Teeth
-
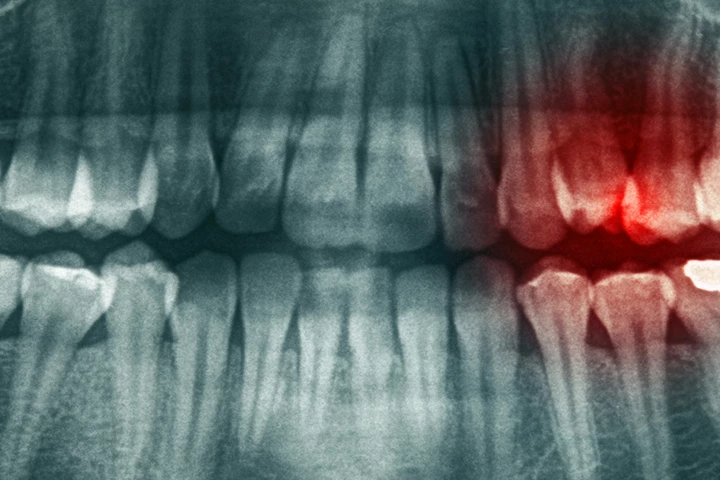
A new study found that combining exercise with omega-3 supplements reduced inflammation and, thereby, the severity of a chronic tooth infection. It suggests a simple means of controlling these infections, which can result in bone and tooth loss.
-
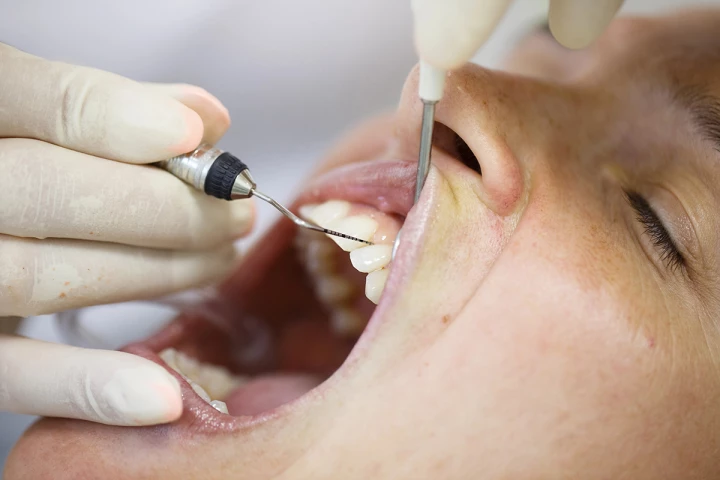
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
Scientists have developed an innovative new stem cell-infused implant that "grows" into the gum and fuses with existing nerves to function much like a real tooth. It's also gentler on the patient, expanding like memory foam to sit securely in place.
-
I didn't know it was possible to pay this much for a toothbrush – or that it was possible to pack in so many gadgets. This is a study in outrageous excess and over-engineering... But the end result is frankly amazing.
-
Many of us have had a tooth pulled in the dentist's chair, and even with anesthetic, it's not pleasant. So spare a thought for the people who, for millennia, chose to have good teeth yanked out with no painkillers – all in the name of beauty (mainly).
-
Nightmare fuel? Maybe – but in a historic moment for the dental profession, an AI-controlled autonomous robot has performed an entire procedure on a human patient for the first time, about eight times faster than a human dentist could do it.
-
As if Komodo dragons didn't seem ferocious enough already, scientists have now discovered that the reptiles tear through flesh using a coating of iron on their teeth. It is now believed that dinosaurs such as T. rex may have been similarly endowed.
-
Flossing your teeth on a daily basis can be a time-consuming, fiddly task. The Flaus electric flosser is designed to change that, as it reportedly allows users to perform a thorough and easy flossing in less than one minute.
-
The world's first human trial of a drug that can regenerate teeth will begin in a few months, less than a year on from news of its success in animals. This paves the way for the medicine to be commercially available as early as 2030.
-
Most of us picture megalodon as a Jason-Statham-hunting monster that looked like a giant great white shark, but that probably wasn’t the case. A new study re-examines fossil evidence and suggests the creature was longer and more slender than thought.
-
The most comprehensive genetic map of oral stem cells to date has provided new insight into their specialized development pathways and opens the door to targeted regenerative medicine and interventions, such as therapies to grow or repair bone.
-
Researchers have examined the teeth of Swedish Vikings and found that aside from decay and loss, they engaged in surprisingly advanced dental practices not dissimilar from modern practices. The study provides a rare insight into Viking life.
Load More