Skin
-
Researchers have developed an electronic skin that allows humanoid robots to distinguish everyday touch from damaging force. That ability, once reserved for living nervous systems, could reshape how robots interact with the physical world and with humans.
-
The future of acne treatment might look way different than today's oral and topical medications. A new therapeutic patch features dissolving microneedles with hollow bubbles for precisely delivering multiple drugs with different release rates.
-
Blood sampling is painful, plus it only tells you what's going on in the patient's body right when the sample is taken. So, how about this? Permanent skin grafts that glow green when specific biomarker chemicals are present in the bloodstream.
-
For the first time, scientists have demonstrated how tanning beds cause fundamental DNA damage across almost the skin's entire surface that results in a threefold risk of developing melanoma. It puts beyond doubt the dangers of using these devices.
-
A surprising trigger for hair regrowth may lie in the body’s fat cells. Researchers have shown that mild skin irritation can trigger fat cells to go into panic mode, sending signals to dormant follicles that can fuel new hair growth within weeks.
-
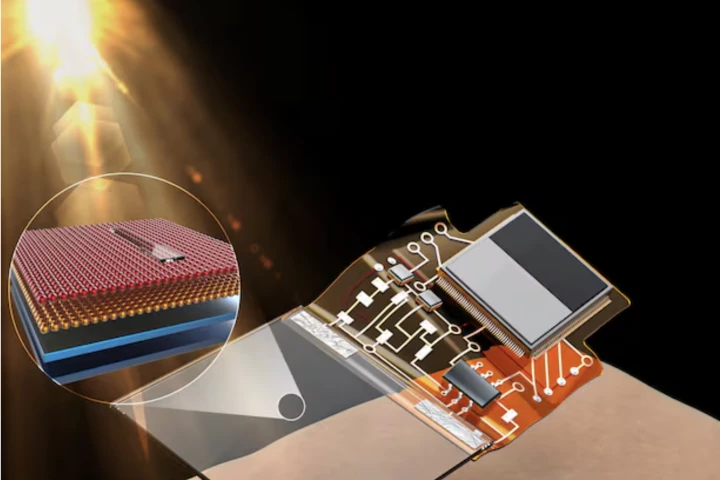
Scientists have developed a fully transparent skin sensor that accurately measures UV radiation, detecting light and converting it to electrical signals. So before the sun's rays reach damaging levels, a phone alert lets users know it's time to cover up.
-
Not all scar moisturizers are created equal. A new study shows that some of the cheapest, most basic creams outperform expensive, heavily marketed products, with one budget option topping the list for moisture retention and barrier repair.
-
Psoriasis may not have a cure, but significant relief might be found at the dinner table. A clinical trial has shown that the Mediterranean diet could dramatically improve symptoms, quality of life and overall health of those with the condition.
-
An inexpensive, over-the-counter form of vitamin B3 cut new skin cancers by an average of 14% in a study of more than 33,000 people. Among those who began taking a daily dose after a first diagnosis, the risk of a repeat skin cancer fell by up to 54%.
-
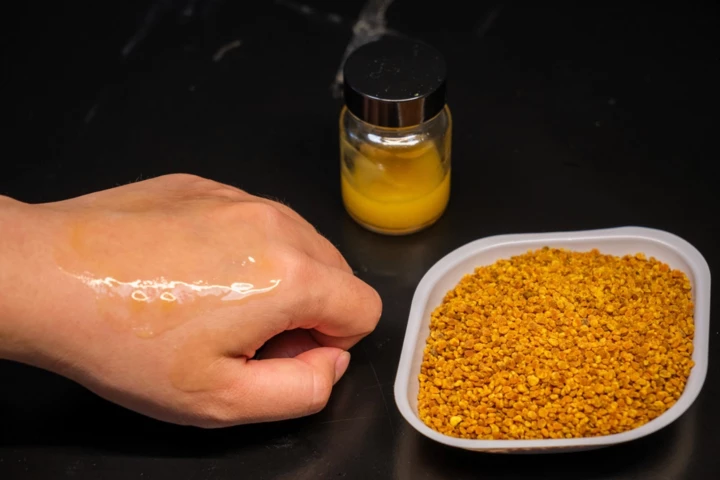
Minerals like titanium dioxide are effective sunscreen ingredients, but they can harm coral reefs if used in their non-nanoparticle form. An experimental new sunscreen forgoes the minerals altogether, replacing them with "just-as-effective" pollen.
-
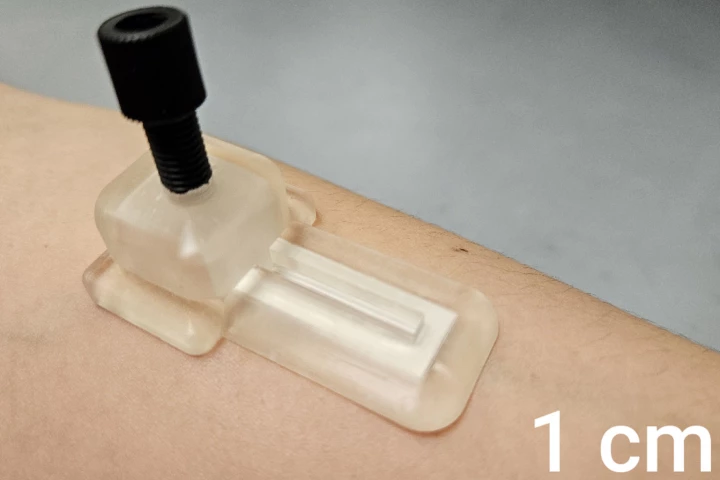
Nobody likes having blood samples taken, which is why it's always good to hear about possible alternatives. One of the latest takes the form of a self-powered skin patch that painlessly gathers biomarker chemicals for up to 24 hours at a time.
-
From vampire legends to lab-grown tissue, the idea that young blood can reverse aging is no longer pure myth. A new study shows that proteins secreted by bone marrow cells, triggered by young blood, can rejuvenate aging skin in the lab.
Load More