Stress
-
For the first time, scientists have uncovered a distinct biological process triggered in those who suffer from high levels of Monday anxiety, resulting in chronic stress. And it can lead to serious health problems if it's left unmanaged.
-
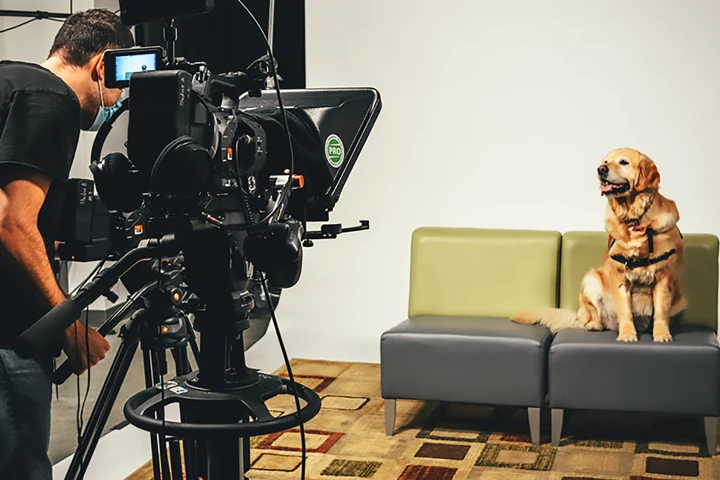
Watching a video of a therapy dog for just five minutes can meaningfully lower stress levels, a new study shows, offering a simple, stigma-free option for those reluctant to seek traditional mental health support.
-
If you have a high level of interaction with patients, students, clients or the general public in your work, you might be at much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. And, if you also have poor support at work, it could worsen your odds further.
-
Spending a few minutes a day doing simple things that bring joy increases well-being, decreases stress, and improves sleep, according to a new study. It shows you don’t need to invest in time-consuming well-being interventions for them to be effective.
-
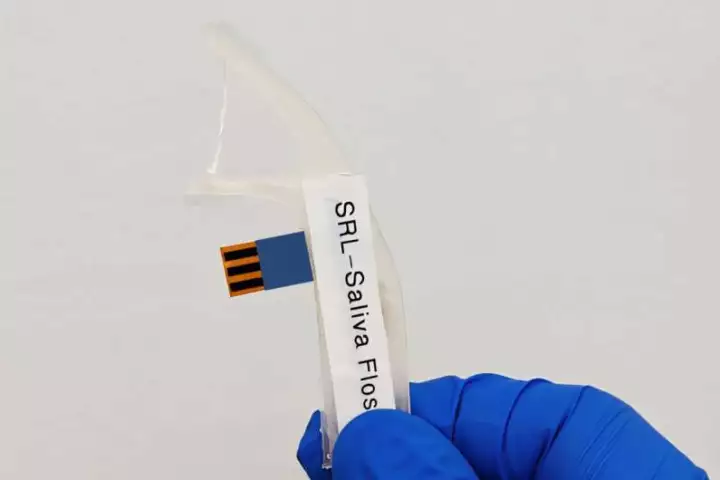
You already know when you are feeling highly stressed, but low-grade background stress is harder to detect. A new dental flosser from researchers at Tufts University aims to make it easier by monitoring the chemistry of your saliva.
-
Pupil dilation and subtle facial changes in response to sound can reveal how severe tinnitus is. Through this, researchers have discovered a new way to objectively gauge how bad the condition is, more accurately diagnosing tinnitus and treating it.
-
We're one step closer to that elusive goal preventing hair loss and enabling new growth, as scientists identify the crucial role that one all-important protein has in protecting the hard-working cells on the production line.
-
Using nanoparticles, researchers have created a sensor that selectively detects levels of cortisol, a well-known stress biomarker. Their cheap and easily reproducible device brings us a step closer to stress testing from the comfort of home.
-
Taking placebos fully aware that they contain no active ingredients can still significantly reduce stress, anxiety and depression according to a new study. It’s suggested that these 'non-deceptive placebos' might be an effective way of improving mental health.
-
In the world of dogs and cats, it wouldn't be a stretch to say that canines seem more optimistic and felines less so. But a dog's optimism can apparently be dampened by their human's emotional state, according to new research.
-
Even the most devout cat person can sometimes struggle to understand their pet – like why they scratch up a new chair. Now, a new study delves deep into the domestic lives of cat families to find out just why this happens, and how it can be prevented.
-
Two dogs in a small study were able to correctly identify what breath smelled like when it was linked to a memory of trauma. The finding might allow dogs to be even better friends when it comes to helping PTSD sufferers cope with their conditions.
Load More