Recycling
-
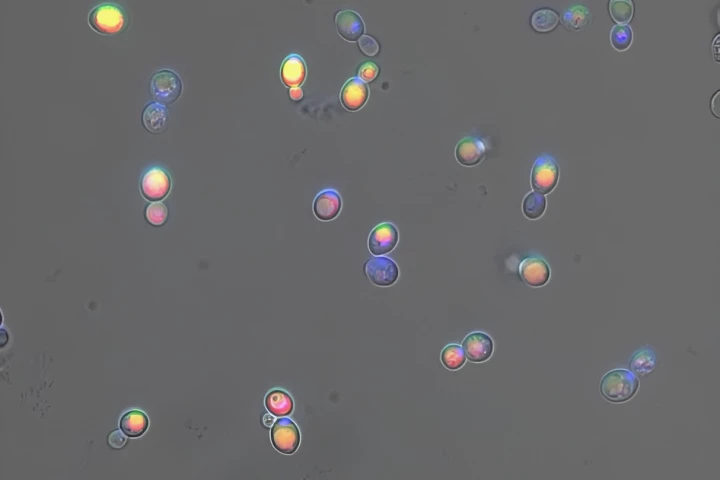
There may be a new use for that urine you've been so thoughtlessly flushing. Scientists say it could be an alternate source of a valuable bone- and tooth-repair material, with a little help from a genetically modified type of yeast.
-
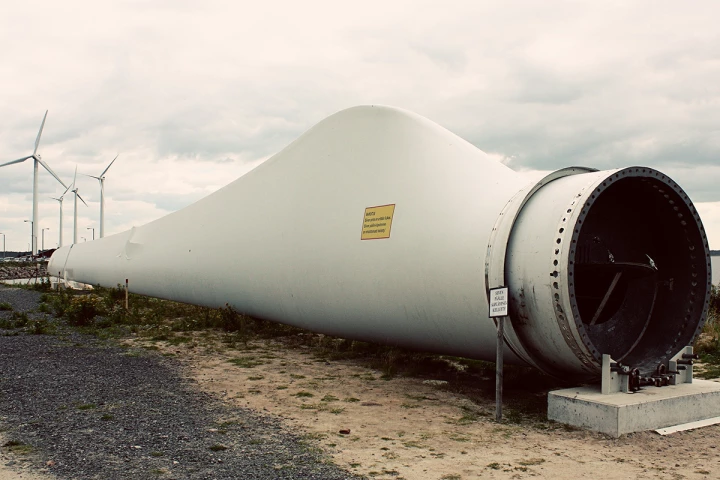
Recycling wind turbine blades is hard because they're built to weather the elements for decades. Researchers have devised a way to use discarded blades to create strong and durable plastics – without resorting to the use of harsh chemicals.
-
It isn't easy to recycle high-voltage batteries from electric cars, but Porsche wants to take a stab at it. The plan: extract raw materials from old EV batteries to make fresh ones for its own electric models.
-
Lego is the largest tire manufacturer by volume in the world – even though its tires are among the smallest on the planet. The Danish toy company is now making those tires out of recycled materials like fishing nets, engine oil, and rope.
-
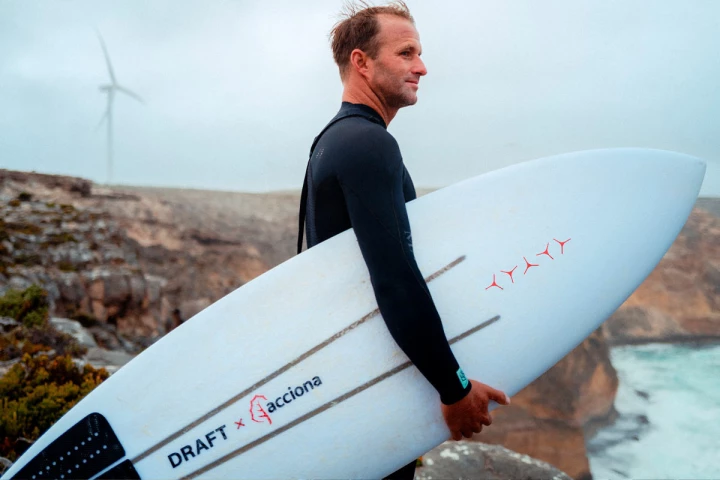
It's both challenging and crucial to recycle wind turbine blades, because they are built to last decades and don't degrade quickly in landfills. An Australian firm has hit upon a radical solution: it's turning those old fins into surfboards.
