Utrecht University
-
Good news for the 51 million Americans with chronic pain: Scientists have unraveled the neuronal disturbances that can see acute pain turn into a long-term nightmare, and with some targeted cell therapy, could potentially stop this process altogether.
-
Researchers have derived an antibiotic from microbes living in the sandy soil of North Carolina. Because it works completely differently than others before it, clovibactin might help turn the tide in the battle against today's nastiest superbugs.
-
All walking animals have something in common – their preferred walking speed is largely determined by what's known as "resonance." Bearing this in mind, scientists have calculated what may have been the default walking speed of Tyrannosaurus rex.
-
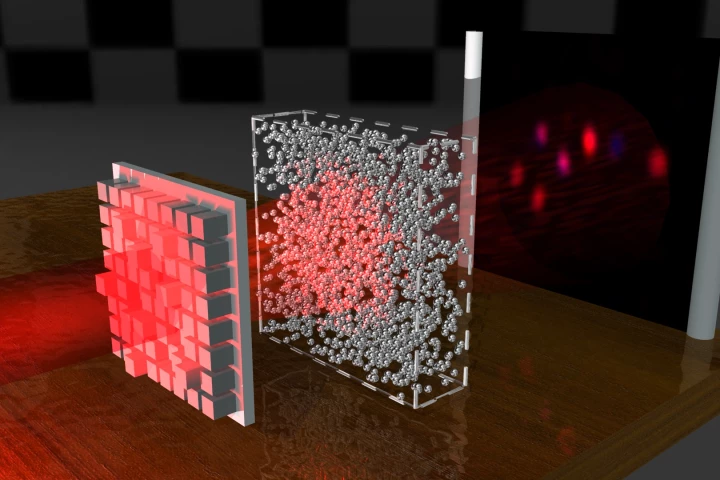
Clouds or sugar cubes block light because they’re disordered media that scatter light waves. Now scientists have found a way to manipulate light waves to pass through, projecting an image on the other side as clearly as if the obstacle wasn’t there.
-
Scientists studying the movement of seafloor sediment have found that underwater avalanches are driving microplastics into the deep ocean, which may help researchers better map the distribution of waste throughout the marine environment.
-
Although snake venom generally has a nasty effect on people, it's also used in the production of antivenoms and other medications. It could soon be much easier to acquire, as scientists have grown mini venom-producing glands in the lab.
-
New technology promises to make the 3D-bioprinting process quicker and thus more practical than ever.
-
Researchers have made a breakthrough in identifying the way cells send up flags to the body's immune system – a discovery that could have a significant impact on how we develop vaccines or treat autoimmune diseases.