University of Melbourne
-
Men who carry two copies of a common genetic variant are twice as likely to develop dementia than women with the same mutations. This discovery may now lead to early detection and novel interventions to block how these variants impact the brain.
-
Finding support and information from medical professionals lacking, people wanting to come off their antidepressant medication are turning to online groups instead, according to new research. The study highlights an ongoing problem that needs addressing.
-
Silicon is so important for electronics and computing that it’s become synonymous with technology, but the stuff has its flaws. Now scientists have created a way to make super-pure silicon chips that could pave the way for stable quantum computers.
-
After confounding scientists for more than 80 years, researchers have finally discovered how the flesh-eating Buruli ulcer is transmitted: mosquitoes. The discovery means practical measures can now be taken to restrict the spread of the disease.
-
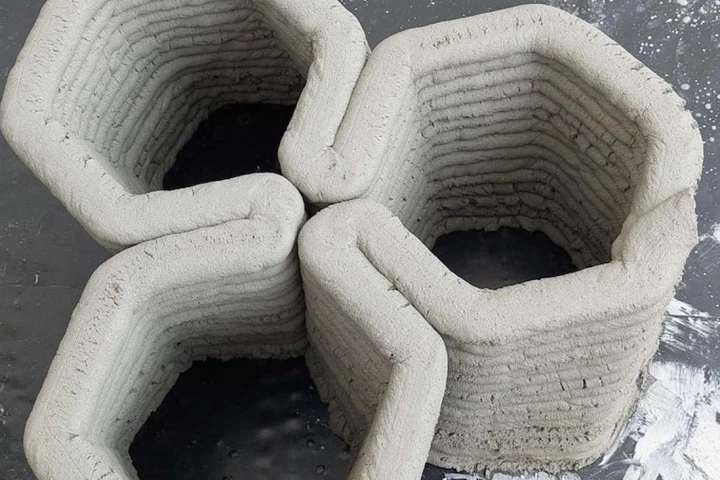
3D-printed concrete structures are claimed to be faster and cheaper to build than their traditional counterparts, but they're not always as strong. That problem may soon be solved by adding a pinch of graphene oxide, which could also be used to detect cracks.
-
Researchers have identified a way of selectively eliminating the ‘bad’ immune cells that contribute to autoimmune skin diseases like psoriasis while leaving the ‘good’ cells intact. The discovery could lead to longer-lasting, more targeted treatments.
-
In 2017, scientists discovered a new species of giant rat that can reportedly crack open coconuts. Now, this extremely rare creature has been captured in the wild on camera for the first time.
-
In a study of studies, researchers concluded that eyeglasses that block blue light might not deliver on claims made by advertisers or optometrist offices. They caution consumers to think twice about shelling out the extra cash for the specs.
-
A new study has found a novel, non-surgical method that is very effective at healing a common sporting injury, rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL. The method could be a way to help sufferers avoid surgery altogether.
-
A new study may have bad news for people who take so-called ‘smart drugs’, usually prescribed to treat the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), thinking they will increase workplace or academic productivity.
-
Scientists have found a bacteria related to the human chlamydia pathogen in the corals of Australia's Great Barrier Reef – and hope it could lead to game-changing probiotic treatments designed to slow down or reverse the process of coral bleaching.
-
The first dark matter detector in the Southern Hemisphere has been officially opened. The Stawell Underground Physics Laboratory (SUPL) is built in a disused gold mine in Australia, giving it a unique position on the globe for detecting dark matter.
Load More