University of Turku
-
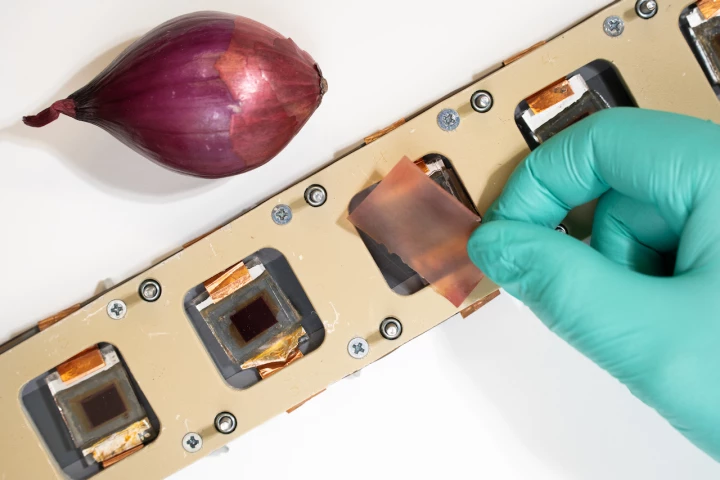
Solar cells are subjected to a lot of harmful ultraviolet light, as they're typically placed for maximum sunlight exposure. A new eco-friendly coating could help protect them from those UV rays, and its active ingredient is extracted from onion skin.
-
Being sedentary at work led to lower blood pressure than standing to work for long periods. The findings are from a new study that also found that prolonged standing can be harmful to the heart and circulation.
-
Detecting the first stages of heart failure could soon be as simple as placing a smartphone on a patient's chest. That's the conclusion of an ongoing study, which is aimed at developing an app for diagnosing the potentially lethal condition as early as possible.
-
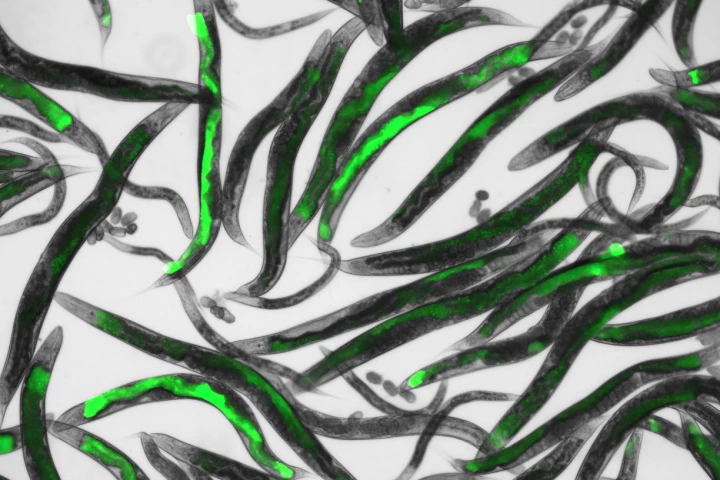
Although the air in our homes or workplaces may seem OK, it might contain harmful compounds emitted by materials like particleboard and carpeting. New research suggests that we may soon be able to tell if that is the case, using tiny glowing worms.
-
Scientists experimenting with next-generation plastics at Finland's University of Turku have developed a self-healing form of the material with some impressive capabilities, most notably an ability to quickly break down after use.
-
A study has found it may be possible to predict a person’s risk of dying more than a decade in advance by analyzing their gut bacteria. The research points to a microbial signature associated with an increased risk of mortality across a 15-year follow up.
-
Phosphorus has been detected on a comet, thus completing the list of life-essential elements found on these cosmic snowballs. The discovery made in data from the Rosetta probe strengthens the idea that life’s ingredients were delivered to Earth by comets.
-
Spiders may seem like they sit on top of the food chain in the bug world, but they’re vulnerable to an even worse fate: parasitic wasps that infect and essentially “zombify” them. And now, researchers have discovered 15 new species of these wasps.
-
A study has uncovered associations between an infant’s gut microbiome composition at the age of 10 weeks, and the development of certain temperament traits at six months age. The research does not imply causation but adds to a growing body of evidence connecting gut bacteria with mood and behavior.
-
While there already are materials that change color in response to UV exposure, those color-changes involve reorganization of the material's molecular structure, so it can only be used a few times. A new material known as SensoGlow, however, can be used to detect and measure UVs over and over.
-
The most common type of arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation is an irregular beating of the heart that can lead to strokes. And unless an electrocardiogram is being used, it can be difficult to detect. Soon, however, an app may be all that's required to do the job.
-
Scientists have recently confirmed that a unique species of monitor lizard, initially described in the early 19th century, is still alive and well on the island of New Ireland. It is said to be "the only large-growing animal endemic to the island that has survived until modern times."
Load More