladder is meant to be climbed one rung at a time with an organism shedding some traits and gaining others on the way up. However, in a very surprising twist, some tomatoes on the Galapagos islands are inching back down the ladder.
-
A new study published in the journal Evolution is challenging the prevailing belief that evolution is a one-way process. The findings suggest some species of fern can evolve backward, reverting to a more primitive form when the environment demands it.
-
Antibiotics can be literal lifesavers, but they are particularly hard on the gut thanks to their indiscriminate destruction of both good and bad bacteria in the body. New research shows a possible way to fight their negative effects based on diet.
-
You don't often find crowds flocking to take in the pungent scent of rotting flesh, yet that's just what happens when a corpse flower blooms at a public garden. But this iconic endangered plant is now facing a new threat – our aversion to paperwork.
-
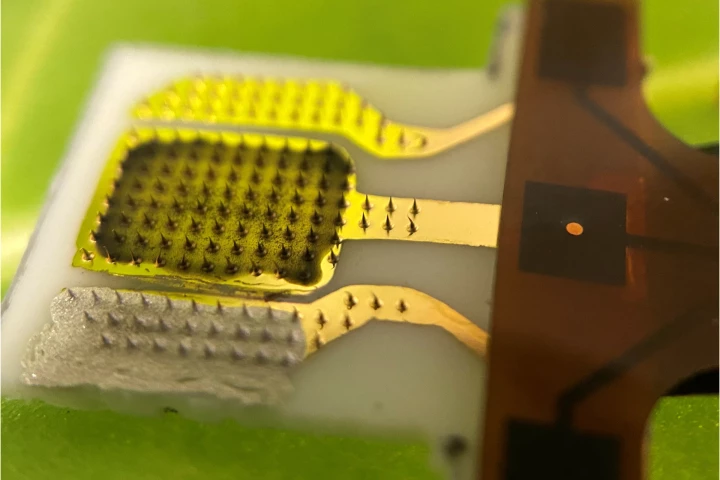
The sooner a farmer knows that their crops are suffering, the faster they can take action to prevent major crop failure. A new plant-leaf-poking sensor could soon help them do so, by sending an alert as soon as the plant gets stressed.
-
Scientists have identified new gene modifications that can make tomatoes and eggplants grow bigger, which could help boost yields in developing countries.
-
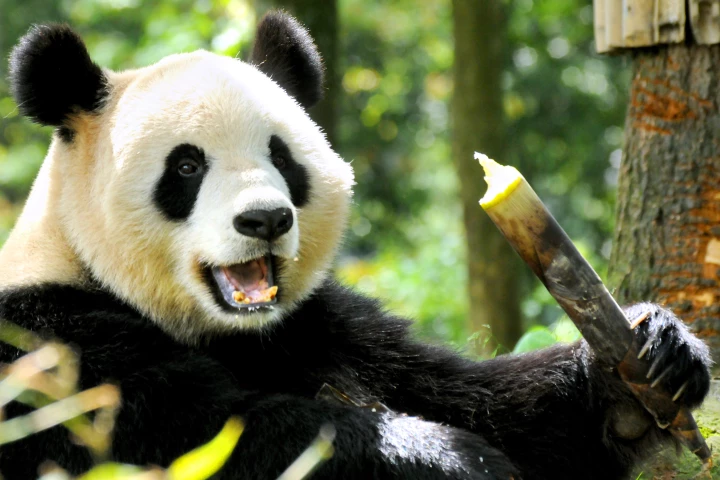
Built to be carnivorous, giant pandas spend up to 16 hours a day on their backsides eating bamboo. But contrary to all the panda jokes, it's not because they're lazy or too dumb to know better. It's far more fascinating – and it may help humans, too.
-
Crop fertilizers are a major source of pollution, as the chemicals make their way out of the soil and into the environment. Scientists are now working on a solution to that problem, by developing a fertilizer that takes the form of tiny glass beads.
-
When most people think of duckweed, they likely picture a green film growing across the surface of a stinky, stagnant slough. The protein-rich plant may soon be on your plate, however, as it's been approved for human consumption in Europe.
-
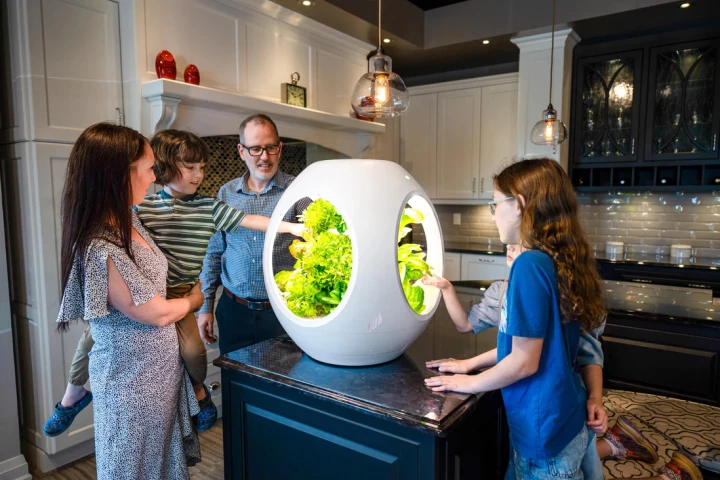
While everyone loves the thought of growing fresh veggies indoors, not everyone has the green thumb required to do so. The Plantaform system was designed with that fact in mind, as it grows edible plants automatically … using a nutrient-rich fog.
-
Common ivy is better known as a garden invader or a rather attractive indoor plant that's prone to triggering allergies. Now, for the first time, it's been found to be very effective in blocking pain signals – by instead invading a key pain receptor.
Load More