University of Edinburgh
-
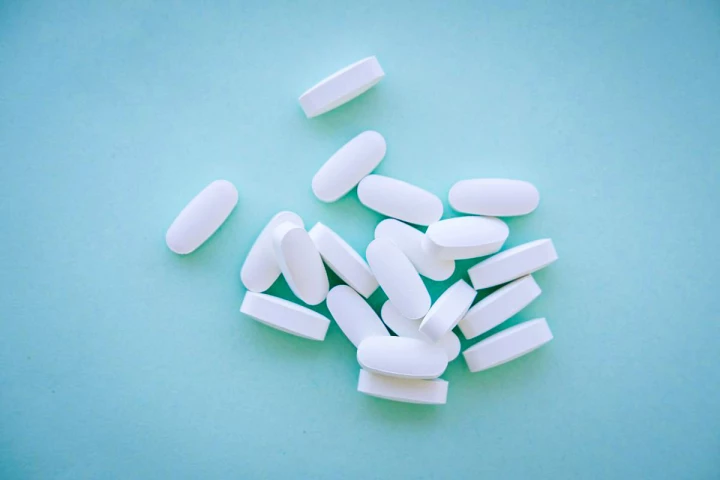
Here's a rather novel way to keep trash out of landfills: engineering biologists have developed a way to turn common plastic bottles into the popular painkiller paracetamol. All it takes is a bit of bacteria and time to ferment the treated waste.
-
People with an autoimmune disease have almost double the risk of developing depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, according to a new study. The findings provide more evidence of a link between inflammation and psychiatric illness.
-
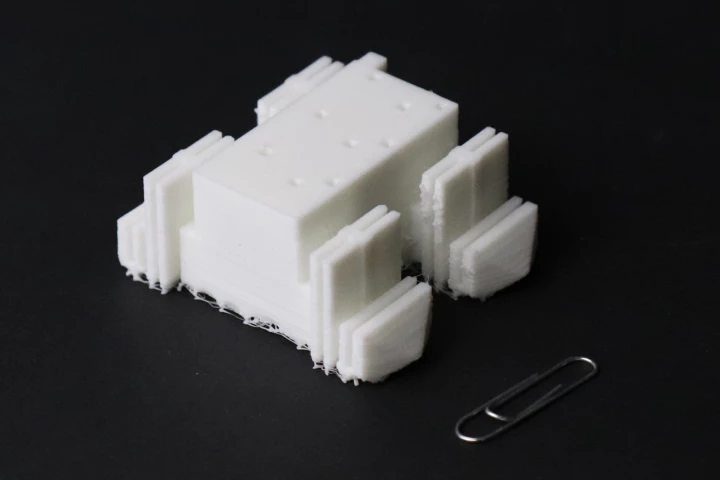
While there are many uses for soft-bodied robots, the things are still only built in small batches. Scientists are out to change that, with a mass-production-capable soft bot that is 3D-printed in a single piece which walks off of the print bed.
-
An unusual partnership between a vacuum maker, a race car legend, and the University of Edinburgh is leading to advances in understanding dementia. Their new study using living tissue has revealed the brain's sweet spot for tau proteins.
-
People with bipolar disorder who followed a ketogenic diet found that their symptoms improved, a new study found. While the study was preliminary, its findings open the door to a new treatment direction for the sometimes difficult-to-treat condition.
-
We've never been closer to accurately assessing whether someone is more susceptible to developing depression due to their biology, with 293 new gene variants found to play a role in ramping up the risk factor. That's 42% more than previously known.
-
Researchers have discovered that the accumulation of aged and failing cells in one diseased organ can cause the failure of multiple healthy organs. The findings have opened the door to preventing multi-organ – or even age-related – disease.
-
Water can hold a huge amount of thermal energy, and a new system to tap into this is being trialed in Scotland. A startup called SeaWarm uses heat stored in bodies of water for buildings, pulling four times more heat out than electricity used.
-
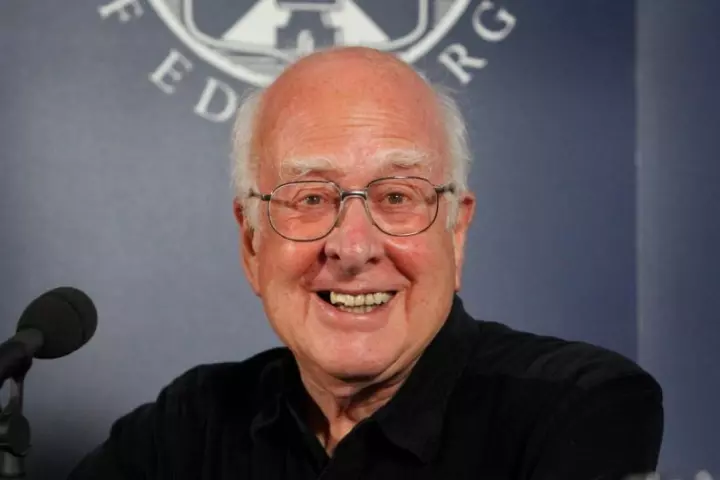
Professor Peter Higgs has died aged 94. The theoretical physicist was best known for his prediction of a key elementary particle, the Higgs boson, which earned him the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physics soon after its discovery.
-
It slices, it dices, it's super strong and conductive, and now an ultra-pure form of ‘wonder material’ graphene has been inhaled during a human trial without affecting lung or cardiovascular function, opening the door to a novel drug delivery mode.
-
The first study of its kind has looked at every UK resident – more than 67 million people – across four months, and found that, as vaccine uptake tapered off in 2022, 7,180 hospitalizations and deaths could have been avoided had jabs been up to date.
-
It’s taken more than three decades, but scientists have cracked the code and created a material that’s near-impossible to break and rivals diamond as the hardest substance on the planet. The applications for this long-sought-after substance are vast.
Load More