University of Helsinki
-
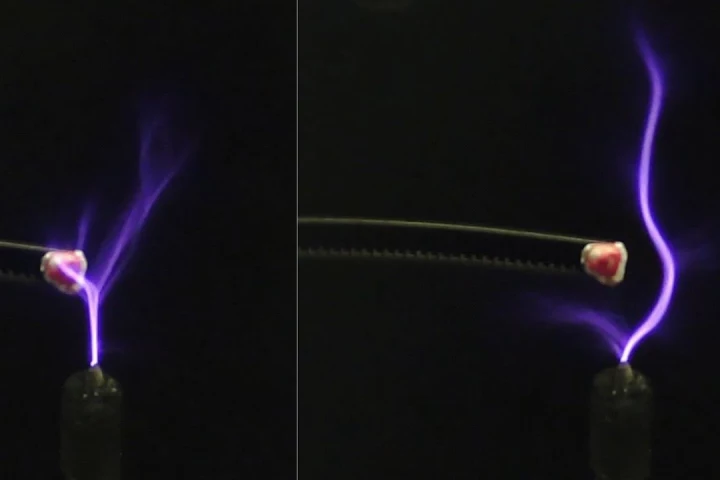
Electricity is chaotic, and we normally need to constrain it to wires and circuits to make use of it. Scientists in Europe and Canada have now managed to guide sparks through thin air and even around obstacles using ultrasound waves.
-
Science's war against the super-small and, sometimes, super-deadly bacteria that have evolved to resist destruction by antibiotics may have just enlisted new, unlikely allies: invertebrate creatures living in the frigid depths of the Arctic Ocean.
-
Detecting the first stages of heart failure could soon be as simple as placing a smartphone on a patient's chest. That's the conclusion of an ongoing study, which is aimed at developing an app for diagnosing the potentially lethal condition as early as possible.
-
Often, the decision to get a Rottweiler over a Chihuahua is made based on personality. A new study has found that while the breed is an important factor, a dog’s personality is determined by a complex interaction between genetics and environment.
-
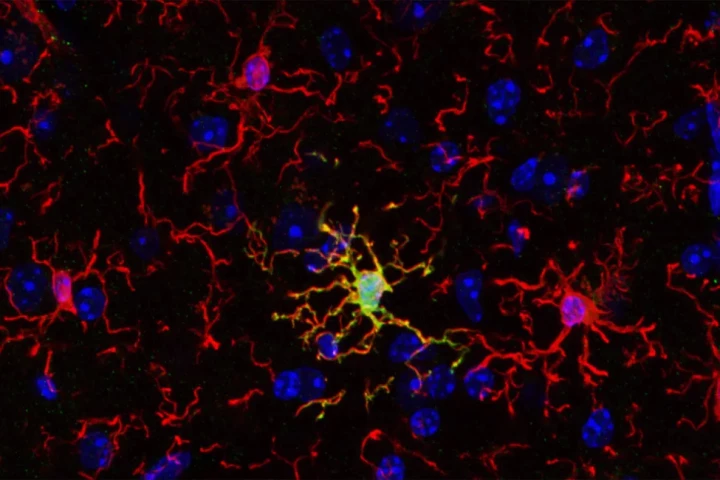
A new study has identified a subset of microglia, the brain's immune cells, and their important role in brain development and cognition that could pave the way for new treatments for neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
-
A new study has found that a species of gut bacteria cause the destructive nerve cell ‘clumps’ that are a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease. The discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for this debilitating disease.
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage is a devastating disease that becomes increasingly deadly for its survivors. Scientists now hope a novel discovery that helps rid the brain of toxic debris can lead to life-saving treatment for the condition that has no cure.
-
Horses were likely the first “vehicle” humans used to travel faster and farther, but when exactly did we start riding them? Scientists have now found archeological evidence that suggests horseback riding started some 5,000 years ago.
-
One of the best ways of tracking an infant's neurological development is to observe their movements as they play. A new "smart" jumpsuit is designed to do so automatically, providing consistently accurate data via machine learning technology.
-
Since early 2020 it has been suggested dogs can sniff out patients with COVID-19. Now, a study has reported on a real-world investigation into this method of detection, finding it's potentially effective, at least in detecting COVID-negative people.
-
A massive international study designed to unearth new knowledge around the causes of migraines has turned up some interesting new insights, with the authors effectively tripling the number of known genetic risk factors for the condition.
-
Egg white powder is a widely used food ingredient, which means that a lot of hens have to be raised on a lot of farms, producing a lot of waste. There may soon be a greener alternative, however, thanks to a fungus which produces a key egg protein.
Load More