UCLA
-
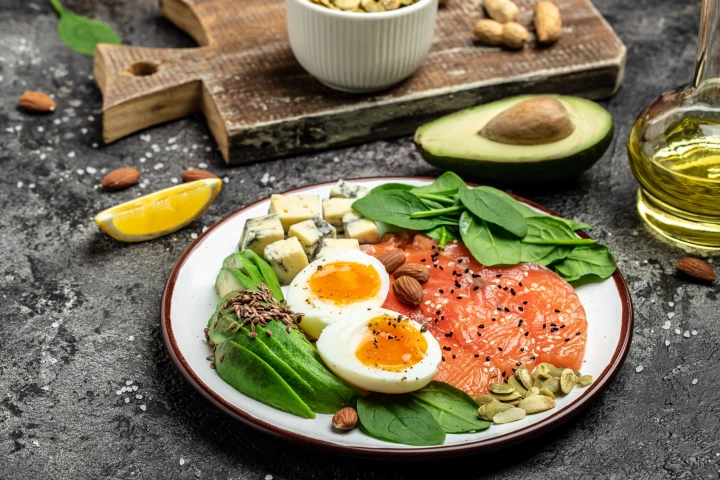
One of the ketogenic diet's major perceived drawbacks is an increase in LDL, or so-called bad cholesterol. A new study, though, says that this cholesterol spike doesn't fit the conventional science in terms of its disease-causing ability.
-
UCLA researchers have developed a tiny sensor to monitor metabolites – substances produced or used when your body breaks down food or medication – far more extensively than current methods. It could unlock better disease diagnosis and drug development.
-
There's newfound hope for stroke patients in recovery, with what researchers believe is the very first drug that can comprehensively deliver rehabilitation without the need for challenging long-term physical therapy.
-
Astronomers have discovered an exoplanet with a tail, like a gigantic comet. The planet, known as WASP-69b, is slowly evaporating in the radiation of its host star.
-
While electroencephalography (EEG) can provide a lot of information on the electrical activity of an individual's brain, that person is required to wear a clumsy skull cap. Such caps could soon be replaced, however, with inkjet-printed scalp tattoos.
-
Not only have researchers identified how a common cellular protein affects aging, but they’ve tweaked the genes that produce it in fruit flies, extending healthy lifespan by 25% to 30%. The discovery opens the door to healthier aging in humans.
-
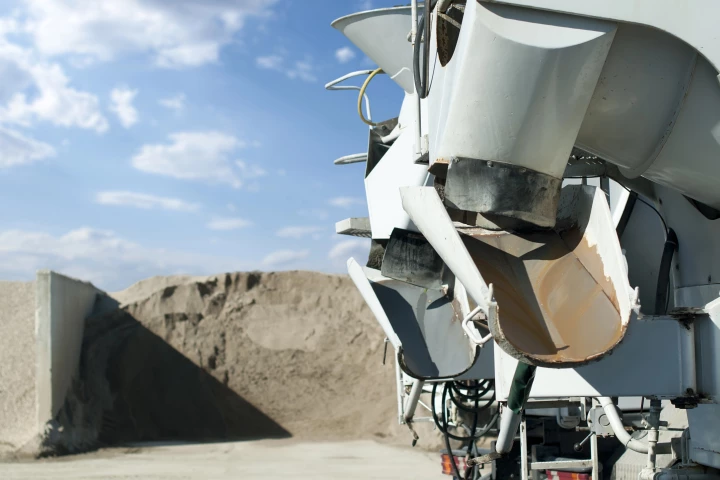
Researchers at UCLA have successfully devised a way to produce cement with 98% less CO2 emissions than traditional methods. The team achieved this by decomposing limestone to access calcium oxide (aka lime) without releasing carbon dioxide.
