UC San Diego
-
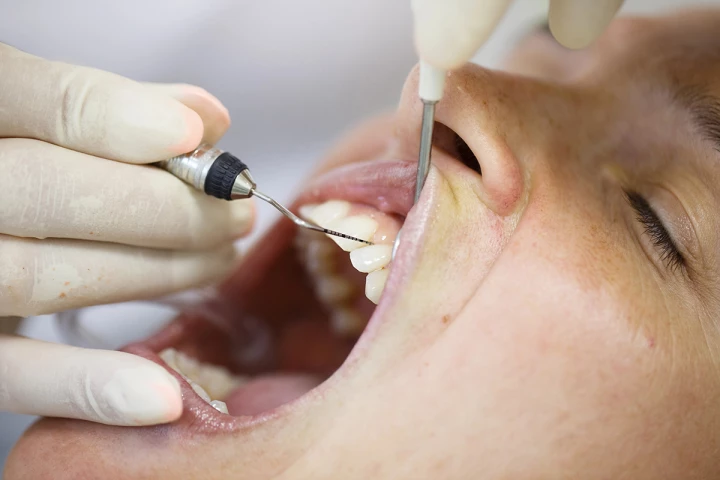
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
Soft corals produce chemicals that could be used to treat human disease. Now, scientists have identified the genes that make these important chemicals, opening the door to creating a limitless supply that can be used to produce and test new drugs.
-
If you're hoping that reef-restoring coral larvae will settle down in damaged reefs, you can't just sit around and wait for it to happen. You have to get out there and entice the larvae, which is exactly what a new algae-based gel is designed to do.
-
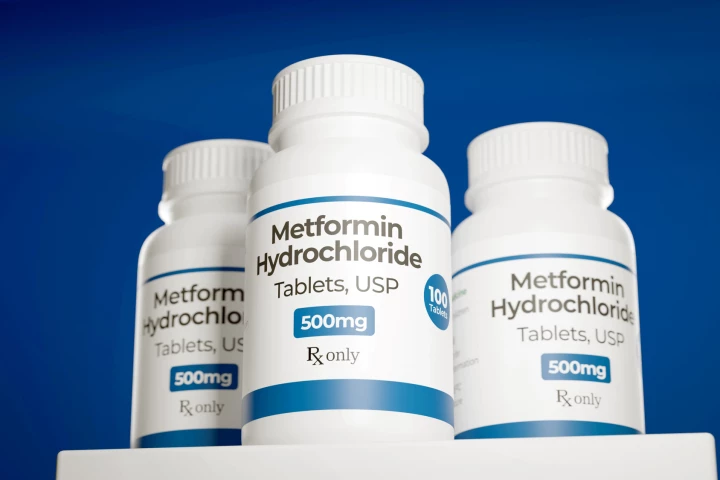
Metformin, a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, has been associated with a 30% lower risk of death, according to a new study. The research adds to the growing body of evidence suggesting that the common drug may possess anti-aging properties.
-
Self-care life hacks, claimed to improve well-being, often go viral on social media platforms like TikTok, sometimes without scientific backing. Experts have provided their opinion on six popular behaviors, so you know what’s good.
-
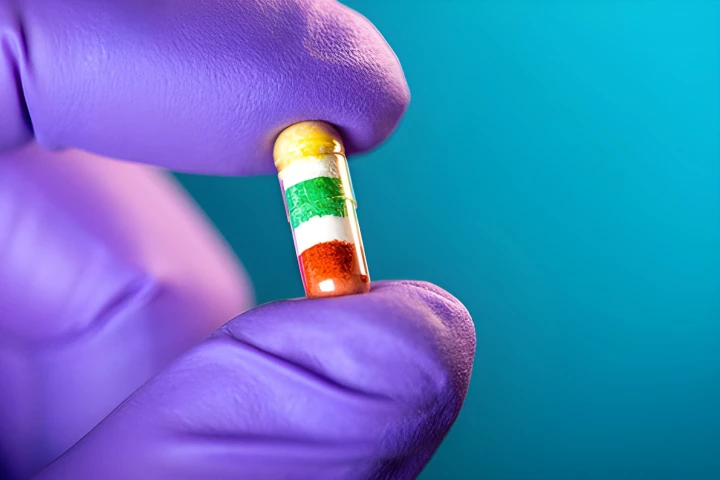
For some common medical conditions, timing is everything when it comes to taking medications. Now, a customizable capsule engineered at UC San Diego could simplify complicated dosing schedules thanks to a unique staged release system.
-
Measuring tape is a neat material, in that it's rigid enough to hold its shape when extended, but flexible enough to give way under pressure. Scientists have taken advantage of that dual nature in a robo-gripper designed for handling fragile items.
-
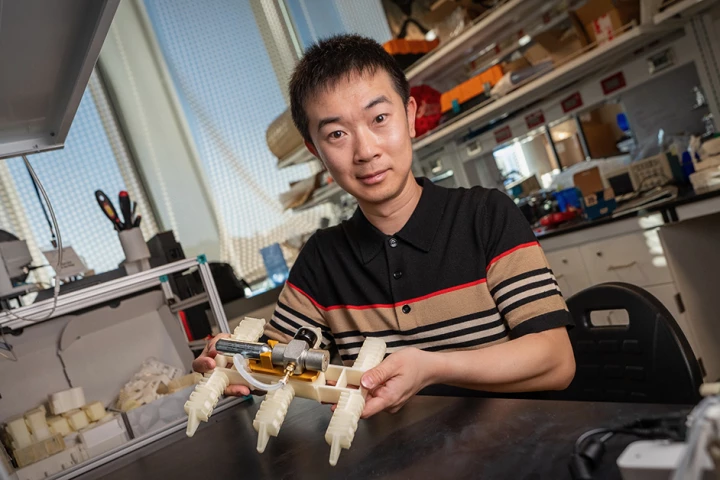
Most people likely think of robots as complex electronic devices, made up of many parts that have to be assembled in factories. An experimental new non-electronic bot, however, can be 3D-printed all in one piece, and it's powered by nothing but air.
-
A new study is presenting a radical new theory of aging, suggesting two competing theories are actually intertwined. And even more controversially, the billions of dollars being invested in anti-aging treatments may be targeting the wrong mechanism.
-
In a move akin to puncturing an egg yolk without breaking the shell or egg white, researchers have figured out how to pierce the nucleus of a cell without hurting the rest of the structure. The breakthrough could be big news for medical treatments.
-
Scientists have discovered the largest known protein in biology. Given the fun name of PKZILLA-1, the protein was found in algae cells and helps them make toxins that are responsible for mass killings of fish.
-
The 3D printing of certain items could soon get a lot faster, simpler and more eco-friendly. That's because scientists have developed a new 3D printing ink which is easily extruded as a liquid, then solidifies on contact with a saltwater solution.
Load More