Sugar
-
If you're trying to avoid sugar in your diet, you'll want to be careful about how you choose and use your artificial sweeteners. A new study shows that a popular sugar substitute called erythritol could increase your risk of suffering a stroke.
-
We all know the many health effects that a diet high in saturated fat and refined sugar has on our bodies. Now, in the first study of its kind on humans, scientists find that it may also be negatively impacting our ability to navigate and learn.
-
Aspartame has long been marketed as a guilt-free alternative to sugar in products like Diet Coke and sugar-free Jell-O. However, the sweetener has now been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks in mice. Should you ditch your fizzy drinks?
-
You lean back from the dinner table, feeling like you physically couldn’t fit another bite in – but then someone offers pie and you just can’t say no. Scientists have now identified the neurons behind the “dessert stomach” phenomenon.
-
In good news for nearly half the world's men, scientists have found that a naturally occurring sugar in humans and animals can be harnessed as a an effective topical gel for baldness. It sets it up as an inexpensive and safer alternative to minoxidil.
-
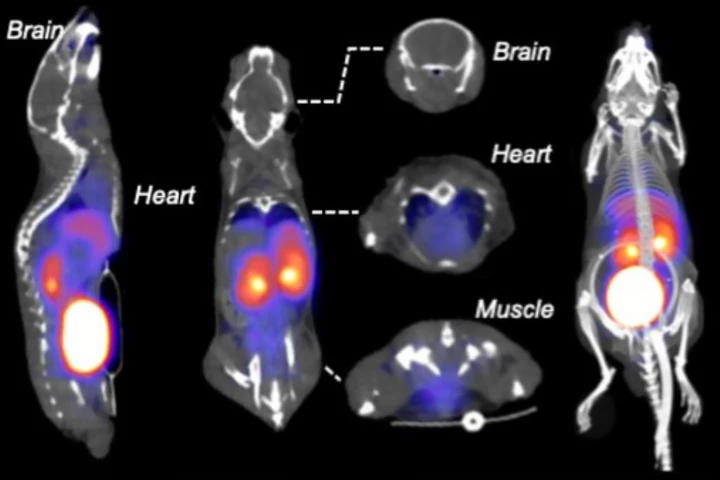
A radioactive form of fructose, a natural sugar found in fruit, can illuminate cancer and inflammation in medical scans. This approach has the potential to make diseases easier to spot than current techniques, leading to better early detection.
-
While chocolate will likely never be an overall healthy food, it would be good if there could at least be a lower-sugar version of it that people liked just as much as the real thing. Well, it turns out that oat flour could help make that happen.
-
After sugarcane crops have been harvested, a great deal of waste known as bagasse is left over. That substance has been incorporated into an eco-friendly building material called Sugarcrete, which recently won an international Climate Positive Award.
-
American adults are eating 400-500 calories – roughly the same energy intake as a recommended main meal – in snacks every day, and it comes with little nutritional value yet a whole lot of sugar.
-
If you overindulge in sugary treats, the good news is that your sweet tooth will be silenced. The bad news, though, is that this triggers a hormonal call out for fatty foods. And even worse news, too much fat will then switch sugar cravings back on.
-
A new study is pointing to a possible mechanism linking obesity with neurodegenerative disease. The work suggests diet-induced insulin resistance can impair the brain’s ability to clear out neuronal debris and contribute to diseases like Alzheimer’s.
-
Natural sugar allulose is 70% as sweet as table sugar, with only 10% of the calories, and does not affect blood glucose or insulin, making it an ideal sugar replacement. Yet producing it has been a huge roadblock. Scientists say they've cracked the code.
Load More