University of Oxford
-
Why do elephants, one of the biggest animals on the planet, paradoxically experience unusually low rates of cancer? The question has led scientists to discover these remarkable mammals carry unique genetic variants that reduce their risk of tumors.
-
A compound derived from a Himalayan fungus has been refined by scientists for a chemotherapy drug with powerful anti-cancer effects. NUC-7738 is yielding encouraging results in ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, and is advancing towards approval.
-
In a massive analysis of 113 clinical trials involving nearly 15,000 adults, researchers found that there's just one method that relieves core symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder – but no existing treatment improves quality of life.
-
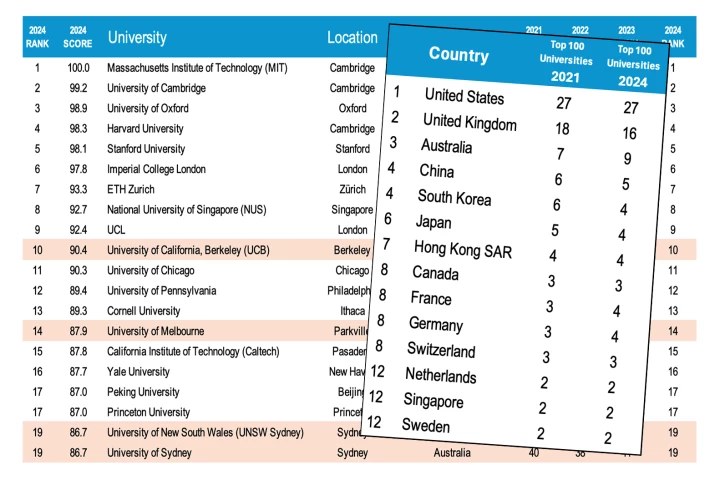
The 2024 QS World University Rankings were released this week, and with three new key metrics added to the scoring process, several universities have rocketed to the international forefront, while traditional icons are being pushed below the fold.
-
Americans aged 25-65 years are dying at far higher rates than their peers from other high-income countries, even surpassing death rates in Central and Eastern Europe. A new study examines what's caused the three-decade rise in midlife mortality.
-
It’s a fundamental principle of physics that particles with opposite charges attract each other, while those with the same charge repel. Scientists have now discovered that under certain conditions, particles can attract those of the same charge.
-
It's a sad and gruesome fact that robotic lawnmowers sometimes run over hedgehogs, maiming and even killing them. That's why scientists have recently developed a rubber hedgehog stand-in, for safety-testing such mowers.
-
A team of scientists from the University of Oxford has concluded that our popular ideas about the colors of the planets Uranus and Neptune are all wrong. Far from being two distinct shades, they are, in fact, nearly the same shade of greenish blue.
-
Despite overall improved mortality rates, the number of people found at home so decomposed that it is impossible to determine their cause of death is on the rise in parts of the UK. A new study tries to parse the cause.
-
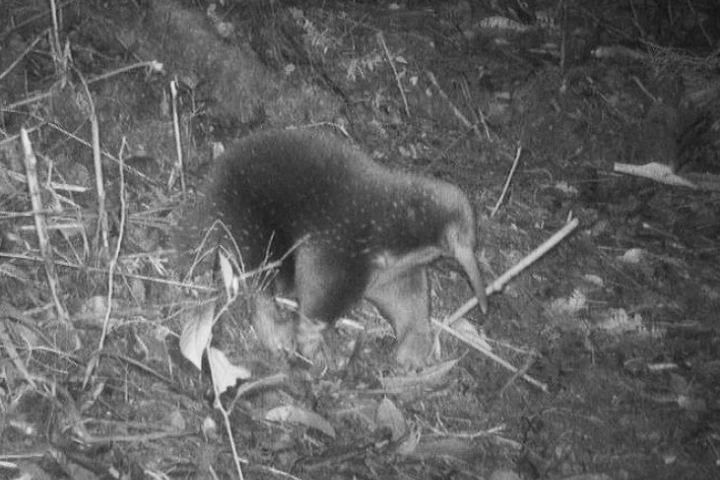
With spines like a hedgehog, feet like a mole and snout like an anteater, this bizarre animal is hard to miss. Yet it has been missing, presumed extinct since 1961 – that was until it had the audacity to saunter past a well-placed research camera.
-
Researchers have used human neural stem cells to 3D print functional brain tissue that mimics the architecture of the cerebral cortex, the brain’s outermost layer, and has the potential to provide individualized repairs to brain injuries.
-
Researchers have developed a new risk 'calculator' that identifies people in midlife at risk of developing dementia in the next 14 years. Moreover, it's based on 11 key risk factors, many of them modifiable.
Load More