Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
-
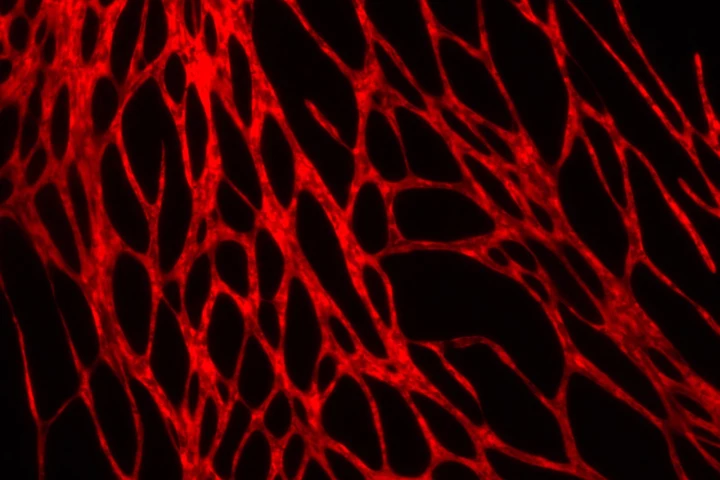
It certainly would be great if instead of having to be harvested from a patient's own body, permanent skin grafts could be 3D-printed as needed. Well, we may be getting closer to that point, as scientists have now bioprinted living skin complete with blood vessels.
-
The hole in the ozone layer may be on the mend, but its environmental impacts are ongoing. A new review study has examined the effects that the extra UV radiation is having on the environment, such as shifting climate zones, changing ocean temperatures and making some species more vulnerable.
-
Remember the garbage-collecting Oscar the Grouch, from Sesame Street? Well, an orbital-debris-gathering spacecraft now bears his name. Known as OSCaR ("Obsolete Spacecraft Capture and Removal"), the semi-autonomous craft is currently being developed at New York's Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
-
It’s no easy feat to find dark matter, since it's invisible and barely interacts with regular matter. Now the results are in from one of the most comprehensive dark matter experiments ever run, and while the stuff was again a no-show, the study helps scientists zero in on where it might be hiding.
-
Sufferers of type 1 diabetes regularly need to inject themselves with insulin in order to regulate levels of sugar in their blood. But scientists have remotely manipulated insulin production in mice using electromagnetic waves suggesting more comfortable treatments may not be all that far away.
-
A group of researchers from Tufts University, Brown University and the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are collaborating with the US Navy in a multi-year effort to explore how they might create robots endowed with their own sense of morality.
-
IBM's Watson supercomputer is going to Rensselaer Polytechnic University where it will be the object of Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and will (virtually) attend courses in English and math to hone its analytic skills.
-
Scientists have shown that anodes made from graphene oxide paper could allow Li-ion batteries to charge and discharge ten times faster than is presently possible.
-
VirtualDose utilizes computer models of different body types to advise physicians on which CT scanning configurations will produce the least amount of radiation.
-
Scientists have developed a tiny sensor, that could wirelessly transmit data on the status of orthopedic implants.
-
Foam made from graphene has been shown to be ten times more effective than traditional polymer sensors, when it comes to detecting gases associated with explosives.
-
Researchers have created an efficient new thermoelectric nanomaterial, that could be used to harvest waste heat for conversion into electricity.
Load More