UC San Diego
-
By adjusting a typical polymer synthesis, researchers have created a spray-on polymer solution that could save billions of tons of crops. It's harmless to plants, and weakens the cell membranes of a variety of harmful bacteria.
-
An armband-mounted electronic patch uses motion and muscle sensors, a Bluetooth controller, and a stretchable battery to control tech. Thanks to AI-screening of data-noise, a shaky controller no longer means shaky control.
-
Terrified of bloodwork, needles, and clinic bills? Science is getting closer and closer to collecting our health data in fast, affordable, and pain-free ways – the latest example being a cup sticker that measures vitamin C levels in the user's sweat.
-
Some things we eat or drink raise our risk of deadly diseases. Strangely, once we have those diseases, a recent paper claims the same factors can help us live longer. Does this survival twist, dubbed "Cuomo's Paradox," challenge decades of nutritional advice?
-
People with cannabis use disorder had more than triple the odds of developing oral cancer, a large five-year study found, raising red flags about the carcinogenic risks of heavy cannabis use, especially in its smoked form.
-
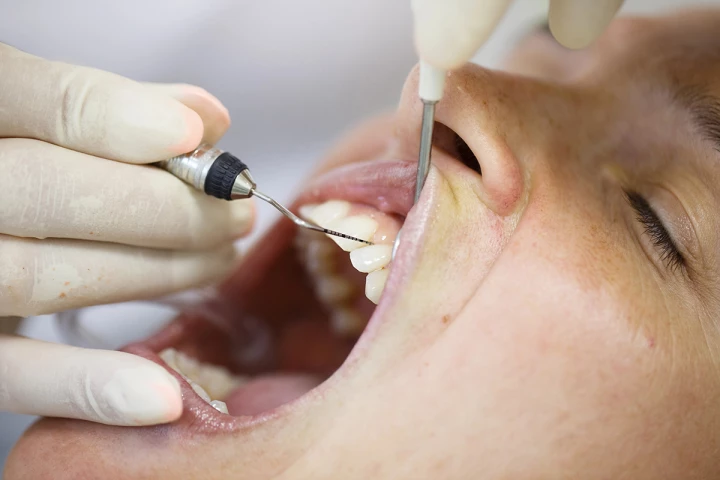
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
Soft corals produce chemicals that could be used to treat human disease. Now, scientists have identified the genes that make these important chemicals, opening the door to creating a limitless supply that can be used to produce and test new drugs.
-
If you're hoping that reef-restoring coral larvae will settle down in damaged reefs, you can't just sit around and wait for it to happen. You have to get out there and entice the larvae, which is exactly what a new algae-based gel is designed to do.
-
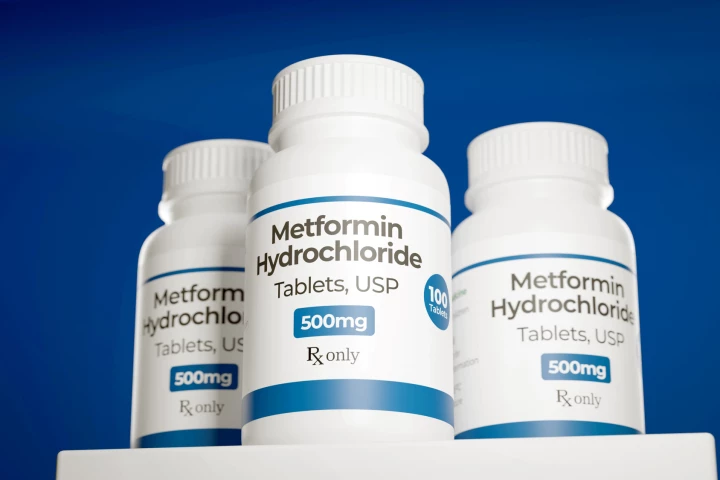
Metformin, a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, has been associated with a 30% lower risk of death, according to a new study. The research adds to the growing body of evidence suggesting that the common drug may possess anti-aging properties.
-
Self-care life hacks, claimed to improve well-being, often go viral on social media platforms like TikTok, sometimes without scientific backing. Experts have provided their opinion on six popular behaviors, so you know what’s good.
-
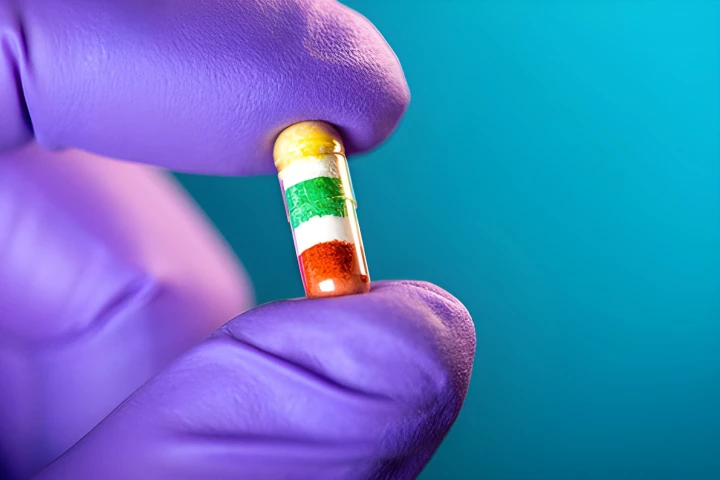
For some common medical conditions, timing is everything when it comes to taking medications. Now, a customizable capsule engineered at UC San Diego could simplify complicated dosing schedules thanks to a unique staged release system.
-
Measuring tape is a neat material, in that it's rigid enough to hold its shape when extended, but flexible enough to give way under pressure. Scientists have taken advantage of that dual nature in a robo-gripper designed for handling fragile items.
Load More