-
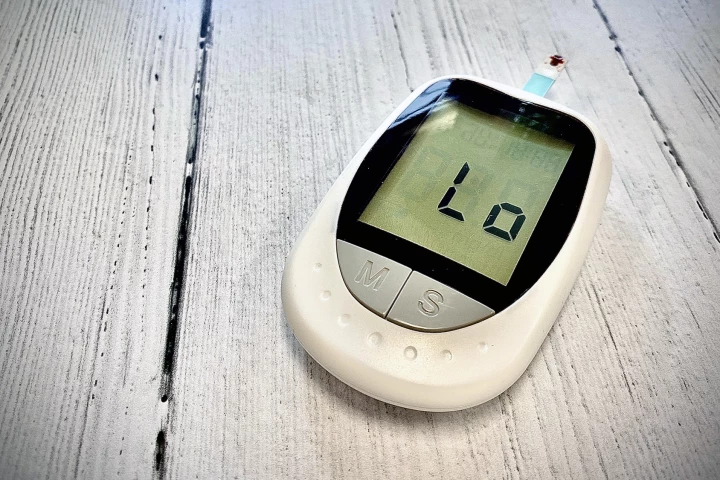
Nanosized particles that release glucagon, the hormone responsible for raising blood glucose levels, on-demand could mean that diabetics don’t need to worry about potentially dangerous low blood sugar levels, according to new research.
-
Manuka honey reduced breast cancer cell growth by 84% without harming healthy cells or causing major side effects, according to preliminary studies. The findings open the door to developing a natural, non-toxic supplementary, or potentially stand-alone, anticancer treatment.
-
Instead of focusing on fighting the plaques linked to Alzheimer's, researchers took a look at boosting electrical oscillations in the brain. The molecule they invented got the job done in mice, offering hope for a new treatment path for humans.
-
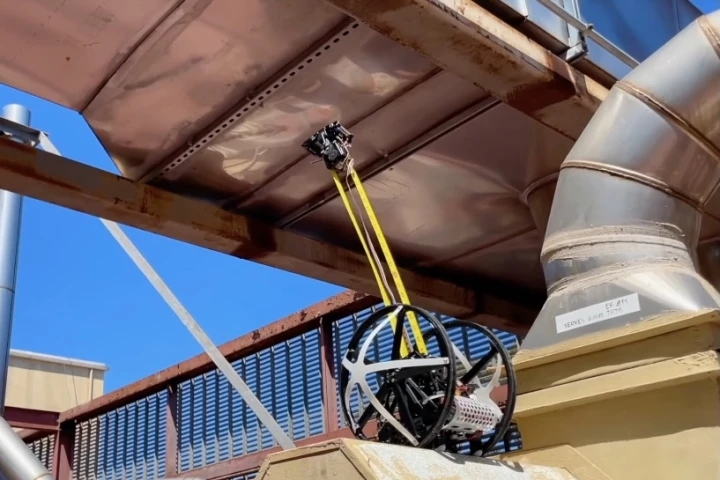
A new wheeled robot is able to climb metal structures in a clever and unique way – it uses an extendible tape-measure limb. Descendants of the bot may one day find use inspecting or repairing things like towers, bridges, power stations and ships.
-
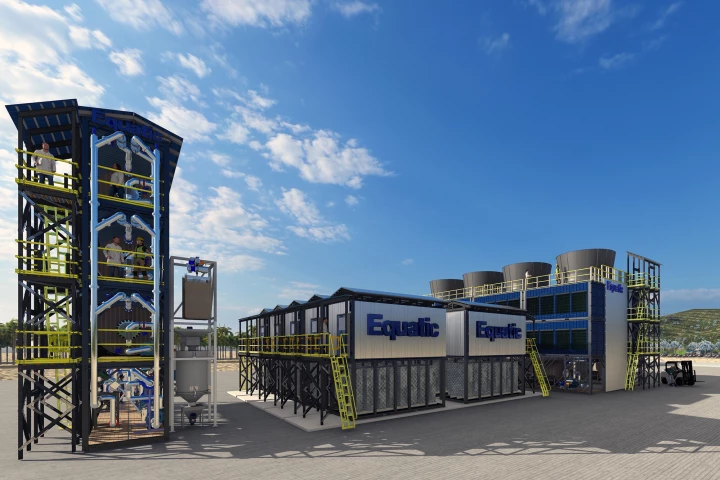
The world’s largest ocean-based carbon dioxide removal plant is being built in Singapore, and will be capable of capturing 8 million lb of CO2 per year while also producing 231,000 lb of carbon-negative hydrogen.
Load More