UCLA
-
Zinc oxide remains one of the best forms of sun protection thanks to its ability to block both UVB and UVA rays. However, few really appreciate its thick white look – except, maybe, lifeguards in the '80s. UCLA researchers believe they have a solution.
-
Metallic theta-phase tantalum nitride exhibits an ultra-high thermal conductivity like no other material. This could be a desirable alternative to copper for computers and AI hardware, and even aerospace systems that need to run cool.
-
When COVID-19 lockdowns emptied city streets, urban environments changed almost overnight. New research suggests that Los Angeles city birds responded just as quickly, with measurable shifts in beak shape in offspring born during the lockdown period.
-
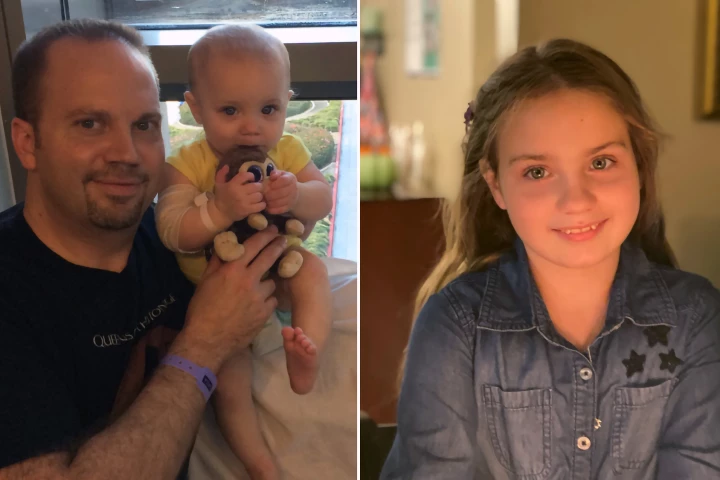
A one-time gene therapy using a patient’s own stem cells has effectively cured a deadly immune disorder in 95% of treated children, offering a lasting, donor-free solution to ADA-SCID, known as the “bubble boy” disease.
-
A new study shows that a personalized, precise form of brain stimulation, HD-tDCS, can rapidly ease depression symptoms – and even reduce anxiety – offering a promising drug-free alternative with only mild side effects.
-
When scientists study obesity, it's often focused on genetics, physical activity and poor eating habits. However, new findings show that stress, hardship, isolation and social inequality create the biological environment that underpins the epidemic.
-
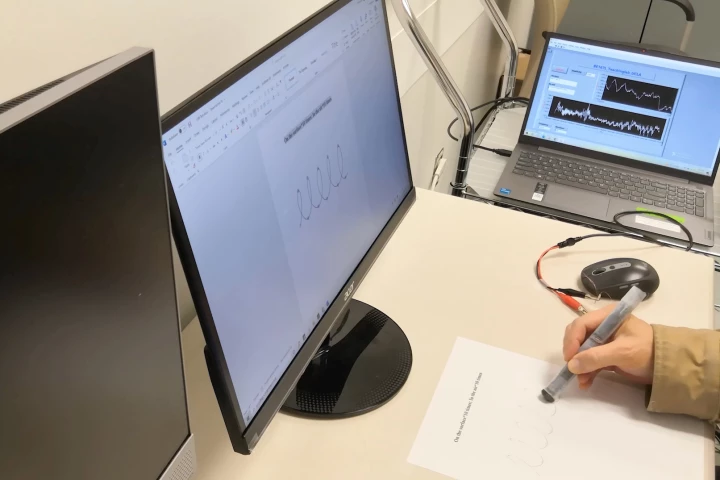
We've already seen a pen that helps people with Parkinson's disease to write clearly, but this one is a little different. By assessing its user's hand movements as they write, it can provide an early warning that they're developing the condition.
-
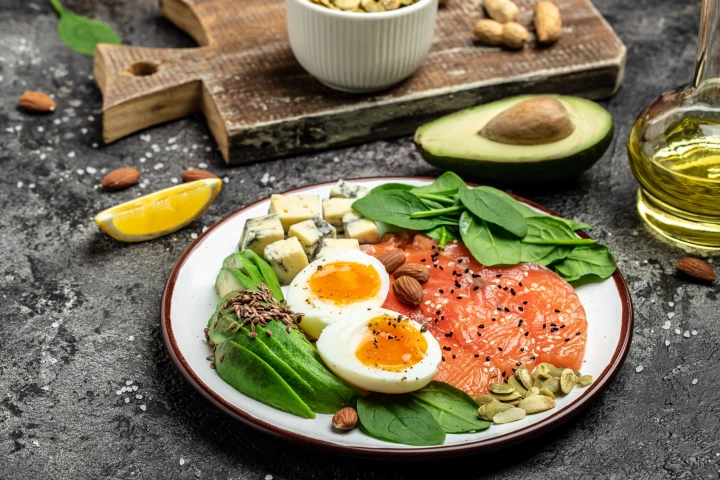
One of the ketogenic diet's major perceived drawbacks is an increase in LDL, or so-called bad cholesterol. A new study, though, says that this cholesterol spike doesn't fit the conventional science in terms of its disease-causing ability.
-
UCLA researchers have developed a tiny sensor to monitor metabolites – substances produced or used when your body breaks down food or medication – far more extensively than current methods. It could unlock better disease diagnosis and drug development.
-
There's newfound hope for stroke patients in recovery, with what researchers believe is the very first drug that can comprehensively deliver rehabilitation without the need for challenging long-term physical therapy.
-
Astronomers have discovered an exoplanet with a tail, like a gigantic comet. The planet, known as WASP-69b, is slowly evaporating in the radiation of its host star.
-
While electroencephalography (EEG) can provide a lot of information on the electrical activity of an individual's brain, that person is required to wear a clumsy skull cap. Such caps could soon be replaced, however, with inkjet-printed scalp tattoos.
Load More