University of Copenhagen
-
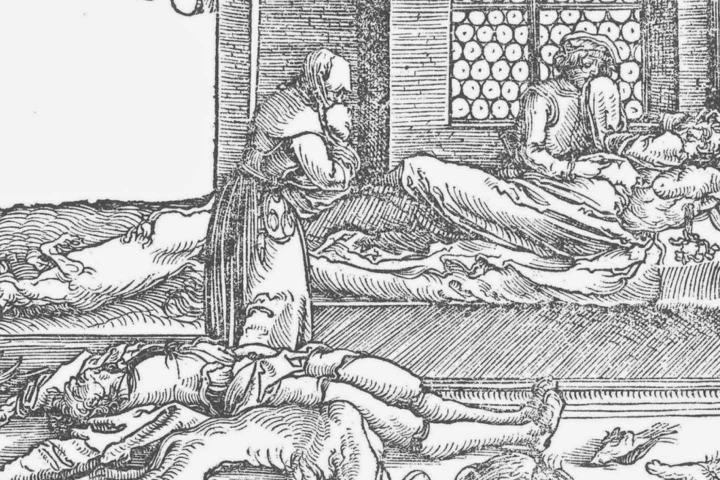
Humans have been getting infected by ancient bacteria and viruses for at least 37,000 years. Now, for the first time, pathogen DNA has uncovered a pivotal disease "turning point" that happened 6,500 years ago, which would forever change our lives.
-
Researchers have a new angle to add to the nature vs. nurture debate about what shapes human behavior. A massive survey revealed a link between aversive societal conditions, and the "dark" personality characteristics that people may develop.
-
The James Webb Space Telescope has captured direct images of galaxies being born at the cosmic dawn. This is the first time this has ever been witnessed by astronomers, confirming models for galaxy formation.
-
The current breakthrough weight-loss drugs are only the beginning, according to Danish researchers hard at work on a new treatment that targets the brain's natural plasticity, which could offset bad side effects and provide more long-term benefits.
-
A plant known as the “Seven Steps of Death” holds within its poisonous growth a hotly touted anti-obesity compound, celastrol. For the first time, this compound has been genetically mapped and then synthesized safely, purely and quickly in a yeast host.
-
The animal kingdom has no shortage of weird and wonderful surprises, and this year biologists gave us some real treats to talk about. From microscopic bacteria to huge cetaceans, here are the most bizarre animal stories we covered in 2023.
-
Gigantic waves can seemingly come out of nowhere, threatening ships and oil rigs. Now, an AI system trained on centuries of data has been able to predict when these rogue waves will occur, revealing new insights into how they form.
-
Genitalia in the animal kingdom is rarely dull, from penis 'sword' fighting flatworms, to echidnas with four-headed phalluses. Let us introduce a new odd member contender: a beetle with an appendage that looks like you could crack open a beer with it.
-
Hijacking the body of another animal is nothing new in the opportunistic world of parasitism. But for the first time, scientists have observed how one crafty flatworm can switch ‘zombie mode’ on and off, leaving its host ant stuck between life and death.
-
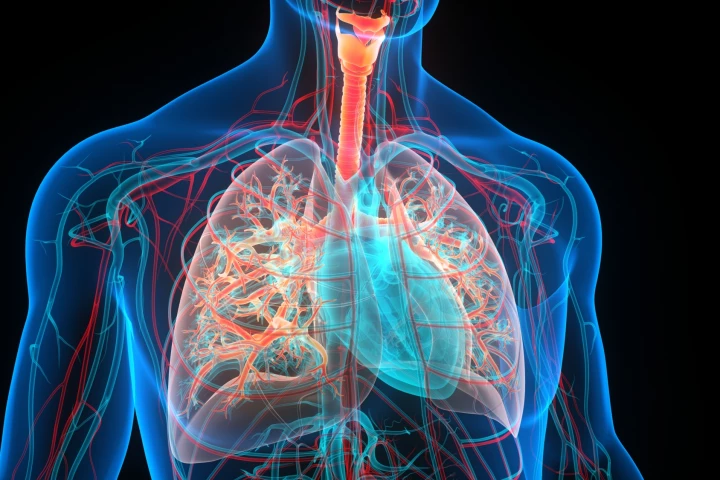
A new study suggests that people with low levels of vitamin K in their blood are more likely to have reduced lung function and to report lung problems like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or wheezing.
-
Researchers have developed a way of recycling polyester. Their new method is simple, non-toxic for humans and the environment and, what’s more, it preserves the integrity of the cotton removed from the fabric so that it’s ready for reuse.
-
Researchers have transplanted specialized brain support cells into mice and found that they replaced unhealthy and aged cells. The findings open the door to developing an effective treatment for a range of neurological conditions.
Load More