-
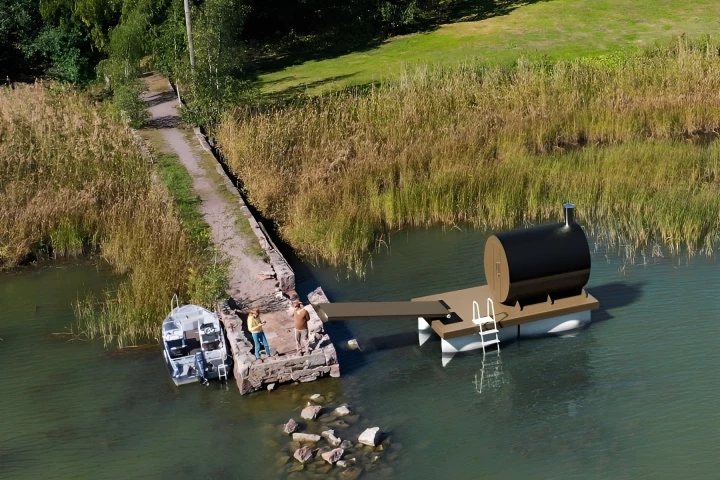
Old, discarded wind turbine blades don't biodegrade. They do, however, float if sealed. Finnish startup Reverlast is capitalizing on that fact, by taking end-of-use blades and converting them into stylish floating docks.
-
Although it is possible to recycle Plexiglass, it's a complex and inefficient process, so it generally just isn't done. A simple new technique, however, is claimed to break the plastic down into all of its building blocks for near-complete recycling.
-
While it's great that many types of paper can now be recycled, textile waste is still mostly dumped or burned. A new technique could change that by combining the two materials, using discarded cotton clothing to boost the strength of packaging paper.
-
As much as wind turbines are great for producing clean energy, disposing of them when the time comes can be challenging. Researchers in China have hit upon a clever way to use discarded blades to build long-lasting roads.
-
Motorcycle-related waste is a serious problem. And apparently, there’s more waste from motorcycle gear than from the actual machine itself – particularly helmets. Dainese has thus started a ground-breaking helmet recycling strategy.
-
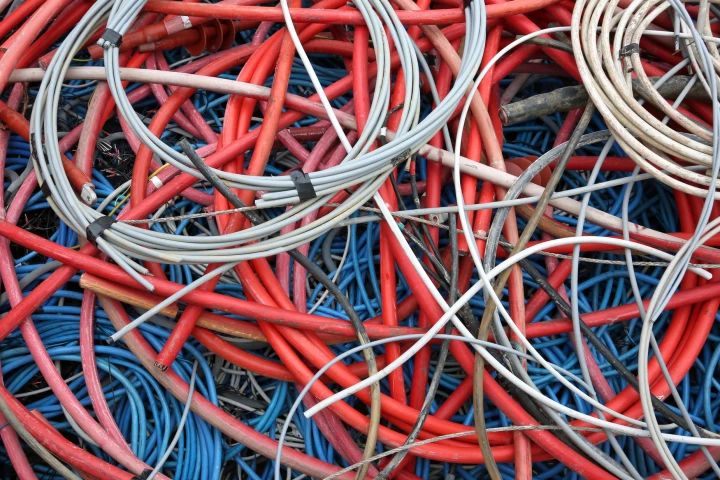
Italian and Japanese researchers have developed a novel method to free copper wire from its PVC coating, by treating electric cables with microwaves. The technique could go a long way towards helping tackle the growing problem of e-waste.
-
Many objects are made of black plastic, which has so far proven to be very hard to recycle. US scientists have devised a new method of recycling black polystyrene, however, using sunlight and an ingredient that's already present in the plastic.
Load More