University of Georgia
-
New research has linked higher plasma levels of the healthy fats omega-3 and omega-6 to a reduced risk of developing particular types of cancer. The study adds to the on-again/off-again relationship that exists between scientists and the common supplements.
-
Scientists at the University of Georgia have created a "superfoam" with two very valuable potential applications. It could be used not only to clean up oil spills, but also to keep infections from occurring at medical implant sites.
-
A new vaccine targeting the three most common human fungal infections is showing promising results in early preclinical studies. The data paves the way for future human trials in the hopes of preventing infections linked to over one million deaths a year.
-
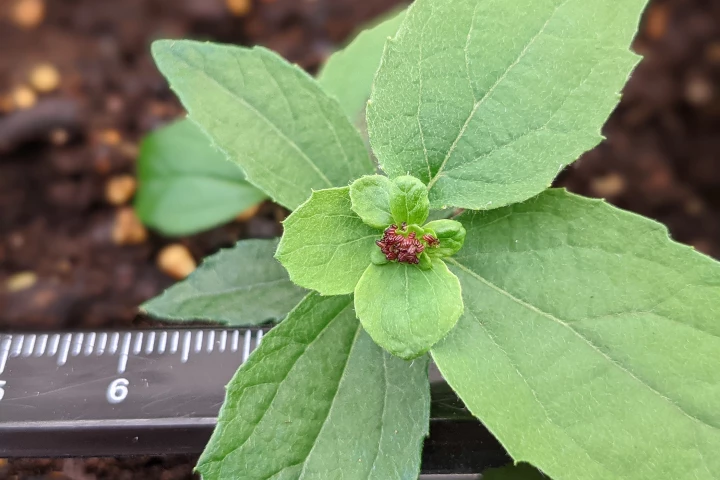
Breeding plants can give them new beneficial traits, but trees have a frustratingly long reproductive cycle. Now, scientists at the University of Georgia have used CRISPR gene-editing to make poplar trees flower within months rather than a decade.
-
While we may think of blue jeans as kind of earthy, basic clothing, the process by which they're dyed is definitely not eco-friendly. That may soon no longer be the case, however, thanks to the development of a new coloration technique.
-
As work continues to clean up the mess left by the meltdown of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011, scientists are enlisting some local help in their efforts to survey the damage, in the form of rat snakes that frequent the area.
-
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, or “superbugs,” pose one of the most dangerous looming threats to public health. Now, researchers have found a new potential weakness in some of the worst strains, which makes them choke on their own toxic molecules.
-
A new implantable "brain glue" material could offer a way to intervene in the sequence of events following a traumatic brain injury, by mimicking the supporting structure of brain cells to prevent tissue loss and regenerate neurons.
-
A study investigating the relationship between genetics, diet and heart health is claiming the cardiovascular benefits often linked to taking fish oil supplements may be only apparent in those individuals of a certain genotype.
-
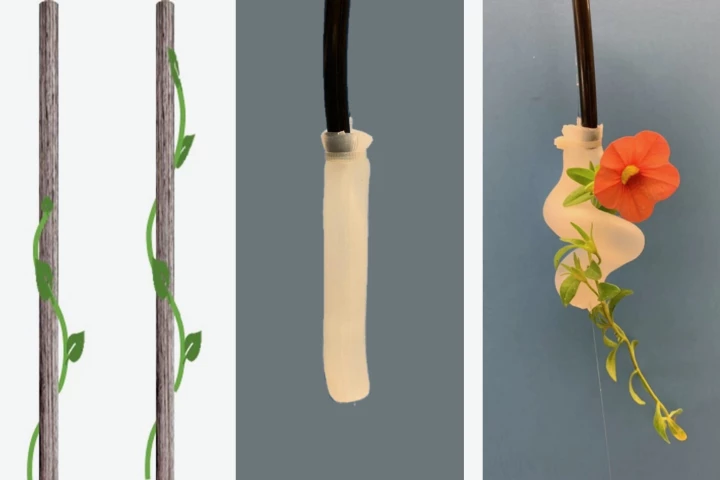
As anyone who has grown climbing plants will know, the things are great at grasping onto thin objects such as strings or bamboo poles. A new robotic gripper, inspired by such plants, could find use in the handling of small, delicate items.
-
Causing the death of cancer cells while leaving healthy ones in tact is central to the goal of safer, more effective forms of treatment for the disease, and scientists have now come up with one that leans heavily a common household item – salt.
-
Researchers have managed to successfully edit the genes of lizards with CRISPR for the first time, turning them albino.
Load More