University of Buffalo
-
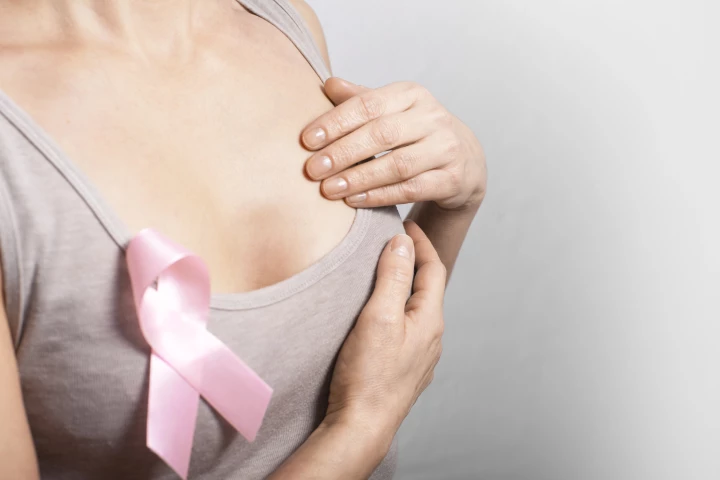
Researchers at the University of Buffalo are hoping to make breast cancer screening easier and quicker than ever before, with a detection technique that only requires patients to press up against a window for a minute to get accurate results in 3D.
-
Scientists at the University of Buffalo experimenting with next-generation battery designs have demonstrated how magnetism might be used to bring a new level of precision to the way we monitor a battery's state of charge.
-
Computer scientists at the University of Buffalo have just offered a compelling example of what deepfake detection could look like, developing a technology that can spot them with 94 percent effectiveness by analyzing tiny reflections in the eyes.
-
Scientists at the University of Buffalo have found a very useful clue shedding light on the migration of canines to the Americas, in the DNA of an ancient bone fragment thought to be the oldest confirmed dog remains in the region.
-
First of all, no one is suggesting that if you suffer from depression and anxiety, you should drink a lot of red wine. That would ultimately NOT help the situation. However, it turns out that a plant-derived compound IN the wine – known as resveratrol – could indeed make a difference.
-
Scientists have developed a technique that lets them directly control physical movements in mice. Using magneto-thermal stimulation, they activated sections of the brain that caused mice to run, turn or stop, which could eventually lead to new therapies for brain disorders or even mental illness.
-
Scientists have created a new multi-layered nanoparticle that effectively converts low-energy light into high-energy light, which may help drive more efficient energy harvesting, novel bio-imaging techniques and superior anti-counterfeit protection.
-
Blocking cheaper and easily available sensors for detecting bacteria or explosives are the limits of SERS technology, which is expensive and requires multiple chips to assess different compounds. However, new technology could change that with an almost-universal surface that's cheap to produce.
-
Researchers from the University at Buffalo School of Engineering have turned to colonies of E. coli bacteria to produce new forms of antibiotics. The study made use of a harmless form of E. coli, and several of the resulting drugs may be equipped to tackle harmful, drug-resistant bacteria.
-
Using newly-developed metamaterials, scientists at the University of Buffalo have created a prototype "hyperlens" that may help image objects in visible light with dimensions so small that they were once only clearly viewable through electron microscopes.
-
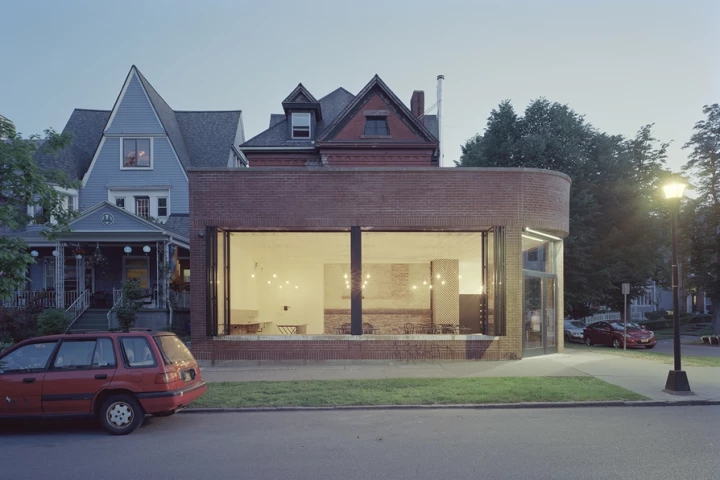
A café in upstate New York has an innovative means of keeping its customers cozy. It features a masonry heater with a flue that runs horizontally and doubles as a bench. The building can apparently be heated for 24 hours following a single, hour-long burn.
-
Tactile graphics company Touch Graphics and the University of Buffalo's IDeA Center have collaborated to create multi-sensory 3D maps that give spoken directions and building information when touched, along with sound effects and overhead video projection related to a particular place.
Load More