Scripps Research Institute
-
If you're hoping that reef-restoring coral larvae will settle down in damaged reefs, you can't just sit around and wait for it to happen. You have to get out there and entice the larvae, which is exactly what a new algae-based gel is designed to do.
-
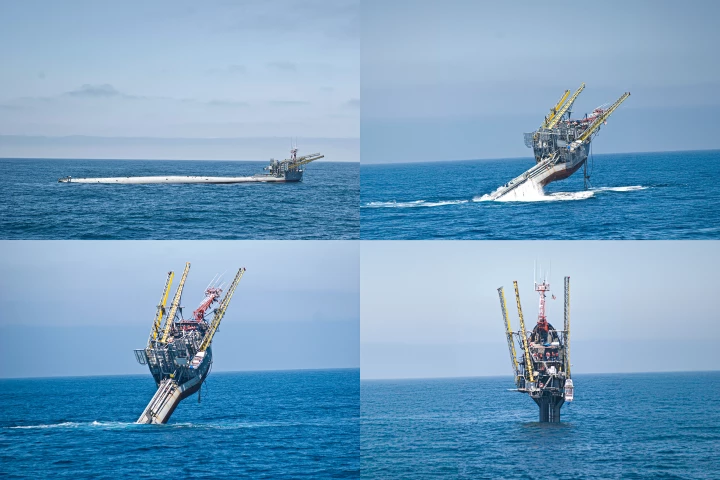
The US Navy and Scripps Institution of Oceanography's unique FLoating Instrument Platform (FLIP) has been saved at the last minute from the breaker's yard. Scheduled to be scrapped in Mexico, it was purchased by undersea design company DEEP.
-
There are few things in this world that are literally unique. One of these, in the true sense of the word, is the FLoating Instrument Platform (FLIP), which was a floating barge built for the US Navy that regularly sank itself on end for science.
-
Imagine a world in which we never catch the flu, have no need for vaccines and can wipe out the virus if an infection has taken hold. A super-effective molecule that stops influenza from even entering our bodies stands to revolutionize how we treat flu.
-
A universal snake-bite antivenom is within reach, with scientists making an antibody that protects against lethal strikes from a range of elapids. No snakes or ‘donor animals' were needed to produce the antivenom, making it sustainable and scalable.
-
Researchers have created a ‘two-headed’ drug that prevents the production of the toxic protein linked to Parkinson’s disease before destroying the RNA machinery that makes it. The drug may be a way of slowing or even stopping the disease’s progression.
-
Researchers have developed an antibody that targets the opioid fentanyl and its derivatives, reversing overdose better than currently available treatments. The novel therapy could be a more effective way of treating life-threatening opioid overdoses.
-
In addition to causing health problems, injury and death, excessive use of alcohol harms individuals, families, and society. A new study found that an anti-inflammatory medication used to treat psoriasis might effectively combat problem drinking.
-
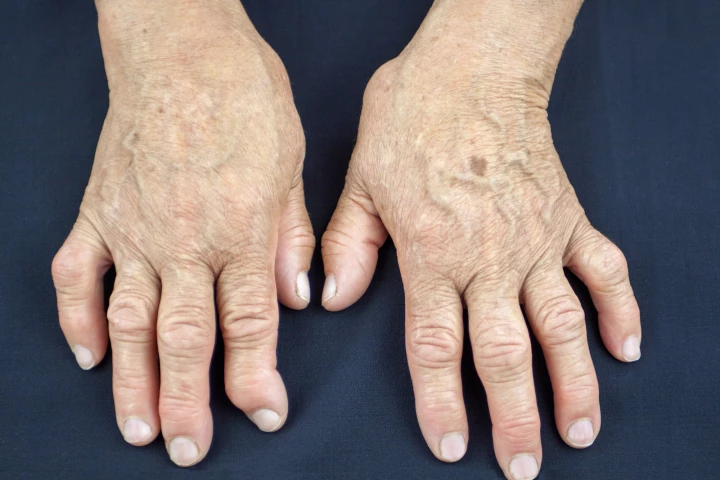
Immune suppression can help relieve symptoms of autoimmune diseases, but it can cause complications. A new nanoparticle therapy selectively targets problematic immune cells, and was able to significantly delay and even prevent arthritis in mice.
-
Our deepening understanding of the different types of fat continues to present new ways to potentially manipulate metabolic processes for better health outcomes, and new research on an existing asthma drug has opened up a promising new pathway.
-
An incredible new study has discovered a novel communication pathway between fat cells and the brain. The findings reveal that the brain can directly send messages to fat tissue and influence metabolic processes.
-
Exactly how non-living molecules sparked life is one of the most puzzling mysteries of science. Scientists have now discovered chemical reactions that can produce the building blocks of life out of materials common in early Earth's primordial soup.
Load More