University of Sydney
-
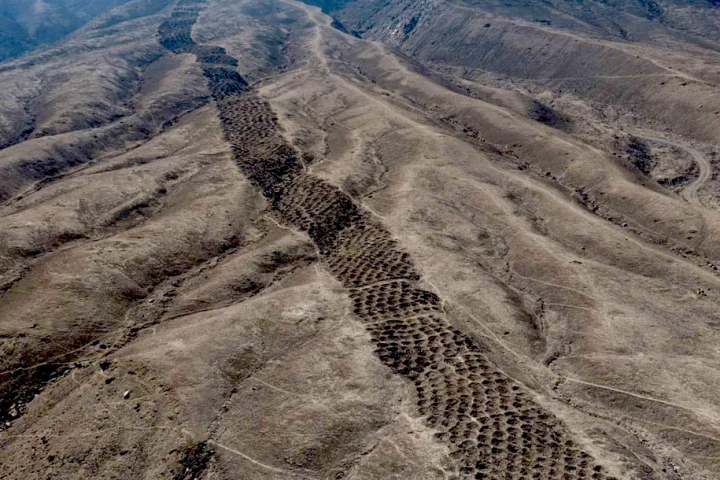
For nearly a century, a strange band of 5,200 holes carved into a hillside has defied explanation. Stretching for nearly a mile along the edge of the Pisco Valley, Monte Serpe – "serpent mountain" – may have finally revealed its secrets to scientists.
-
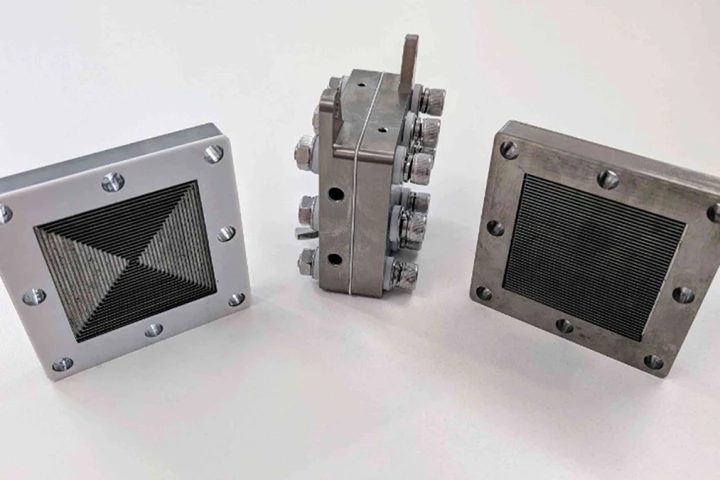
A roof paint that can cool your home and pull fresh water straight out of the air? It's within reach, as scientists scale up production of a new kind of paint-like coating that shields roofing from the sun's rays and harvests dew from its surface.
-
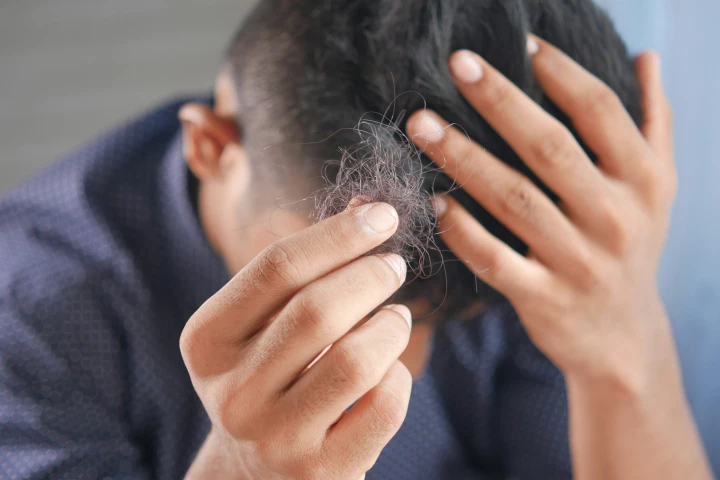
While the topical application of minoxidil is one of the most effective and popular ways to combat male pattern baldness, it is poorly absorbed by the skin. Looking to improve its efficacy, researchers have turned to an unlikely but very sweet ally.
-
A fan might feel like a lifeline in a heatwave, and for older adults it may be of some help – but not as much as it might seem. Using an electric fan in humid heat has a small benefit, but in hot and dry conditions, it can do more harm than good.
-
The fitness community regularly touts the health benefits of getting in 10,000 steps per day. But a new study says that a good deal fewer steps can still deliver significant benefits, including a 47% reduction in dying prematurely.
-
Chemical engineers at the University of Sydney are using human-made lightning to produce ammonia – a key ingredient in fertilizers – from thin air and without the need for high temperatures or pressures.
-
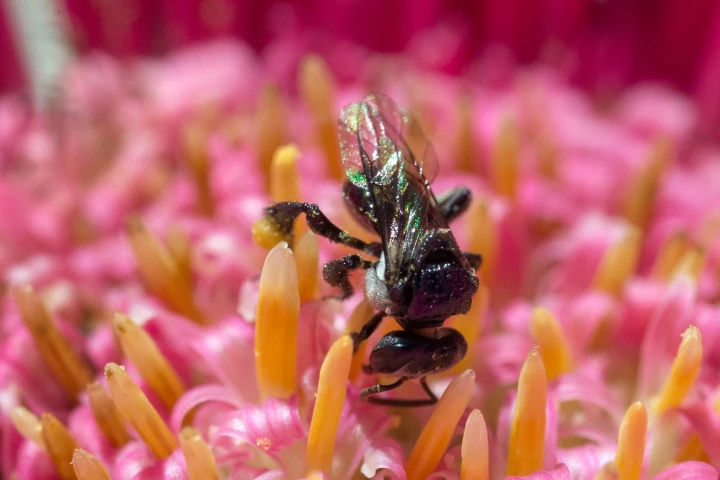
Honey produced by some species of Australian stingless bees possesses impressive bacteria- and fungi-killing properties, according to new research. The honey has the potential to be used alongside or in place of existing antibiotics.
-
A landmark study has found that a workable exercise plan significantly improves survival and health of people who have survived colorectal cancer. So much so that, as one researcher notes, "Our findings will change the way we treat colon cancer."
-
We all know the many health effects that a diet high in saturated fat and refined sugar has on our bodies. Now, in the first study of its kind on humans, scientists find that it may also be negatively impacting our ability to navigate and learn.
-
A study found that almost half of Australian teenagers are living with one or more chronic diseases or developmental conditions. The researchers linked these diseases and conditions to factors such as an unhealthy diet and poor mental health.
-
Australians will wait an average of 12 years before getting treatment for mental health or substance use disorders, according to a new study. It's not all grim news, though. Younger people are much more likely to seek help when they need it.
-
We've never been closer to accurately assessing whether someone is more susceptible to developing depression due to their biology, with 293 new gene variants found to play a role in ramping up the risk factor. That's 42% more than previously known.
Load More