Retina
-
A breakthrough treatment has allowed damaged retinal cells to regenerate themselves. The current research has been conducted on mice, but the pathways are the same in humans, which opens hope for a new way to treat certain kinds of blindness.
-
Researchers have developed a simple, non-invasive method of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease early using an eye scan. It could mean treatment can start sooner or, alternatively, could be used to monitor the disease’s progression.
-
Scientists in the UK have successfully used gene therapy to restore some vision to legally blind children with an inherited retinal condition. All 11 children in the clinical trial saw improvements within weeks of a single surgical treatment.
-
Blinking keeps our eyes moist – but we actually blink way more often than we need to if that was the only reason. Scientists have now found that the involuntary action plays a bigger role than we thought, helping us process visual information.
-
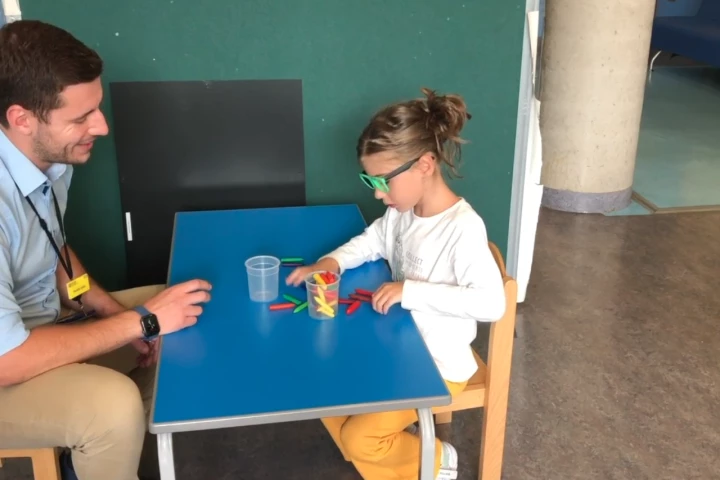
Researchers have used AI to screen photographs of children’s retinas to diagnose autism with 100% accuracy. The findings suggest AI is a viable screening tool for early diagnosis, especially when access to a specialist child psychiatrist is limited.
-
For the first time, scientists have identified a marker in the retina that may lead to Parkinson’s disease, and it can be detected early, which could be life-changing for those at risk of developing this or other degenerative conditions.
-
This stunning image may look like a particularly lively Jackson Pollock painting, but it’s actually an example of a new cell imaging technique. The subject? A human retina.
-
A new technique may one day help restore sight to patients with inherited vision impairment. The regenerative therapy works by expressing genes that convert dormant cells into new light-sensing cells in the retina to replace those lost to disease.
-
Scientists have grown mini eyes from human cells in the lab. These eye organoids provide good models of the real thing to help scientists study diseases that cause blindness and potentially find treatments.
-
A team of researchers in the UK has developed a fully automated artificial intelligence-enabled system that can scan retinal images for vascular health, helping identify those at high risk of heart disease and stroke.
-
Autism and ADHD are becoming better understood, but clinicians can still find the two conditions difficult to tell apart. Now, South Australian researchers say they've produced evidence that the two conditions could be diagnosed using an eye test.
-
Scientists in Europe have discovered a molecular “zipper” mechanism that can lead to cell death in the genetic disease retinitis pigmentosa. The good news is that injecting certain proteins could slow or prevent vision impairment from the disease.
Load More